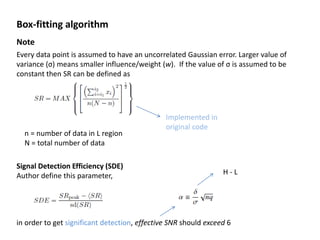
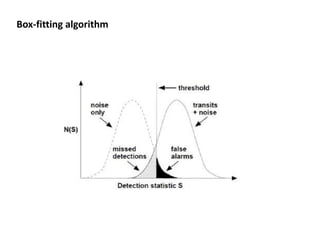
The box-fitting least squares (BLS) algorithm is used to detect periodic transits in light curves. It assumes the light curve only has two discrete values, fits box-shaped functions to folded light curves at different trial periods, and calculates the signal residue to identify the period with the maximum signal. The algorithm iterates over trial periods and transit durations to find the best-fitting five parameters that describe the period, depths, duration, and epoch of any transits present.



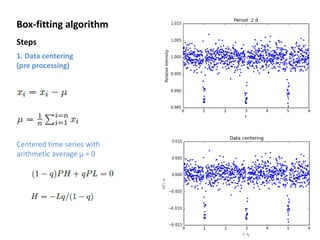

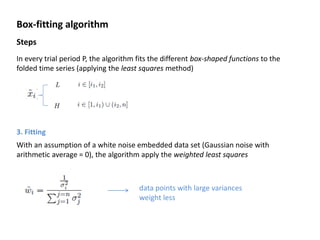

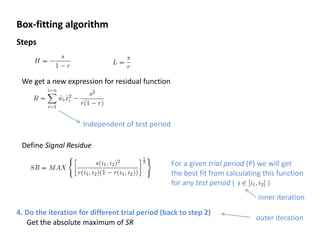
![Box-fitting algorithm
Steps
Input x(t)
Data centering
Data folding
(with trial period (P))
Data binning
ITERATE over P
ITERATE over q ([qmin, qmax]) and over the data xi
Calculate SR for a test
period q ([i1, i2])
Save MAX(SR)
and corresponding
parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/box-fittingpresentation-160521161048/85/Box-fitting-algorithm-presentation-9-320.jpg)