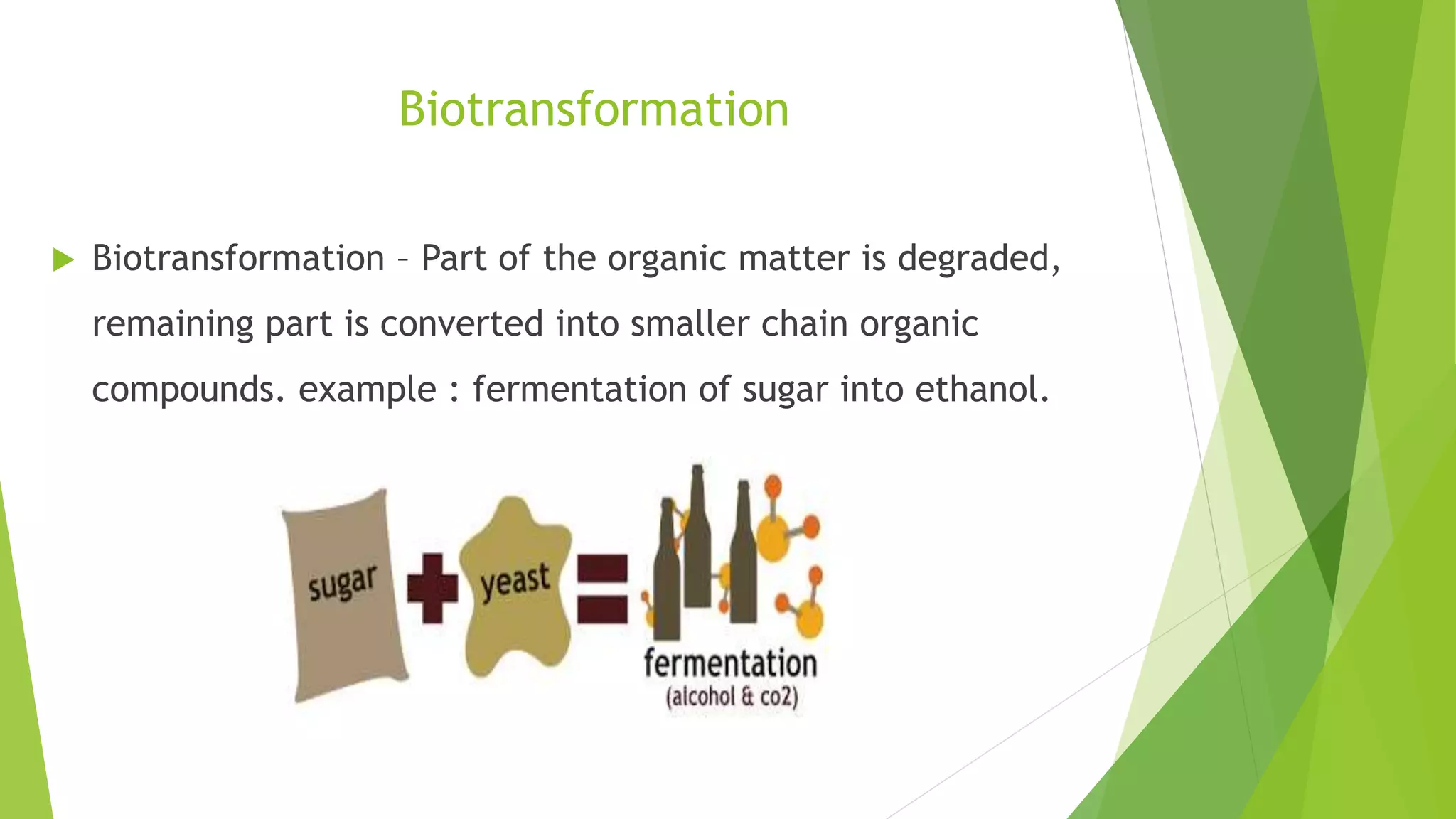
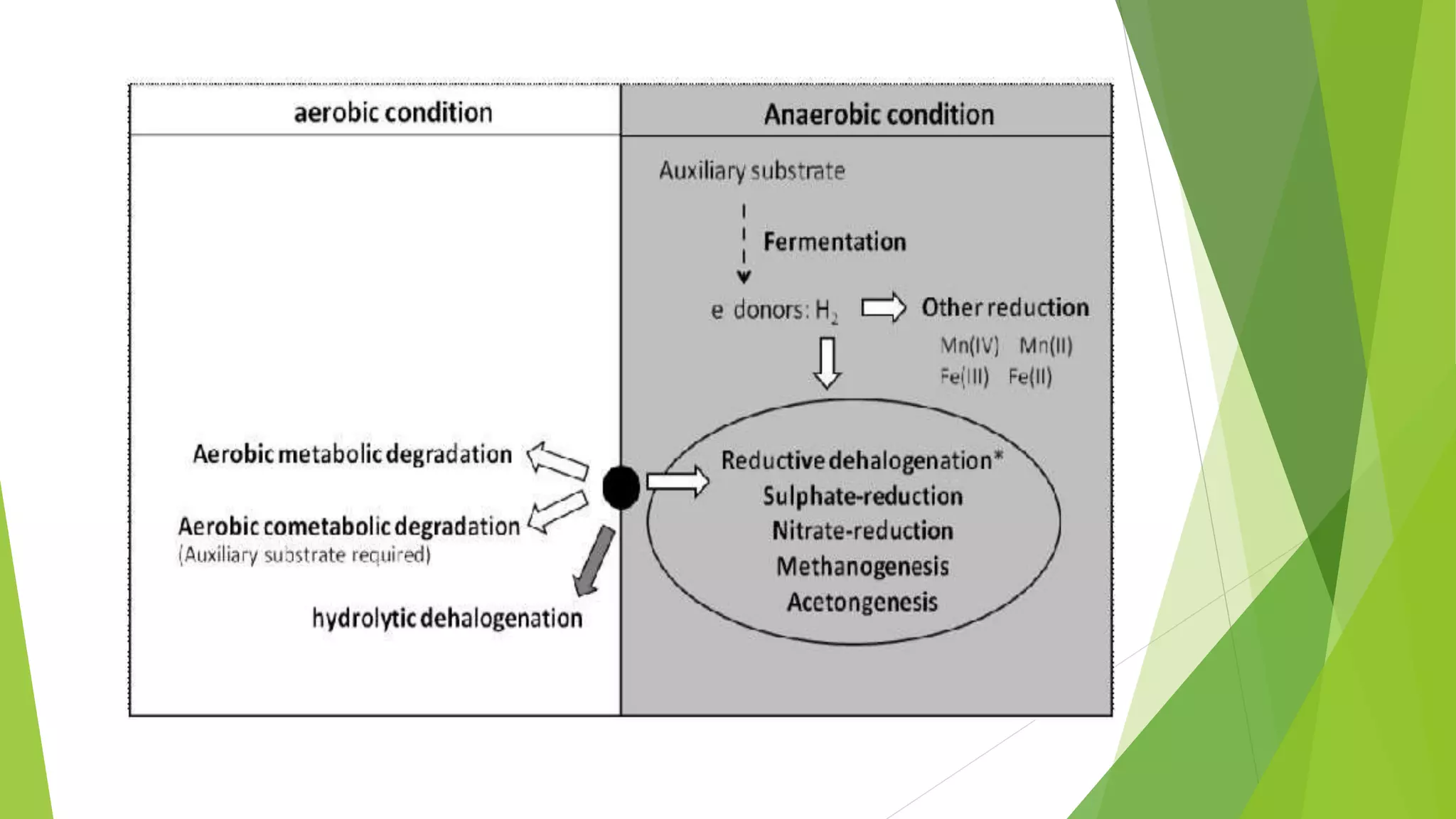
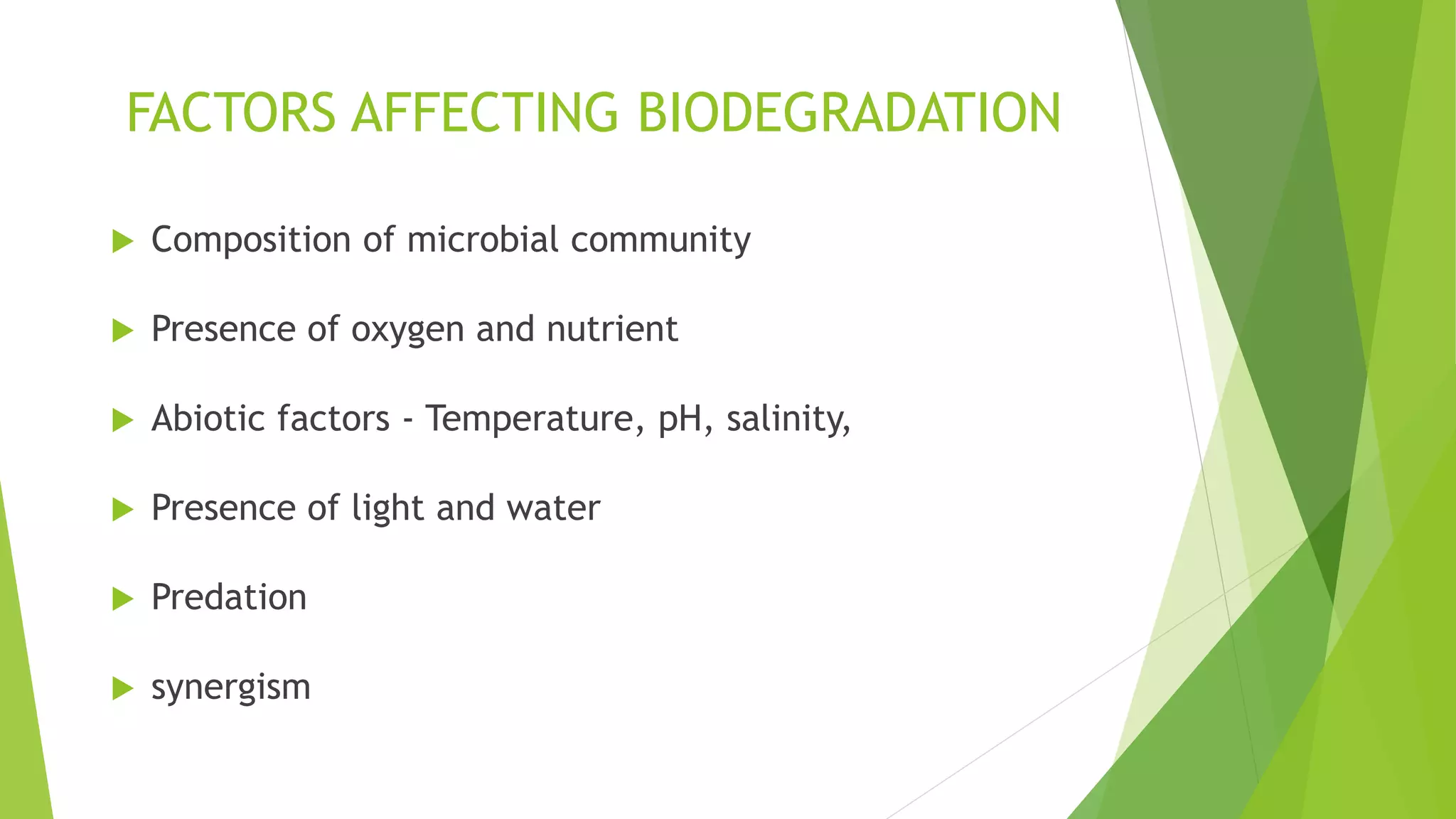
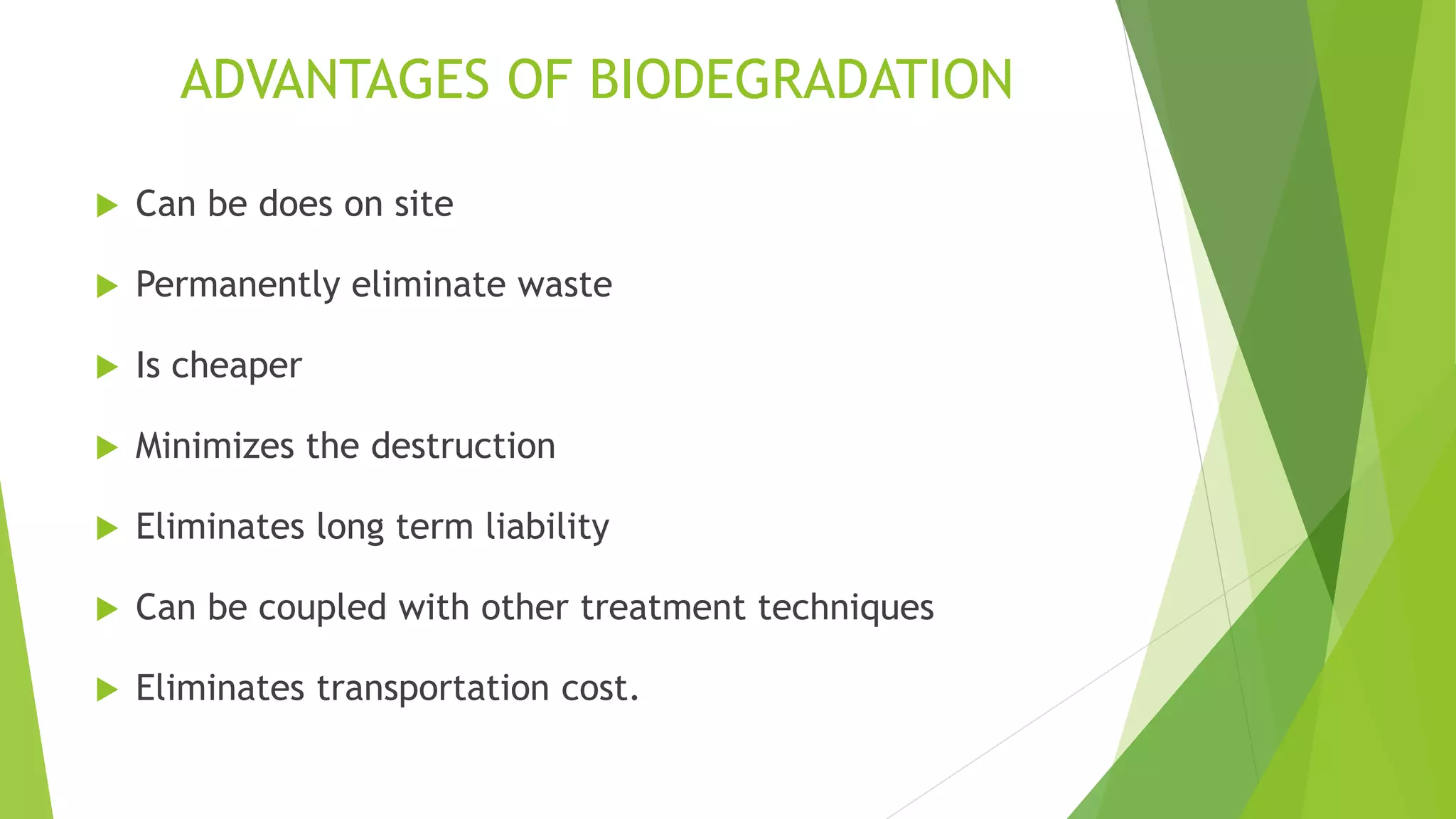
This document discusses biodegradation, which is the breakdown of materials by bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms. Biodegradation can occur aerobically with oxygen or anaerobically without oxygen. It breaks down organic materials into basic components like carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Factors that affect biodegradation include the microbial community present, oxygen levels, temperature, pH and the presence of light and water. Biodegradable plastics have been treated to break down when discarded using additives. While biodegradation can help eliminate waste, some chemicals cannot degrade and unknown byproducts may form.