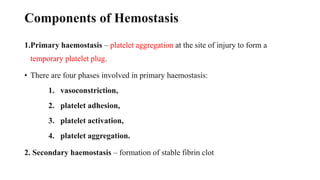
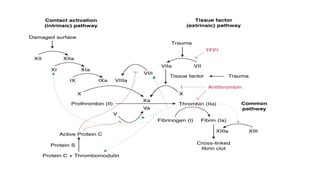
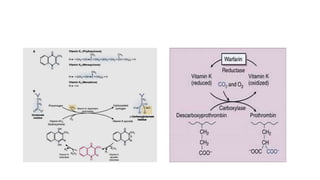
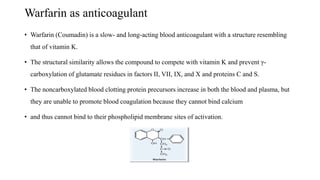
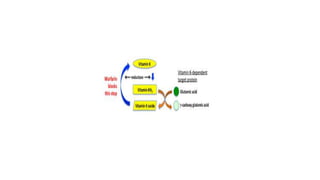
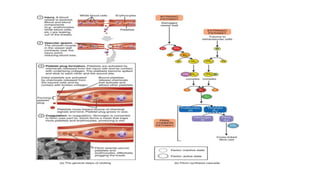
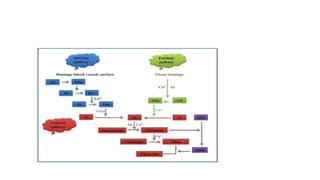
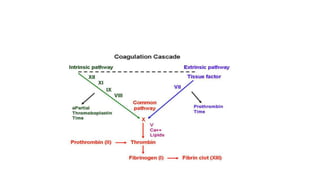
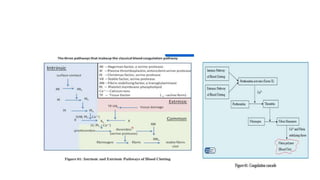
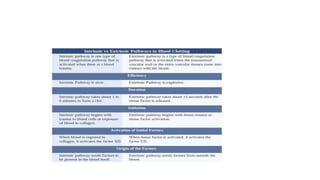
The coagulation pathway involves both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways that activate coagulation factors in a cascade. The intrinsic pathway is initiated inside blood vessels by factor XII contacting collagen. The extrinsic pathway is initiated outside by tissue factor. Both pathways activate factor X and lead to the common pathway where thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin to form a clot. Healthy endothelial cells prevent clotting through mechanisms like producing nitric oxide and prostacyclin to inhibit platelets. Vitamin K is required for carboxylation of coagulation factors VII, IX, X and prothrombin to allow binding to platelet membranes and activation of the coagulation cascade. Warfarin works as an anticoagulant by blocking vitamin K and