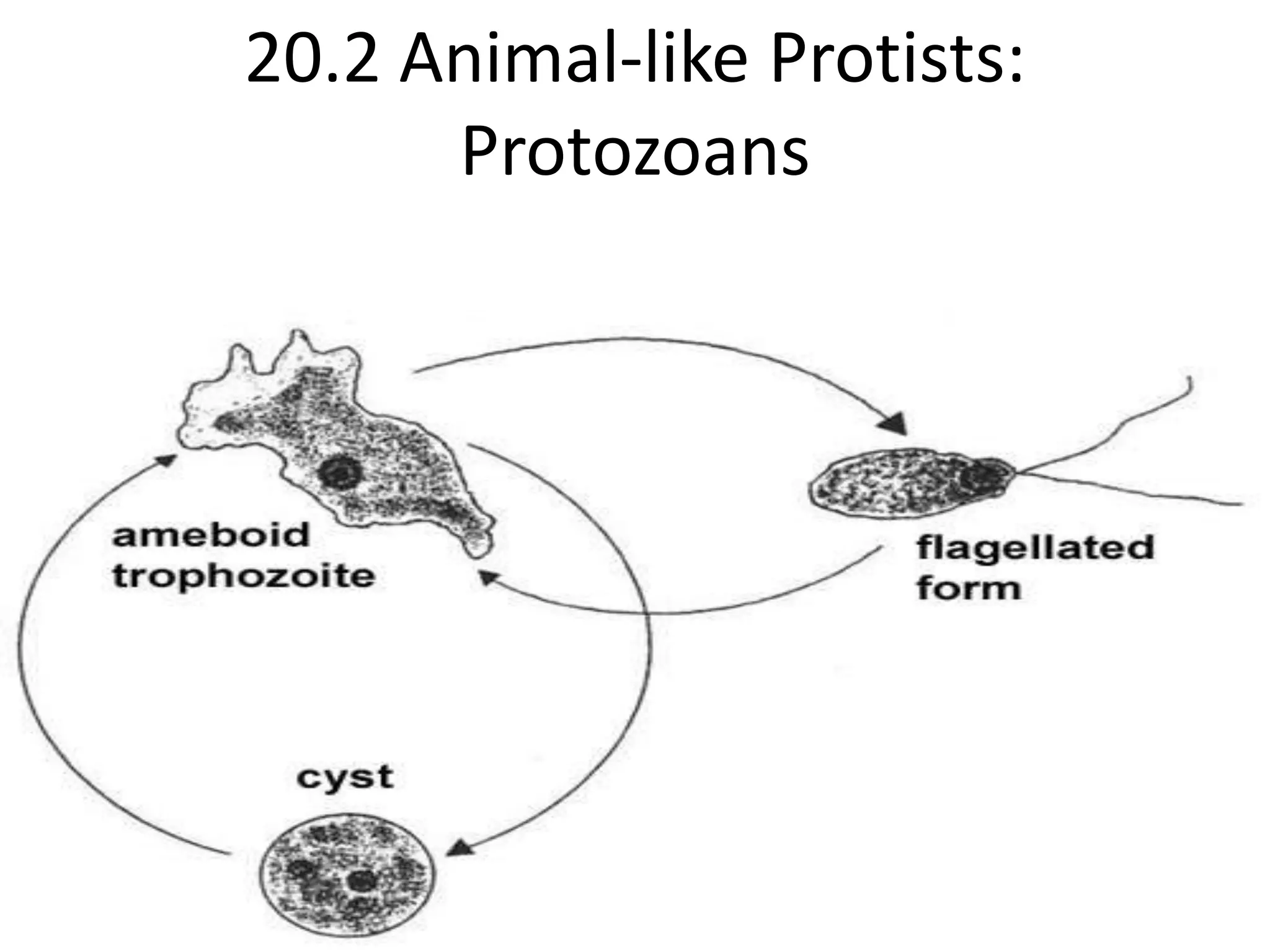
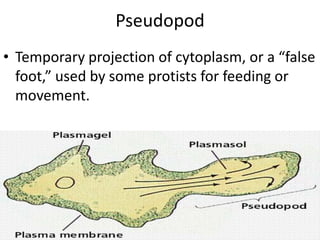
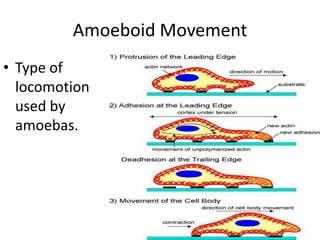
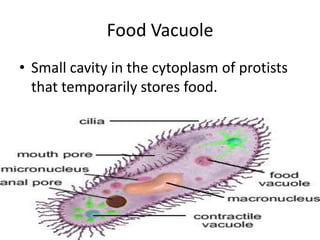
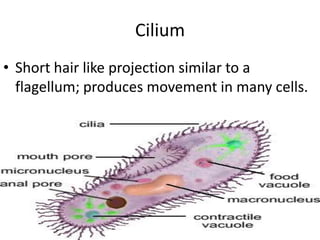
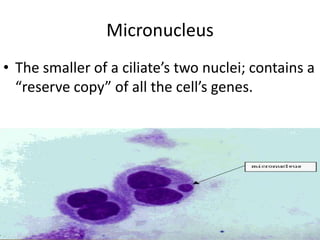
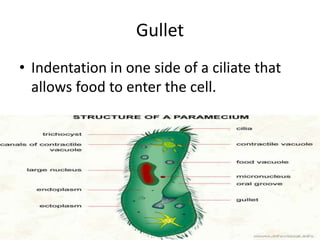
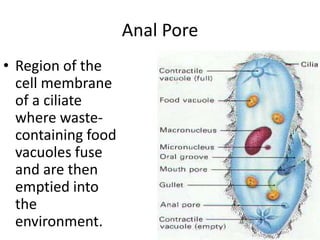
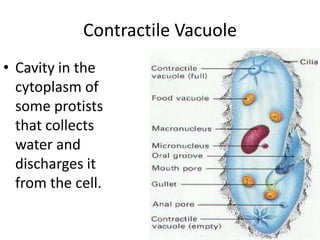
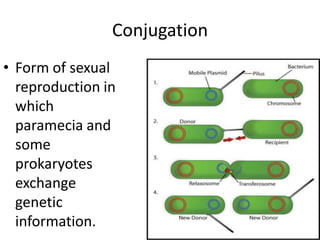
This document defines and describes various structures and processes in animal-like protists called protozoans. It explains pseudopods, amoeboid movement, food vacuoles, cilia, trichocysts, micronuclei, macronuclei, gullets, anal pores, contractile vacuoles, and conjugation. It also notes that zooflagellates use flagella to swim and some protozoans can cause serious diseases.