Embed presentation
Downloaded 37 times


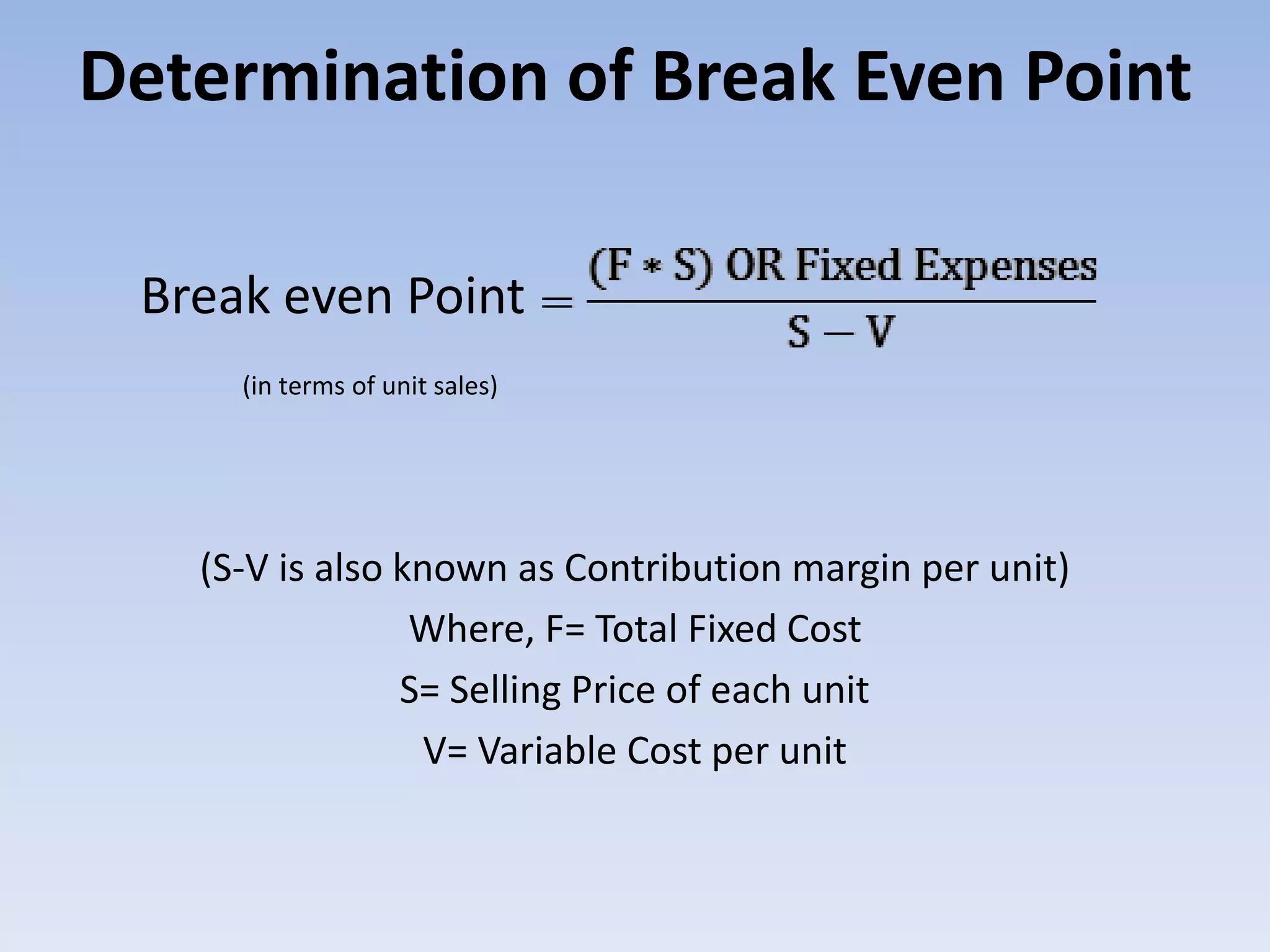



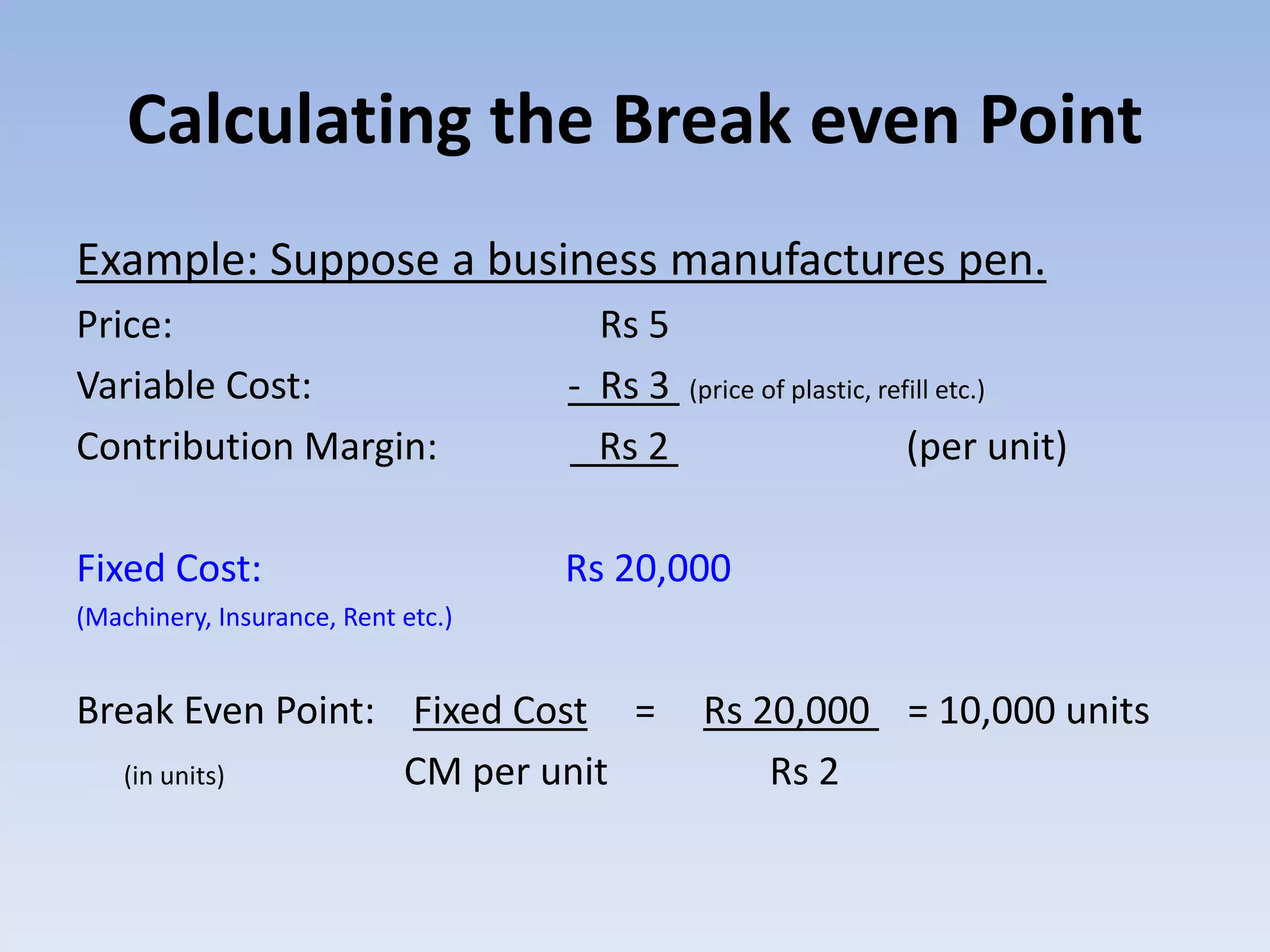



This document discusses break even analysis, which is used to determine the point at which a business neither makes a profit nor suffers a loss. It defines break even point as when total sales equal total costs or net income is zero. The document provides the formulas to calculate break even point in terms of unit sales and monetary sales. It also discusses operating, financial, and economic break even points. An example is given to demonstrate calculating break even point using information on selling price, variable costs, contribution margin, and fixed costs. Finally, the document lists some uses of break even point analysis.









