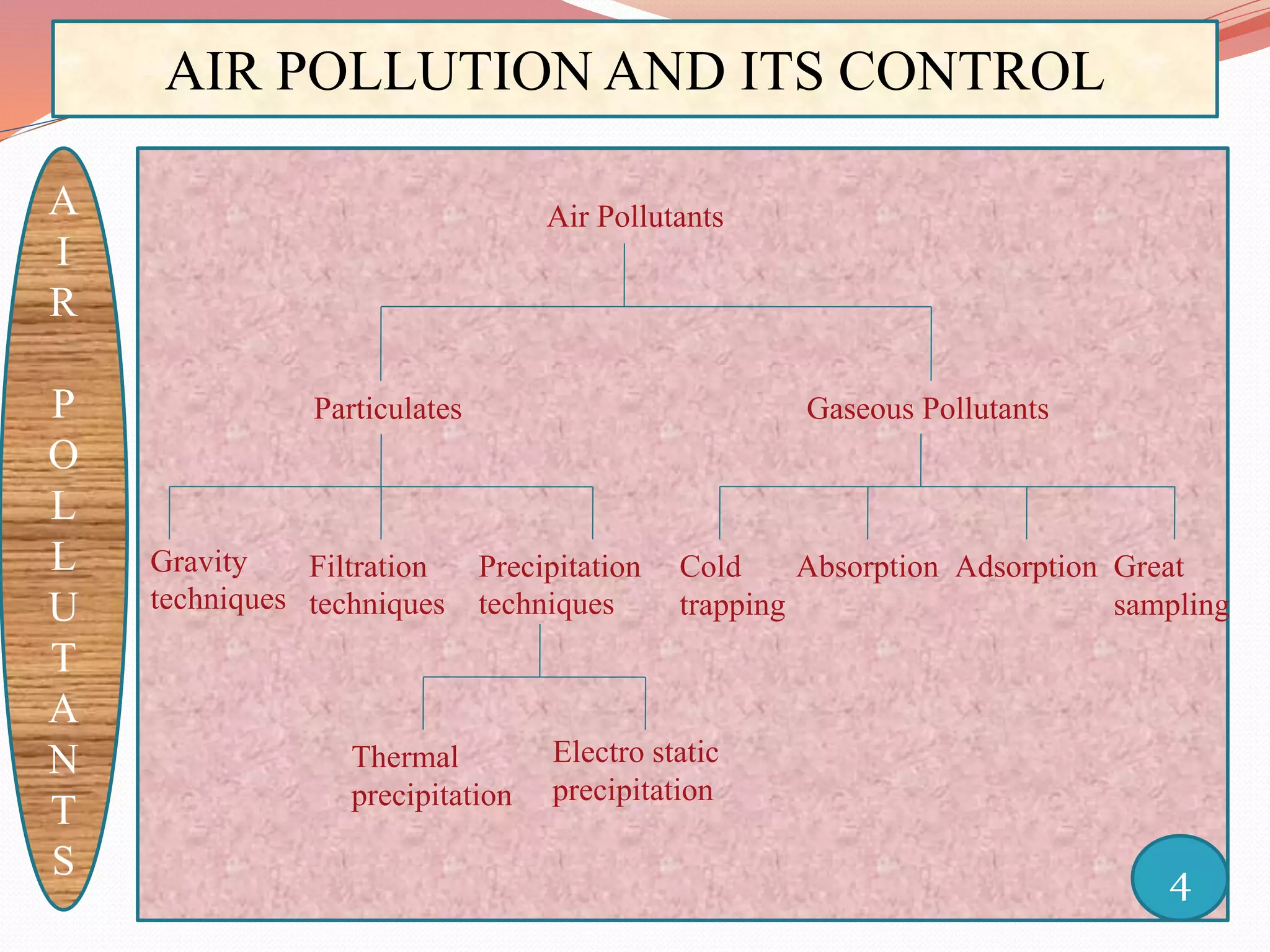
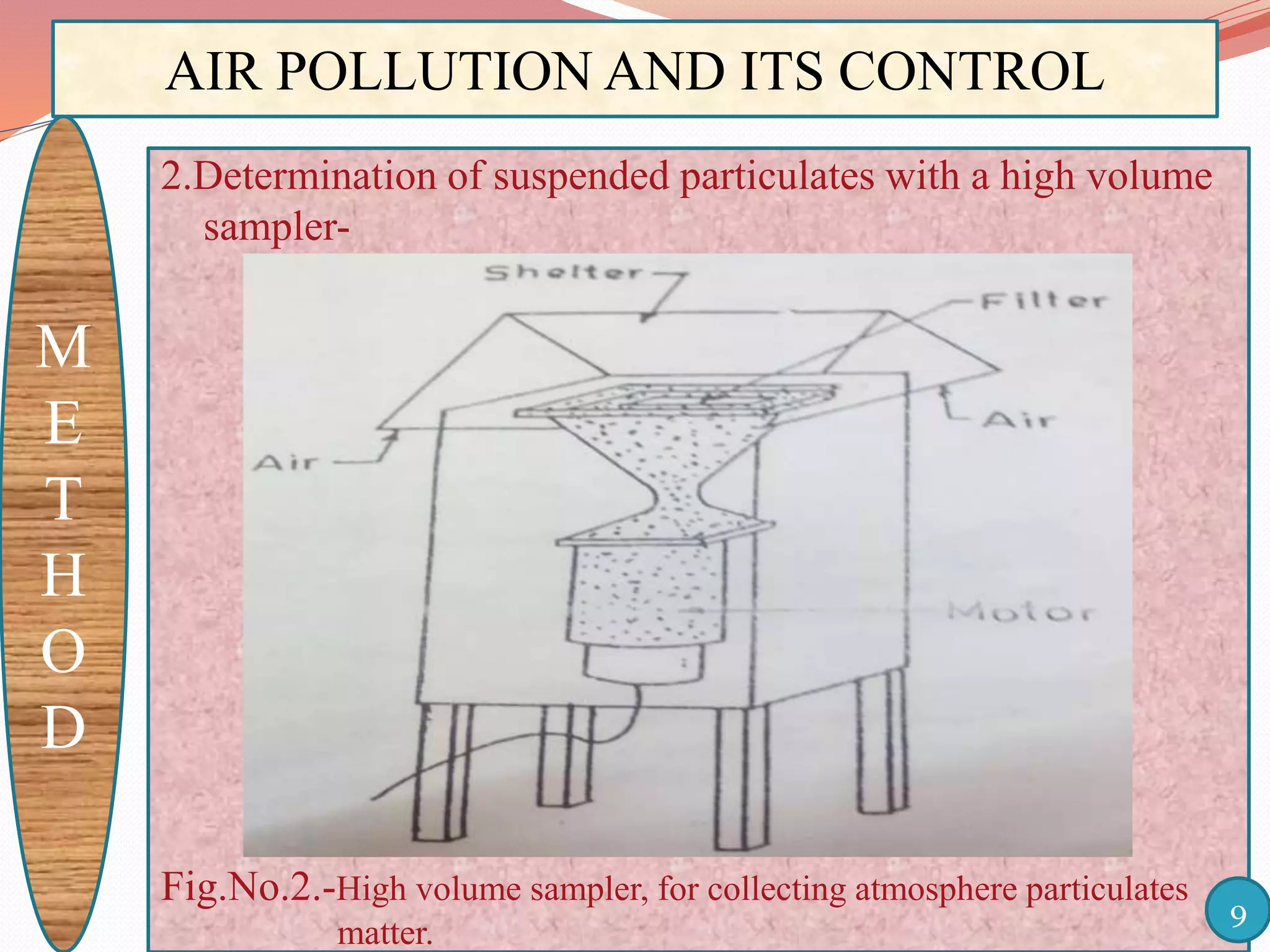
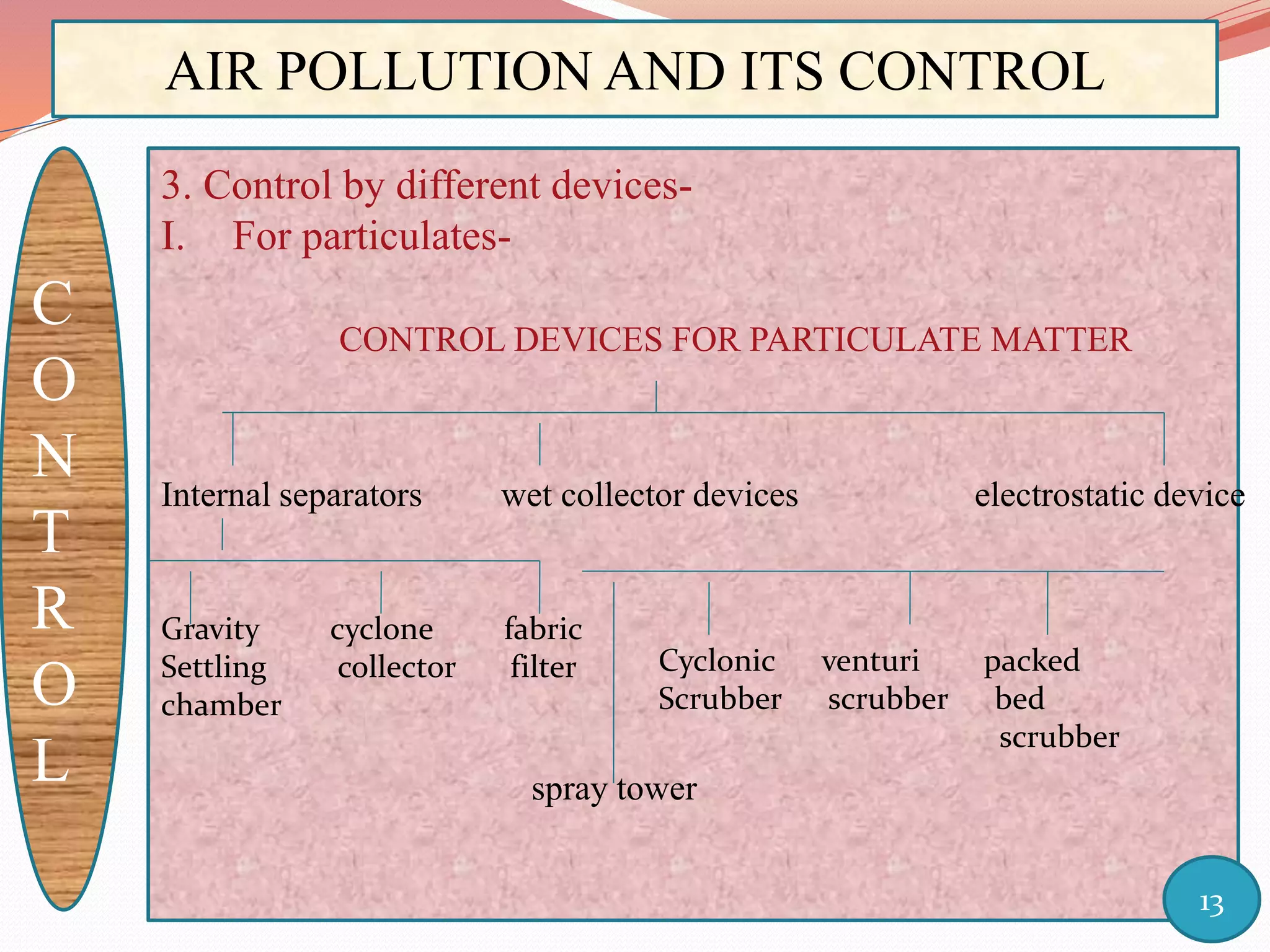
