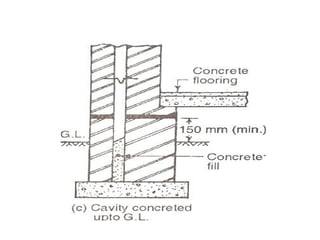
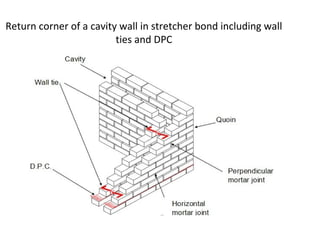
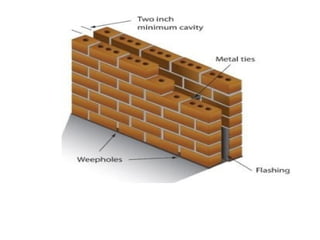
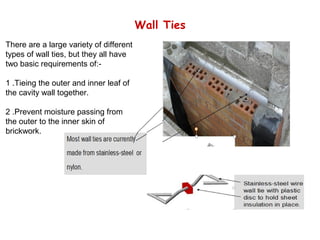
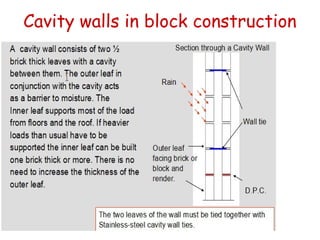
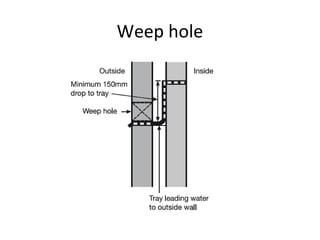
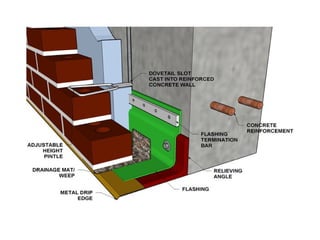
Cavity walls consist of two masonry skins separated by a hollow space. The cavity serves to drain water out of the absorbent masonry skins through weep holes. Cavity wall insulation such as mineral wool, polystyrene beads, or urea formaldehyde foam is used to reduce heat loss by filling the air space. Wall ties connect the two skins to prevent separation, and are spaced according to building regulations. Weep holes above windows and doors allow moisture in the cavity to escape. Cavity walls provide advantages like insulation from sound and moisture, reduced heat transfer, and lower foundation loads.