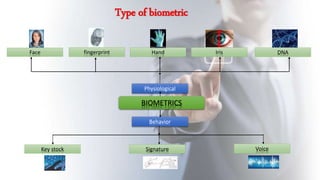
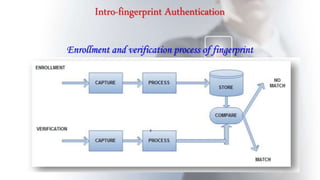
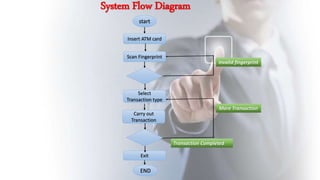
This document discusses using fingerprint biometrics for authentication in ATM machines. It defines ATMs and outlines issues with current identification methods like stolen cards and shared PINs. Fingerprint biometrics could solve these issues through multi-factor authentication combining cards, PINs, and fingerprints. The document then covers fingerprint patterns, how fingerprint scanners work to enroll and verify prints, and the system design of a biometric ATM including hardware and software components. Potential advantages are discussed like increased security over shared passwords, with disadvantages including higher costs.