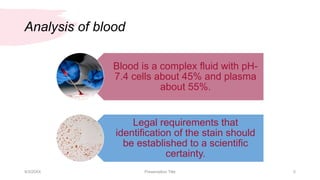
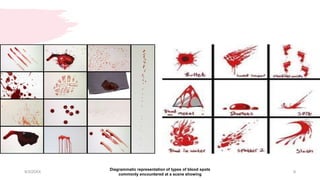
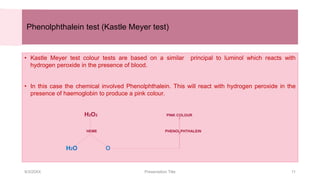
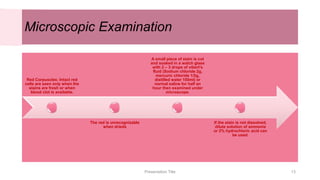
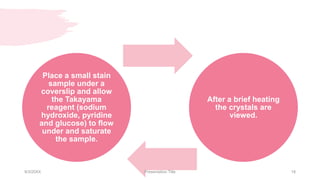
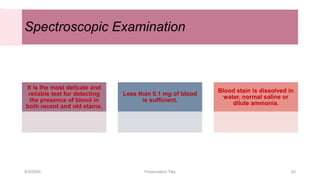
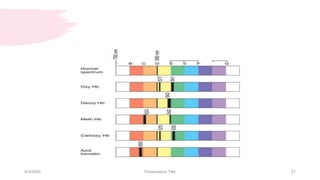
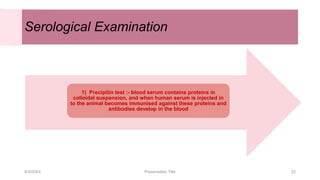
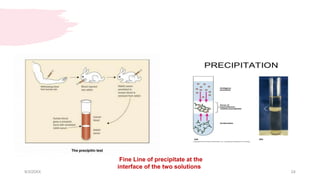
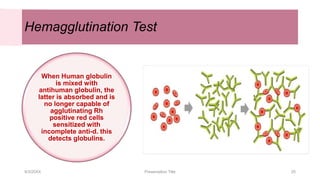
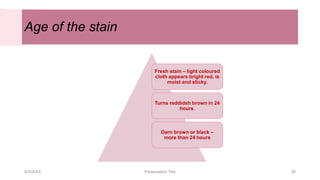
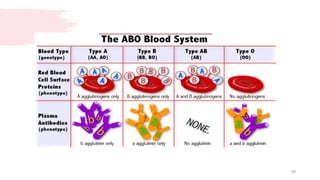
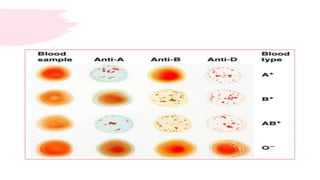
This document discusses the analysis and examination of blood stains from a forensic perspective. It outlines various physical, chemical, and microscopic tests that can be used to analyze blood stains, including benzidine tests to detect the presence of blood, microscopic examination to look for red blood cells, and precipitin tests to determine blood type. It also discusses how blood stain analysis is important for medicolegal cases involving identification of victims or suspects, crime scene reconstruction, and questions of paternity or inheritance.