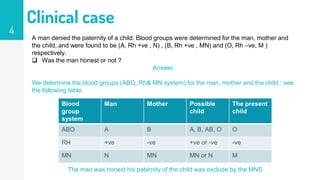
The document discusses methods for determining paternity through genetic testing. It defines key terms like paternity, paternity testing, established paternity, and disproved paternity. It then discusses using blood group testing of a man, mother, and child to determine if the man's paternity was honest or not based on their blood types. The summary concludes by stating that genetic markers like blood groups, HLA, DNA, enzymes, and proteins can all be used in protocols to investigate disputed paternity cases.