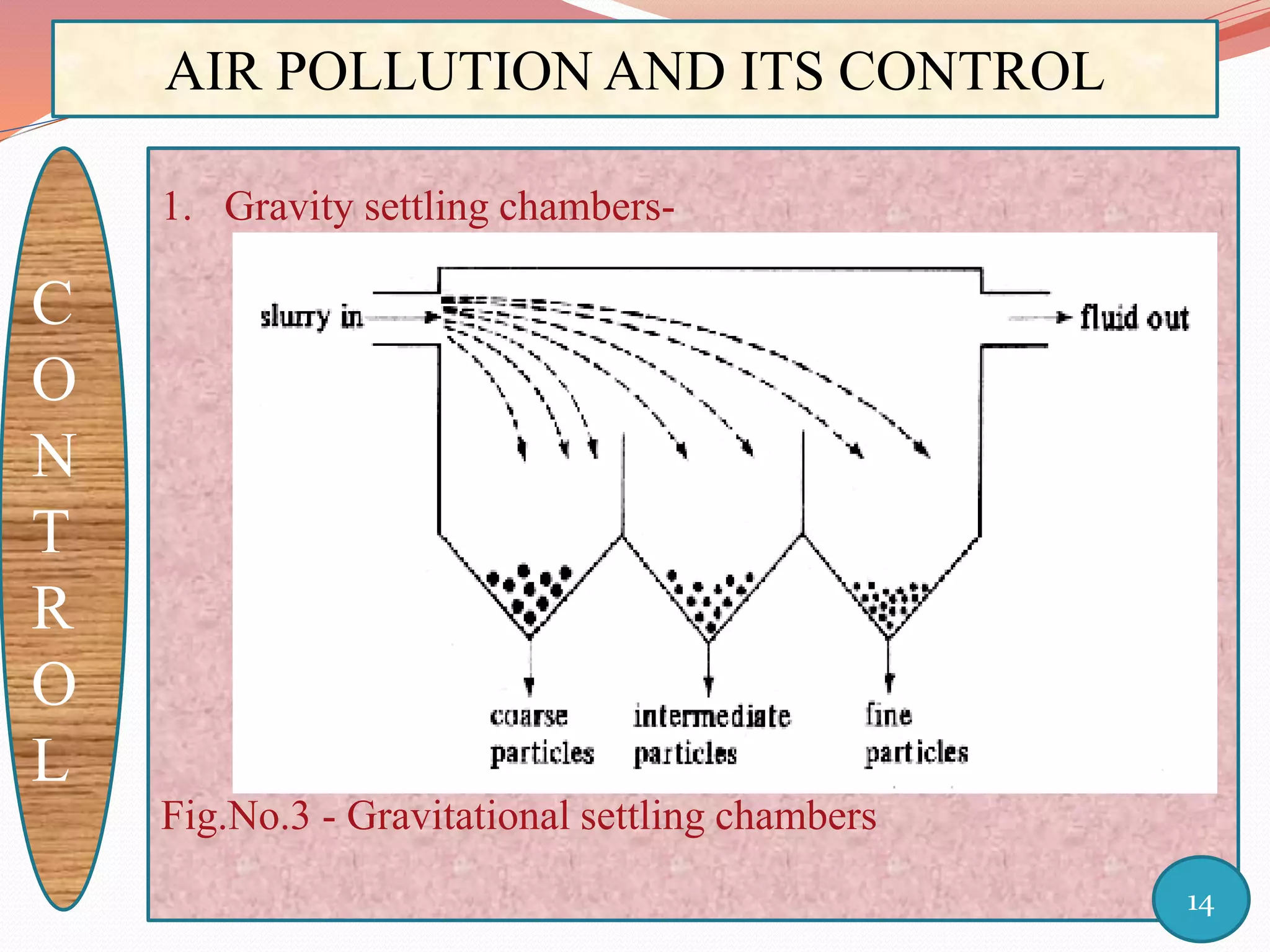
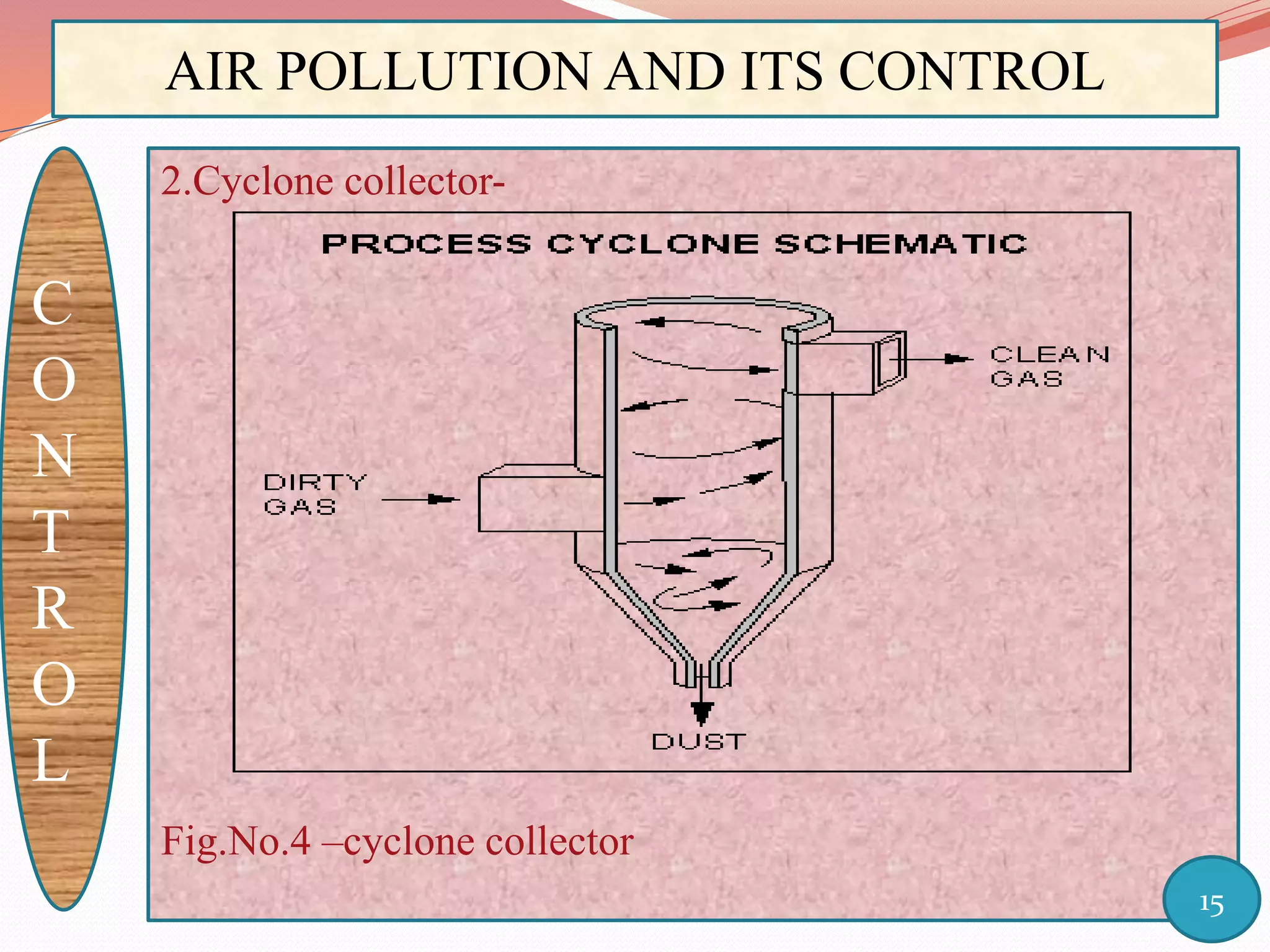
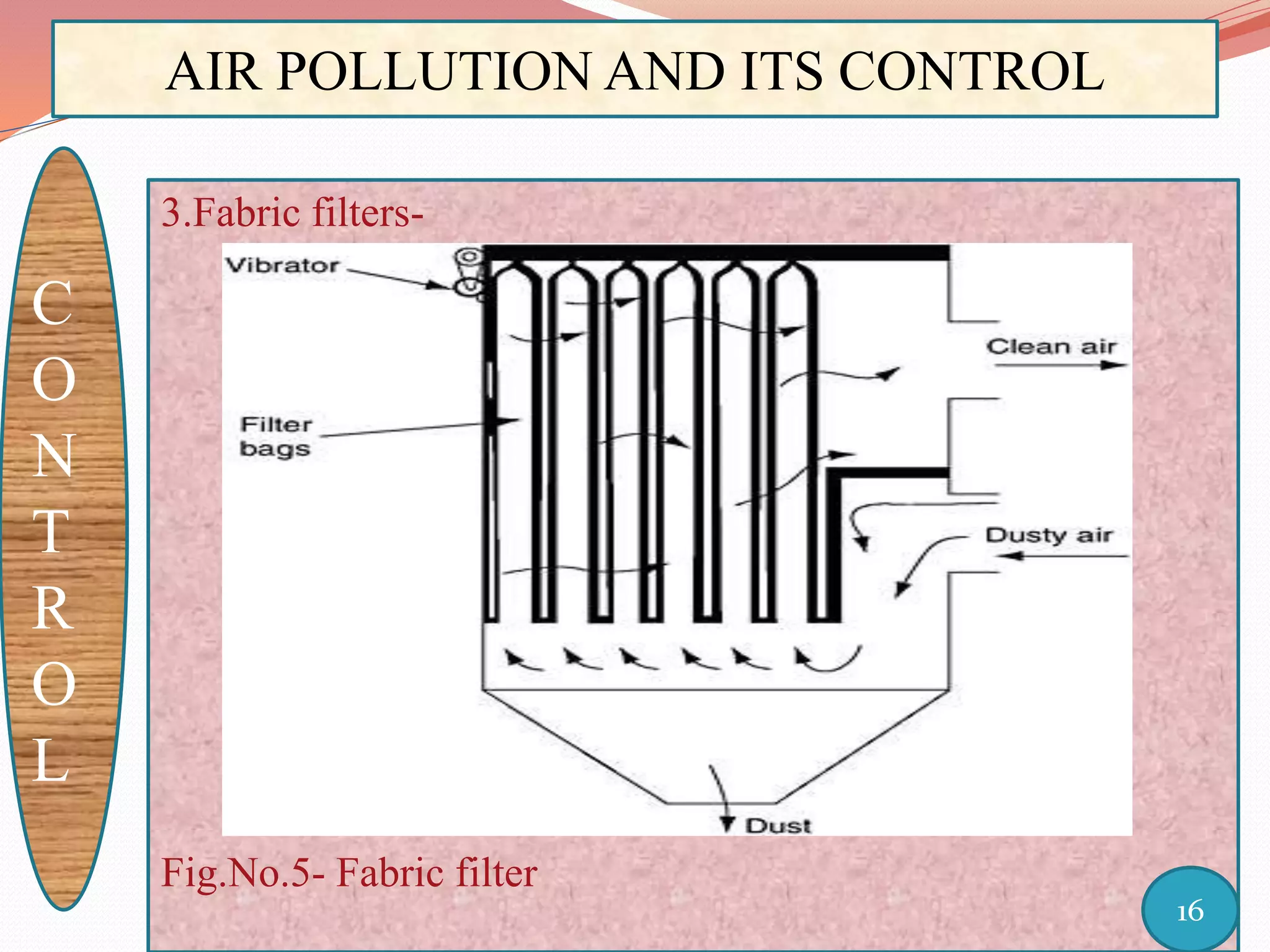
