Embed presentation
Downloaded 133 times
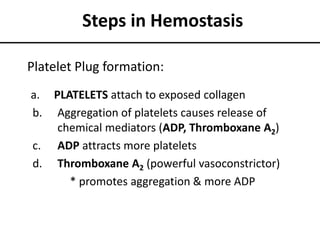
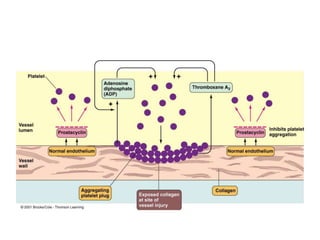

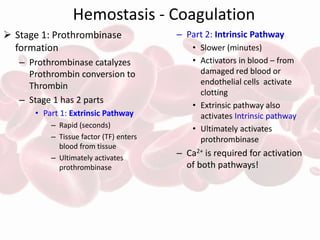
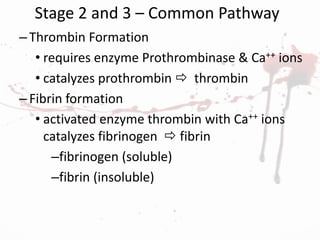
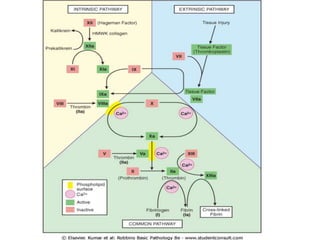
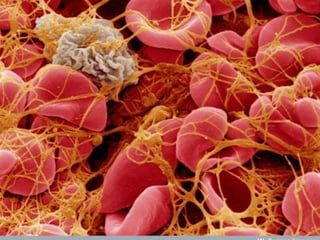




The document summarizes the steps in blood coagulation (hemostasis). It involves platelets attaching to exposed collagen and releasing chemical signals that attract more platelets to form a platelet plug. The coagulation cascade then involves 12 clotting factors in a series of proteolytic reactions through the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways to ultimately form prothrombinase. Prothrombinase converts prothrombin to thrombin, which then converts fibrinogen to fibrin to form a clot in the common pathway. The clot is eventually dissolved by the enzyme plasmin through fibrinolysis.











