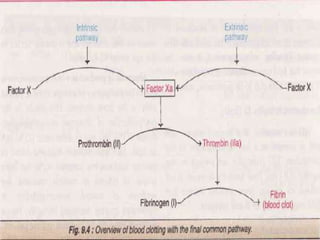
The blood coagulation cascade involves three mechanisms to stop bleeding when blood vessels are damaged: vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, and blood clotting. Blood clotting is a complex series of enzymatic reactions that results in the formation of fibrin threads that trap blood cells to form a clot. There are two pathways - the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways - that activate clotting factors and ultimately convert prothrombin to thrombin which converts fibrinogen to fibrin. Anticoagulants like heparin and coumarins are used to delay the coagulation process in thromboembolic conditions.