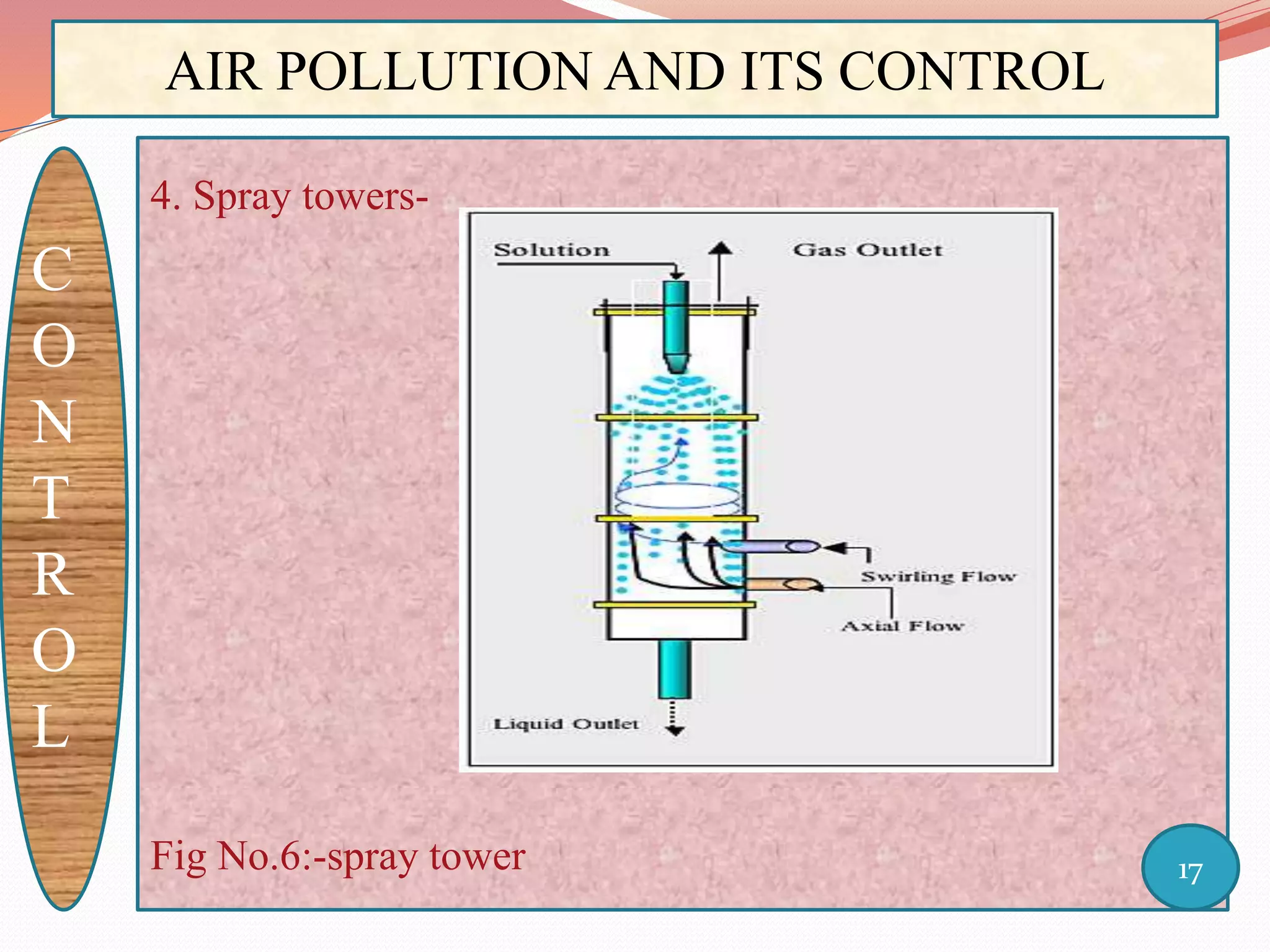
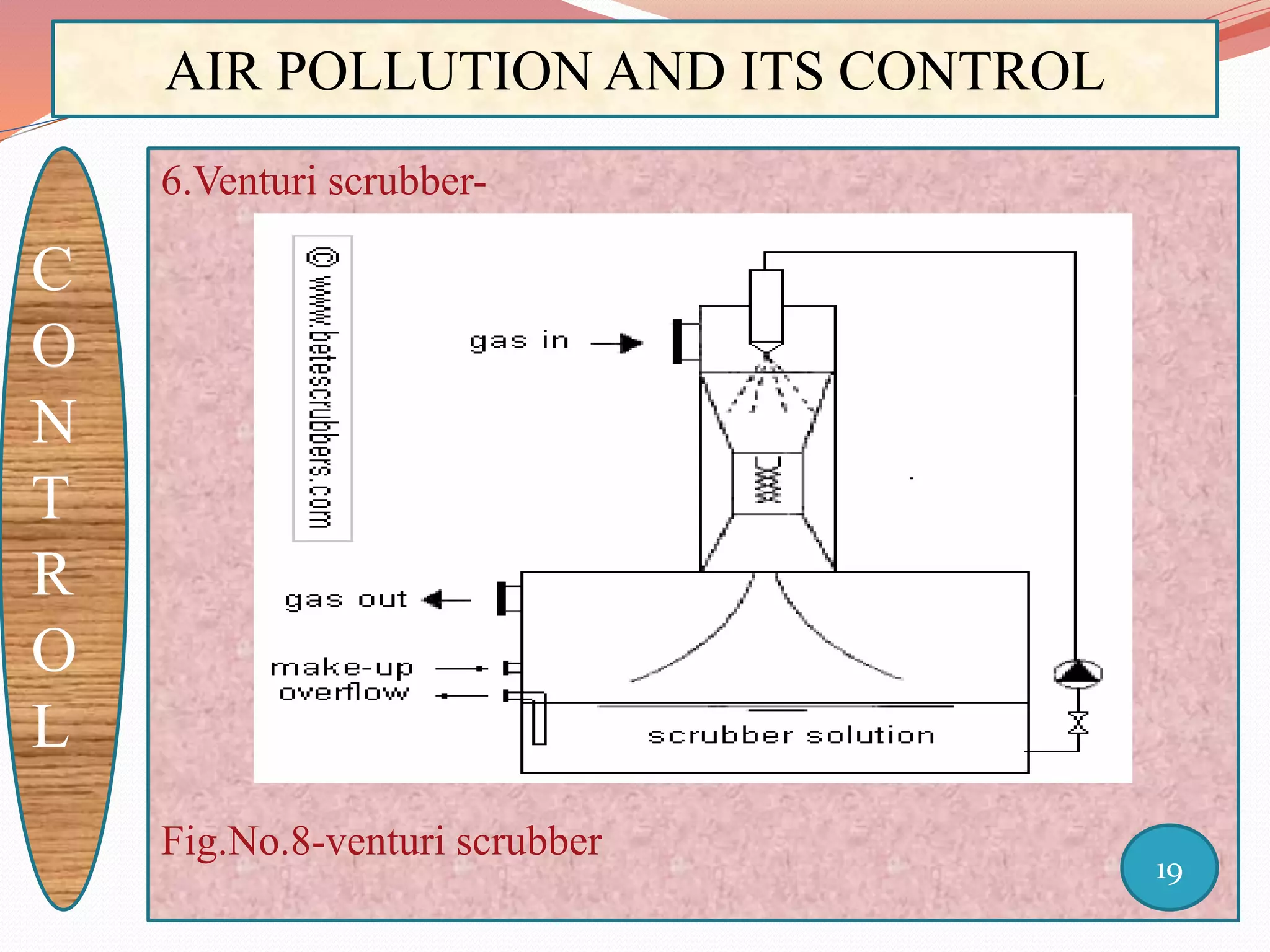
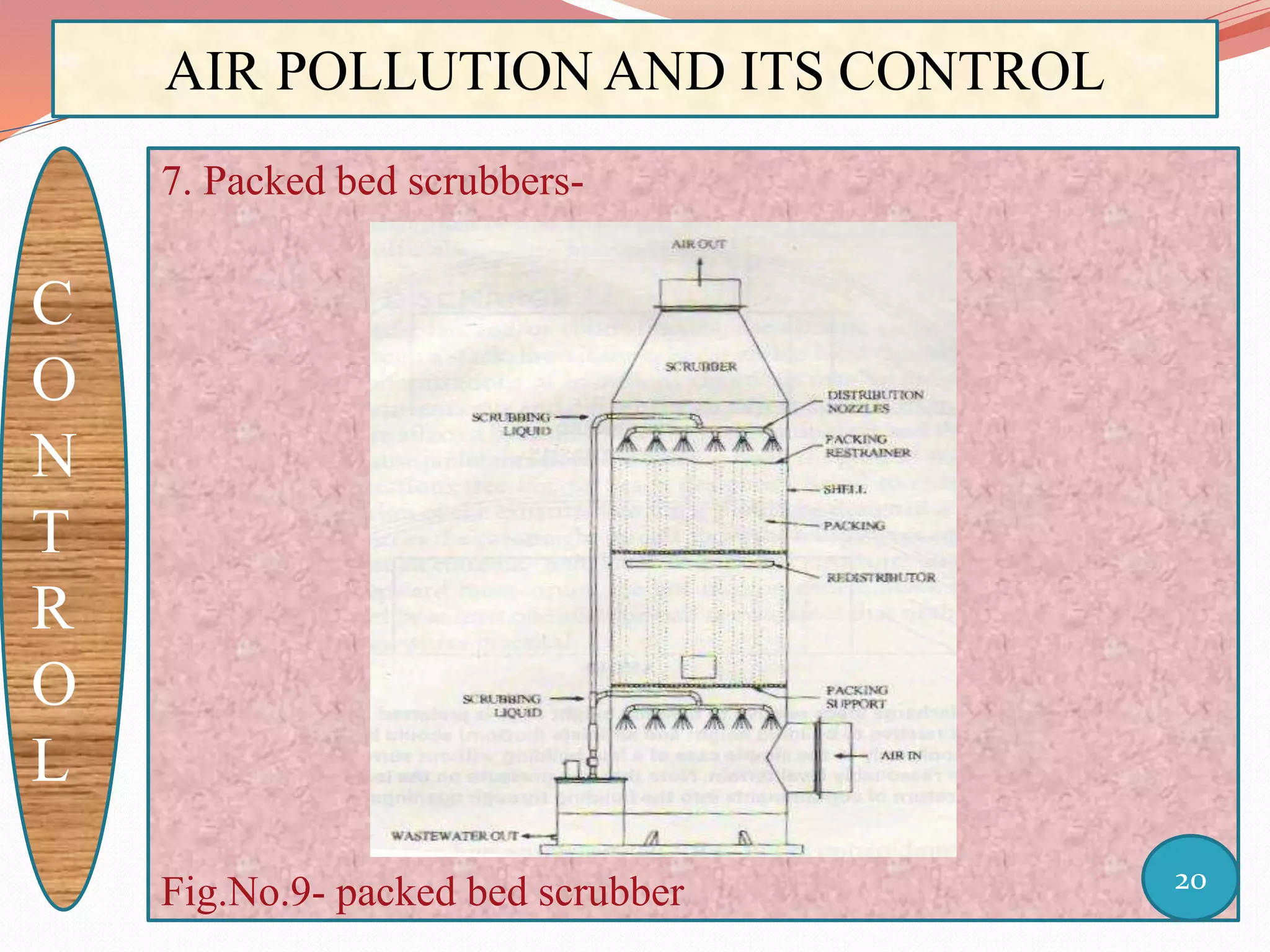
