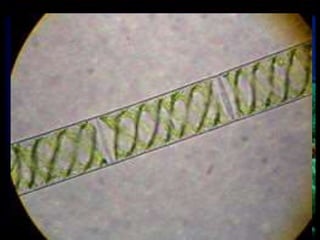
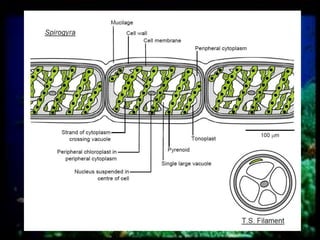
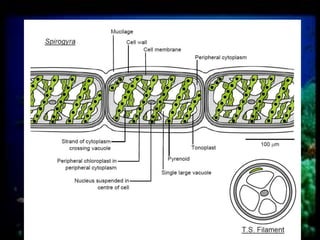
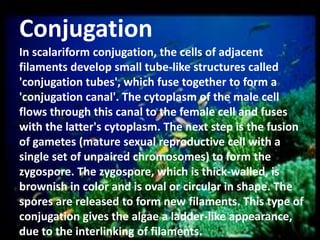
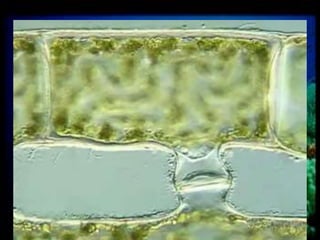
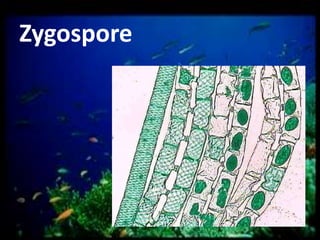
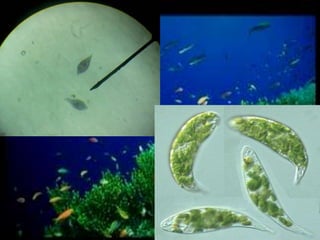
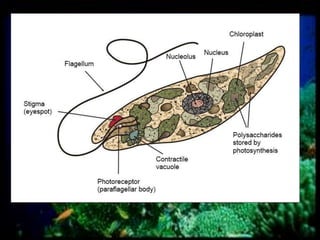
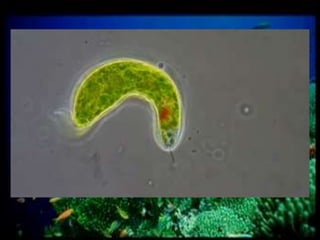
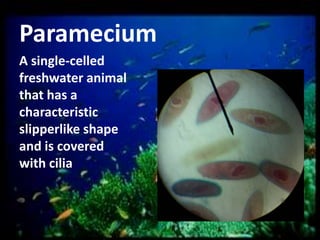
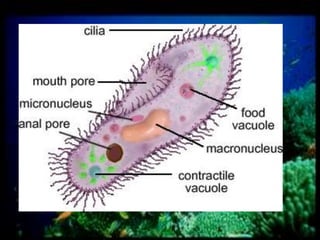
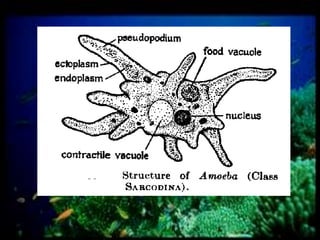
This document discusses different types of protists, including unicellular algae like Spirogyra and diatoms, euglenoids like Euglena, and protozoans like Paramecium and amoeba. Spirogyra are filamentous green algae with spiral chloroplasts that undergo scalariform conjugation, where conjugation tubes fuse gametes between adjacent filaments. Diatoms have silica cell walls and come in many shapes, containing pigments that give them a golden color. Euglena are discoidal microalgae that move using a flagellum and contain a contractile vacuole. Paramecium reproduce asexually through binary fission and sexually through conjugation