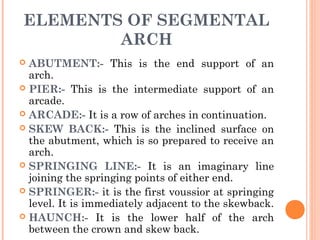
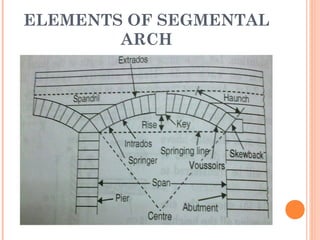
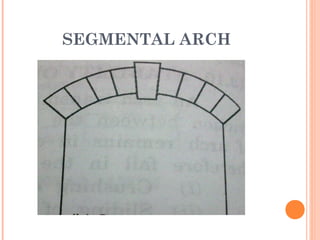
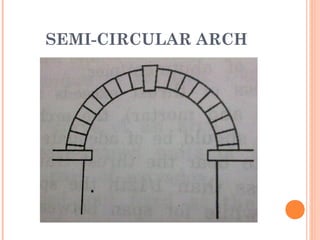
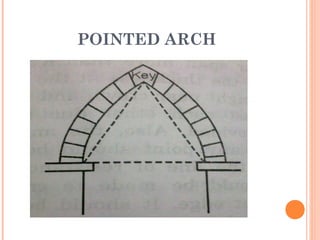
This document discusses arches and their elements. It defines key terms like intrados, extrados, voussoirs, crown, and springing line. It describes how arches transmit loads through compression between wedge-shaped units. Arches are classified by their shape (flat, segmental, semicircular), number of centers (one-centered, two-centered), and construction material (stone, brick, concrete). Common arch types include flat arches, segmental arches, semicircular arches, and pointed Gothic arches.