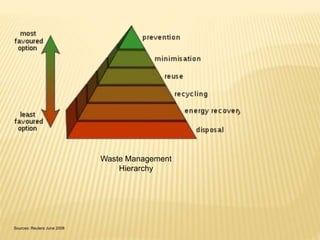
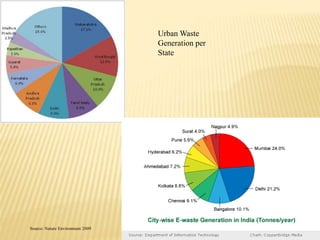
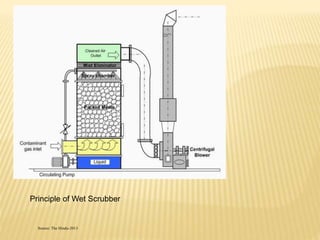
This document discusses bioremediation and waste management. It begins by introducing bioremediation as a technique using microorganisms to remove pollutants from contaminated sites. It then discusses the advantages of bioremediation including being cost effective and environmentally friendly, and the disadvantages such as being time consuming. The document also discusses different methods of waste disposal including landfills, composting, and incineration. It covers the waste management hierarchy and principles of the Basel Convention to minimize hazardous waste.