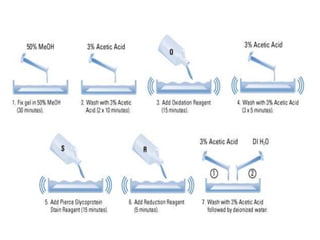
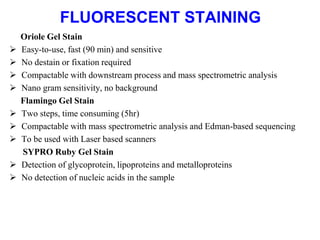
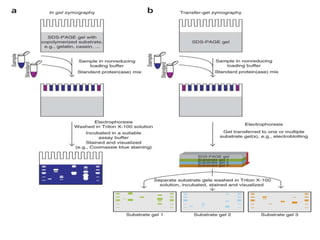
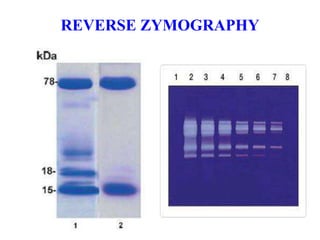
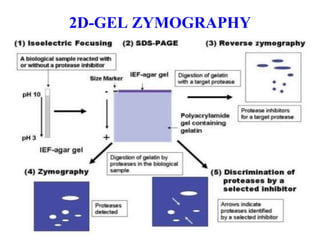
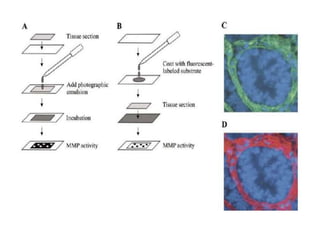
The document discusses various staining methods, including periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) for detecting polysaccharides and several zymography techniques for assessing enzyme or proteolytic activity, particularly matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). It details the processes, applications, and specific types of zymography, such as substrate and reverse zymography, highlighting their utility in biomedical research. Additionally, it outlines the advantages of zymography, including the capability to detect multiple proteases in a single gel without costly materials.