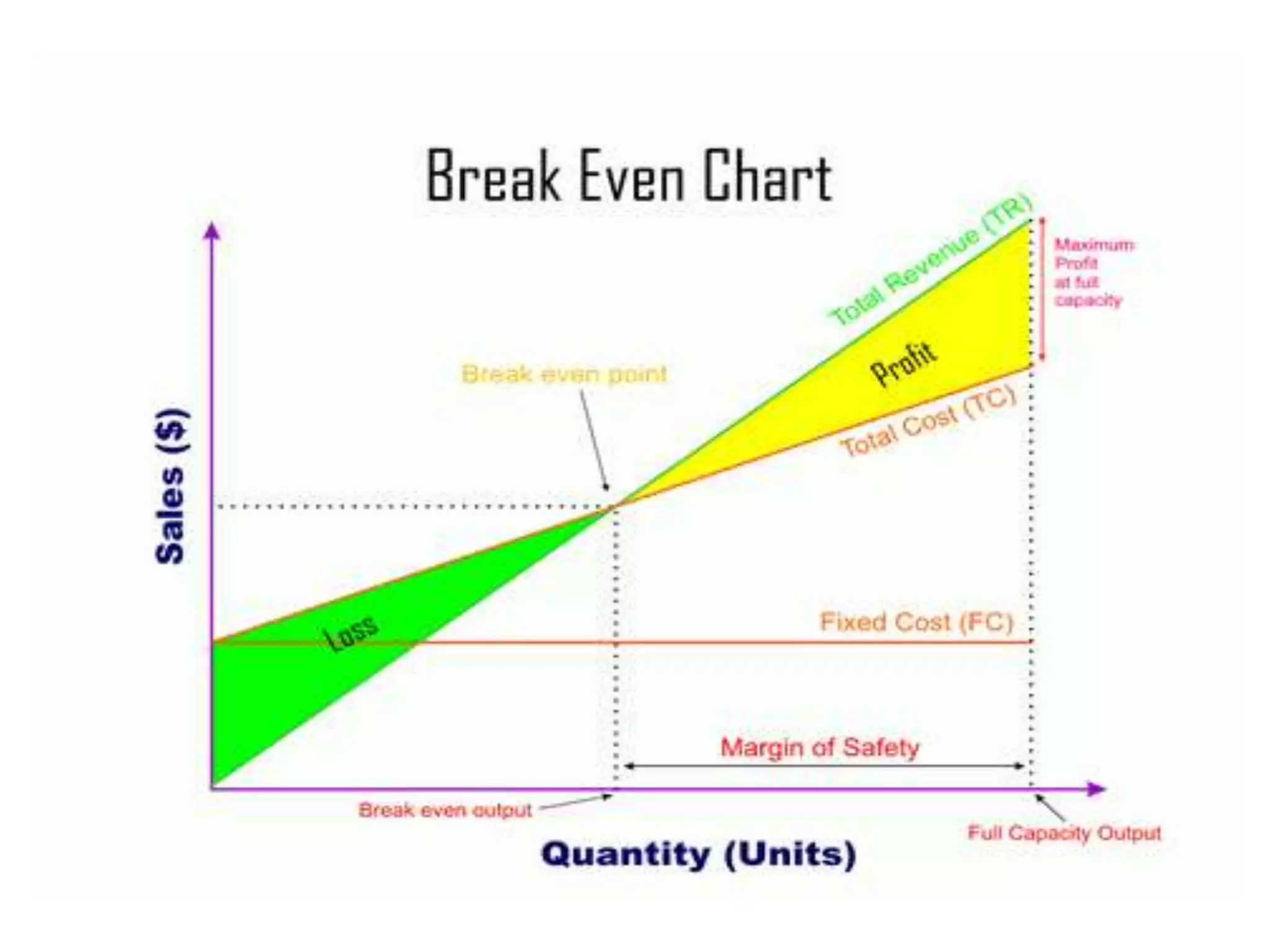
The document discusses marginal costing, a technique that classifies costs into fixed and variable categories, focusing only on variable costs as product costs, and emphasizes the impact on profit. It highlights the advantages, such as simplicity and usefulness for decision-making, as well as limitations, including difficulties in cost segregation and assumptions about fixed costs. Additionally, it explains break-even analysis, its assumptions, uses, and limitations in evaluating production, sales, and profitability.