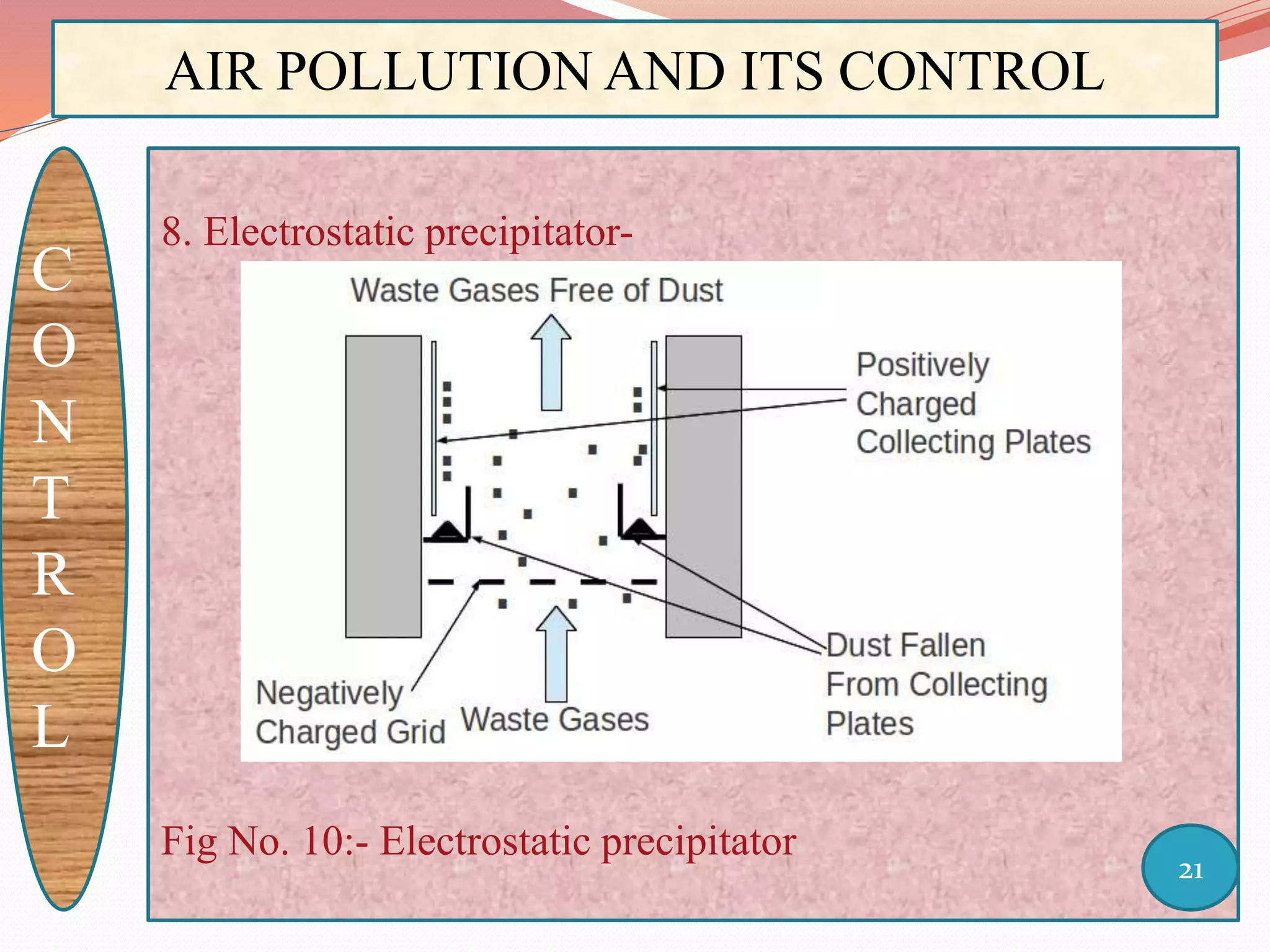
The document discusses air pollution and its control through biotechnology. It begins with an introduction to air pollution, listing common air pollutants such as particulates and gaseous pollutants. It then describes several methods for estimating pollutants and controlling air pollution, including the use of biotechnology approaches like microalgal photosynthesis and biological calcification to reduce carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The document concludes with a summary of the causes and impacts of air pollution and the need for continued control efforts.