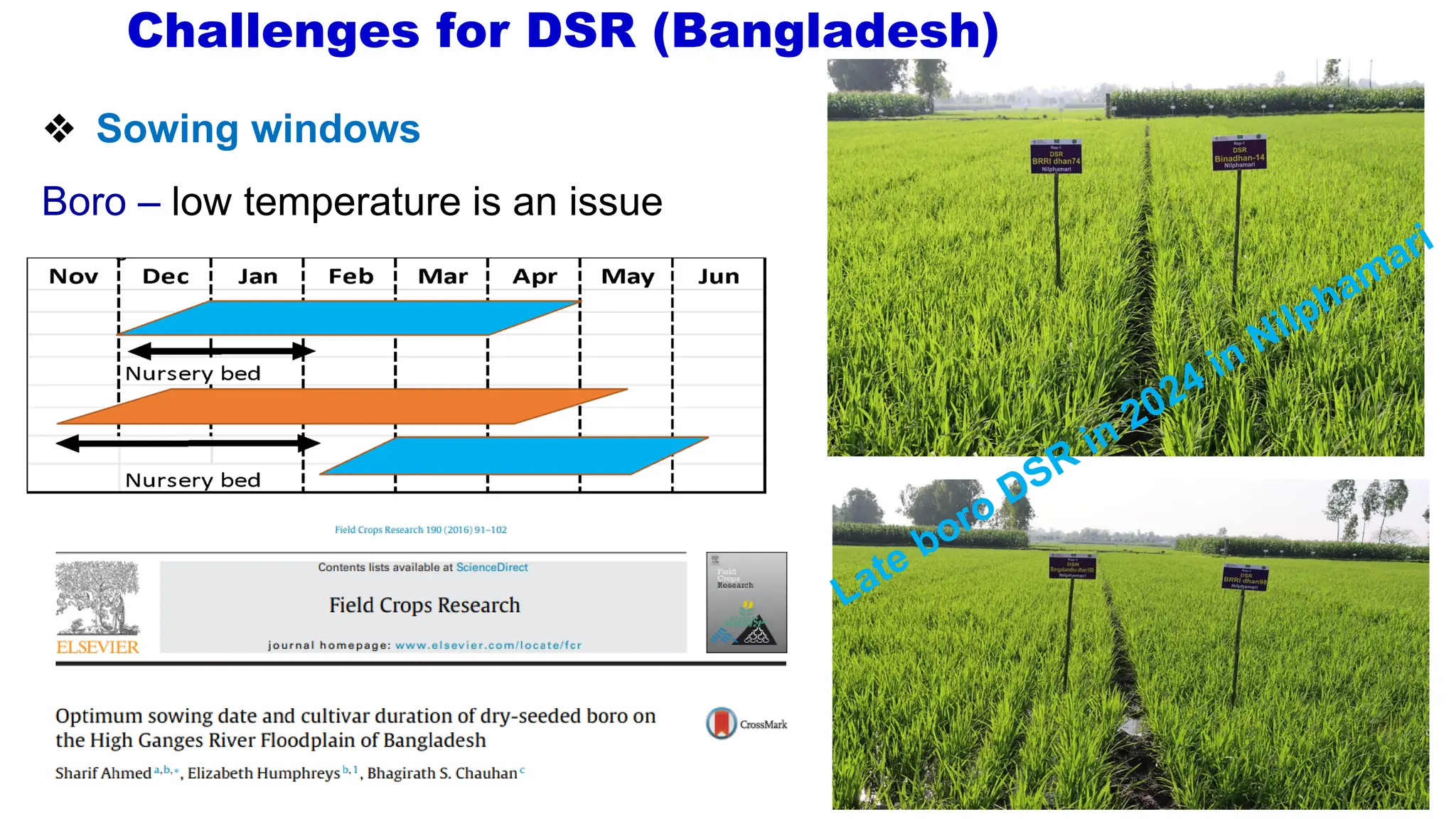
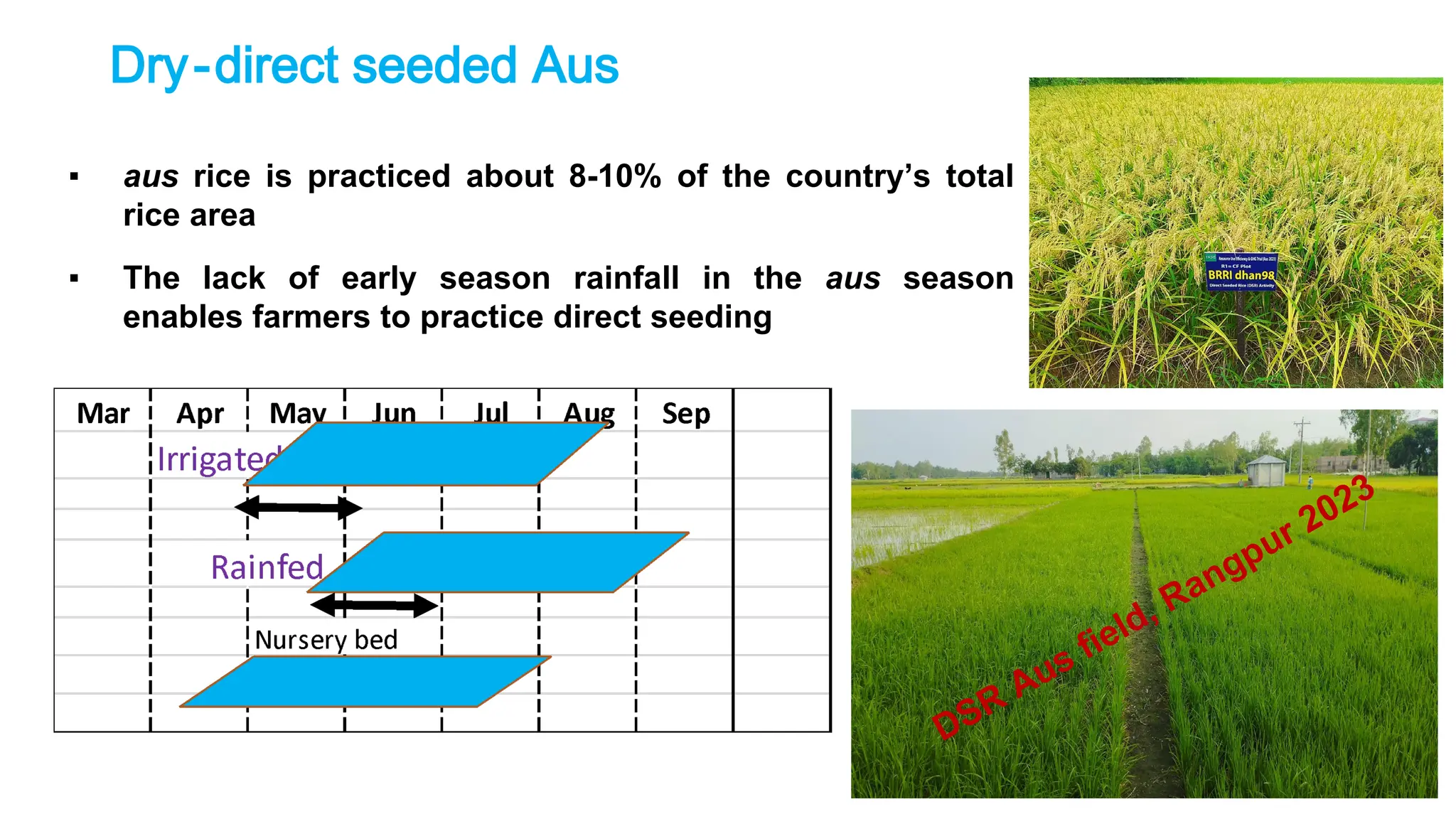
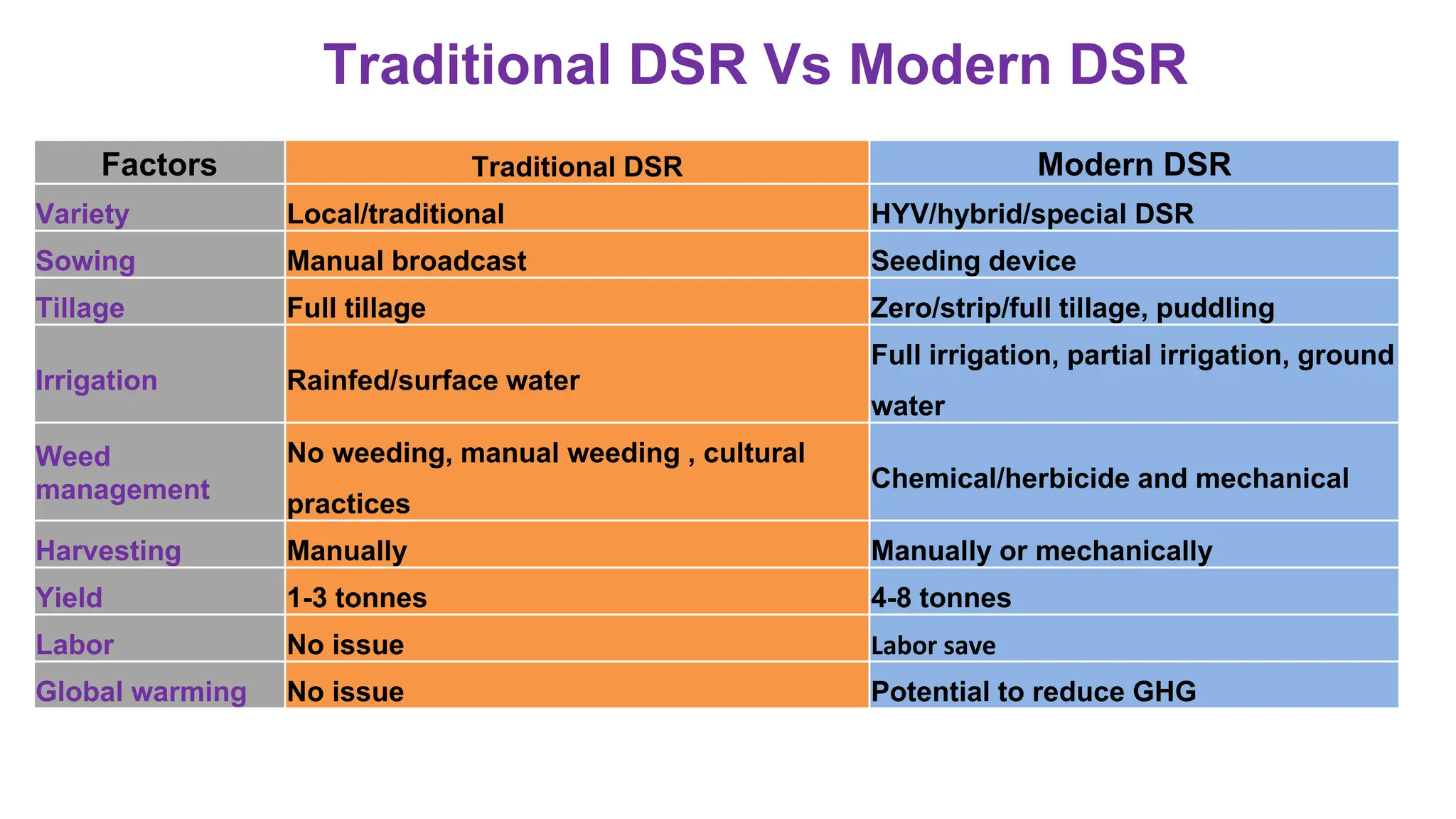
Direct seeded rice (DSR) has become prominent due to advancements in technology and pressing issues like labor and water scarcity, offering both adaptation and mitigation benefits against climate change. DSR involves sowing seeds directly into the field, potentially increasing yields, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and conserving resources compared to traditional puddled transplanted rice (PTR). Challenges for DSR in Bangladesh include optimal sowing windows and weed management, requiring farmers to adapt practices and choose suitable varieties for success.





![Saves labor
Up to 60%
(Addresses:Labor scarcity)
Saves water
Up to 50%
(Addresses: Water scarcity)
Reduces GHG emission
Up to 60%
(Addresses: Climate change)
Increases income by
reducing cost of cultivation
[Addresses: Rising cultivation
cost and declining income]
Positive impact on
succeeding non-rice crop
[Creates enabling condition for
diversification]
DSR offers both adaptation (adapt to water shortage) and mitigation (reduction in GHG
emissions) options to climate change
Benefits of DSR over puddled transplanted rice
Direct Seeded
rice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03220424dsrsaarcworkshopsharif-240613090702-eef0ac09/75/Direct-Seeded-Rice-Climate-Smart-Agriculture-7-2048.jpg)