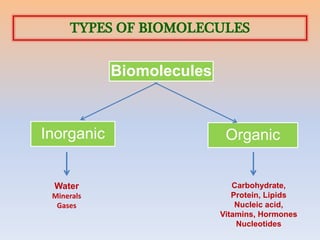
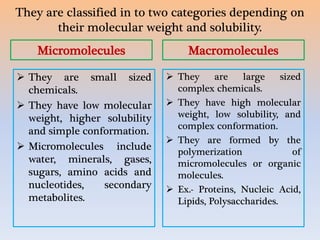
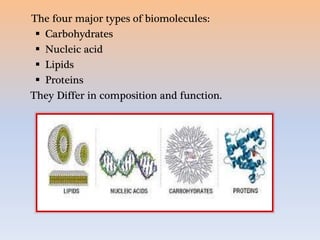
Biomolecules are organic and inorganic chemicals that occur in living organisms. They include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and other molecules. Biomolecules can be classified as either micromolecules, which are small and soluble, or macromolecules, which are large polymers formed from micromolecules. The four major types of biomolecules - carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins - differ in their composition and functions, which include energy storage, heredity, structure, and catalysis of biological processes.