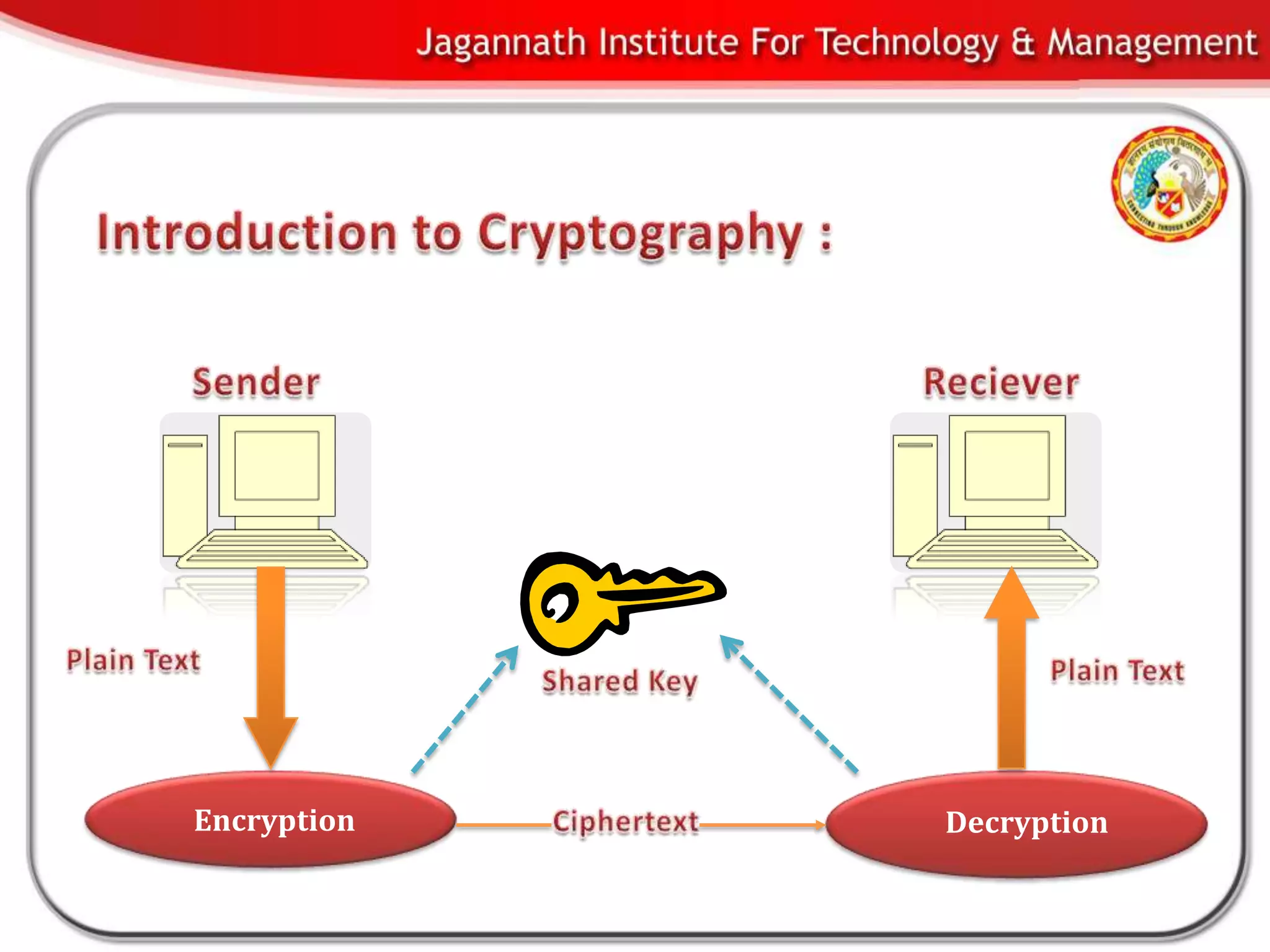
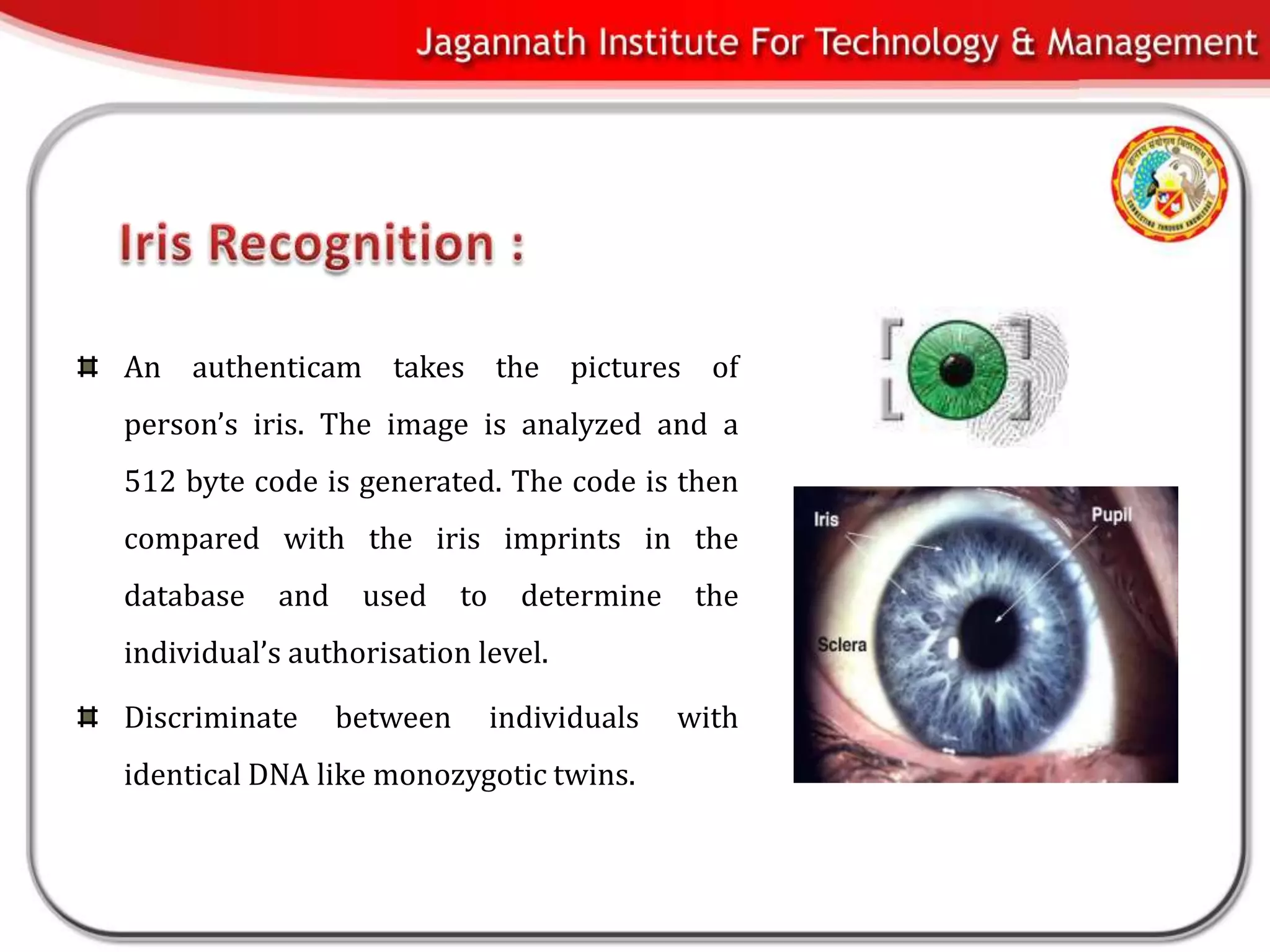
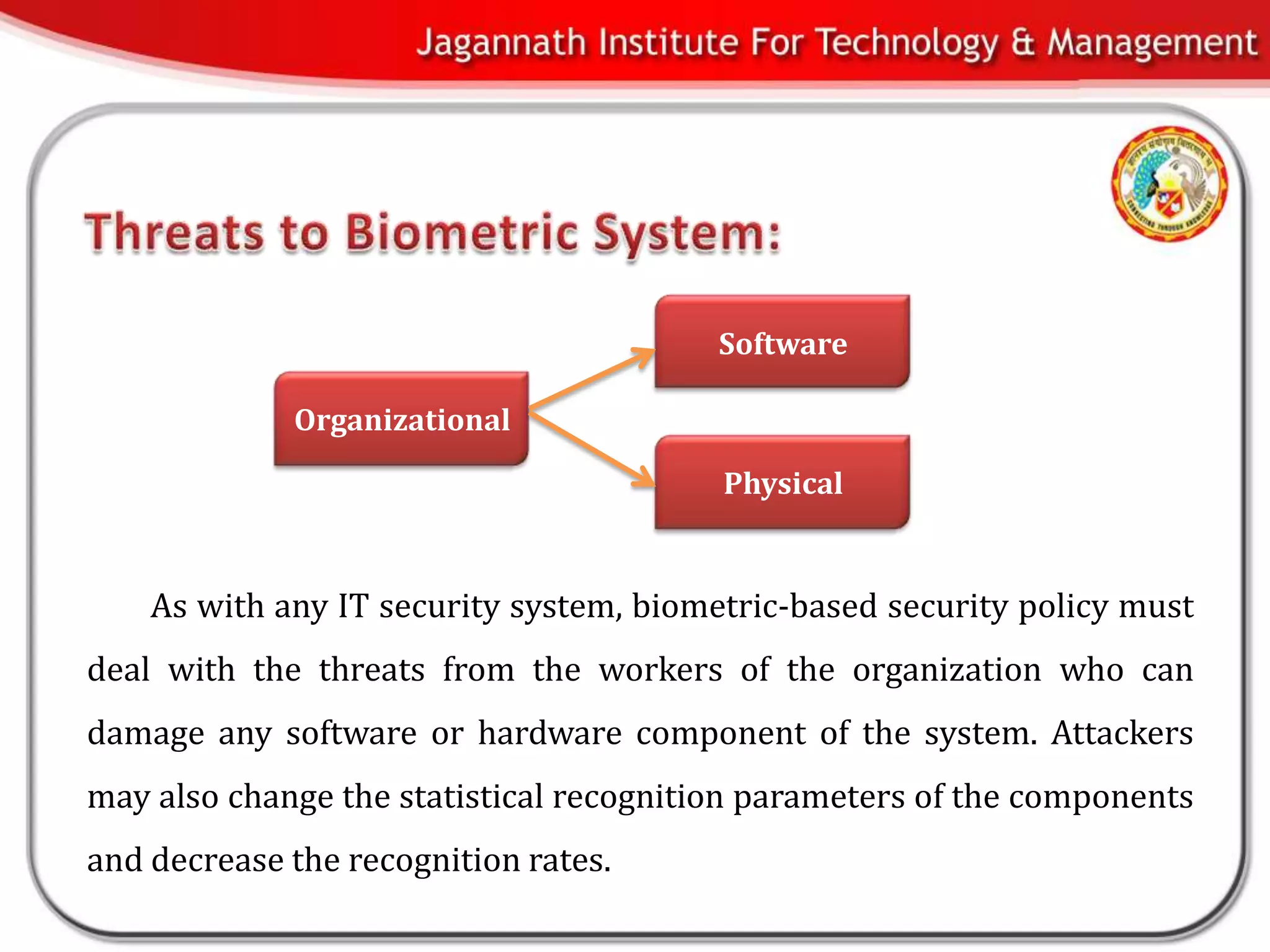
This document discusses biometrics and biometric encryption. It begins with an introduction to biometrics and biometric principles and standards. It then discusses different methods to securely store cryptographic keys using biometrics, including biometric encryption. The document compares userID-based keys to biometric-based keys. It also covers advantages and threats of biometric systems, as well applications of biometric systems. In conclusion, the document provides an overview of biometrics and biometric encryption.