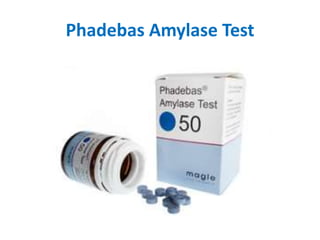
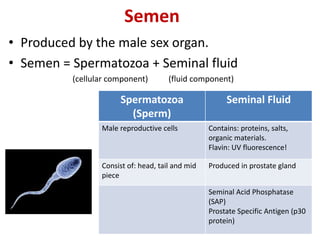
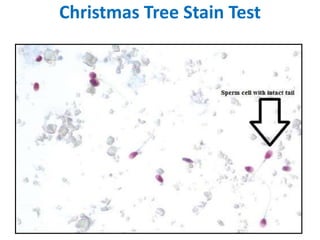
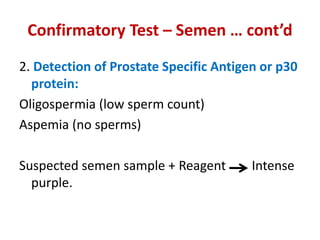
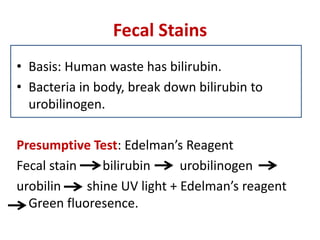
This document discusses various body fluids and the presumptive and confirmatory tests used to identify them at a crime scene. It outlines tests for blood, saliva, urine, semen, fecal stains, and sweat. For blood, tests detect hemoglobin or heme compounds, including the luminol, fluorescein, phenolphthalein, Teichmann, and Takayama tests. Saliva tests identify the enzyme amylase, including using Phadebas tablets. Urine tests detect creatinine or urea. Semen tests identify acid phosphatase or prostate antigens. Fecal tests detect bilirubin breakdown products. And sweat can be identified using crystal violet dye interaction.