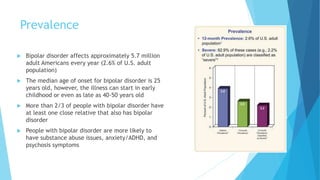
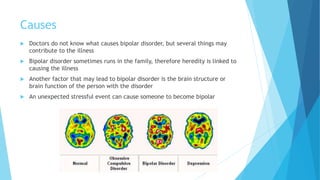
Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder that causes shifts in mood and energy levels, ranging from periods of extremely high or happy mood (mania) to periods of very sad or hopeless mood (depression). These mood swings are more extreme than normal happiness or sadness and can impact sleep, thinking, and daily functioning. Symptoms include changes in emotion, sleep, activity, and behaviors. Bipolar disorder affects approximately 5.7 million Americans and often runs in families, though the exact causes are unknown. Treatment involves medication, psychotherapy, and other therapies to help manage mood symptoms.