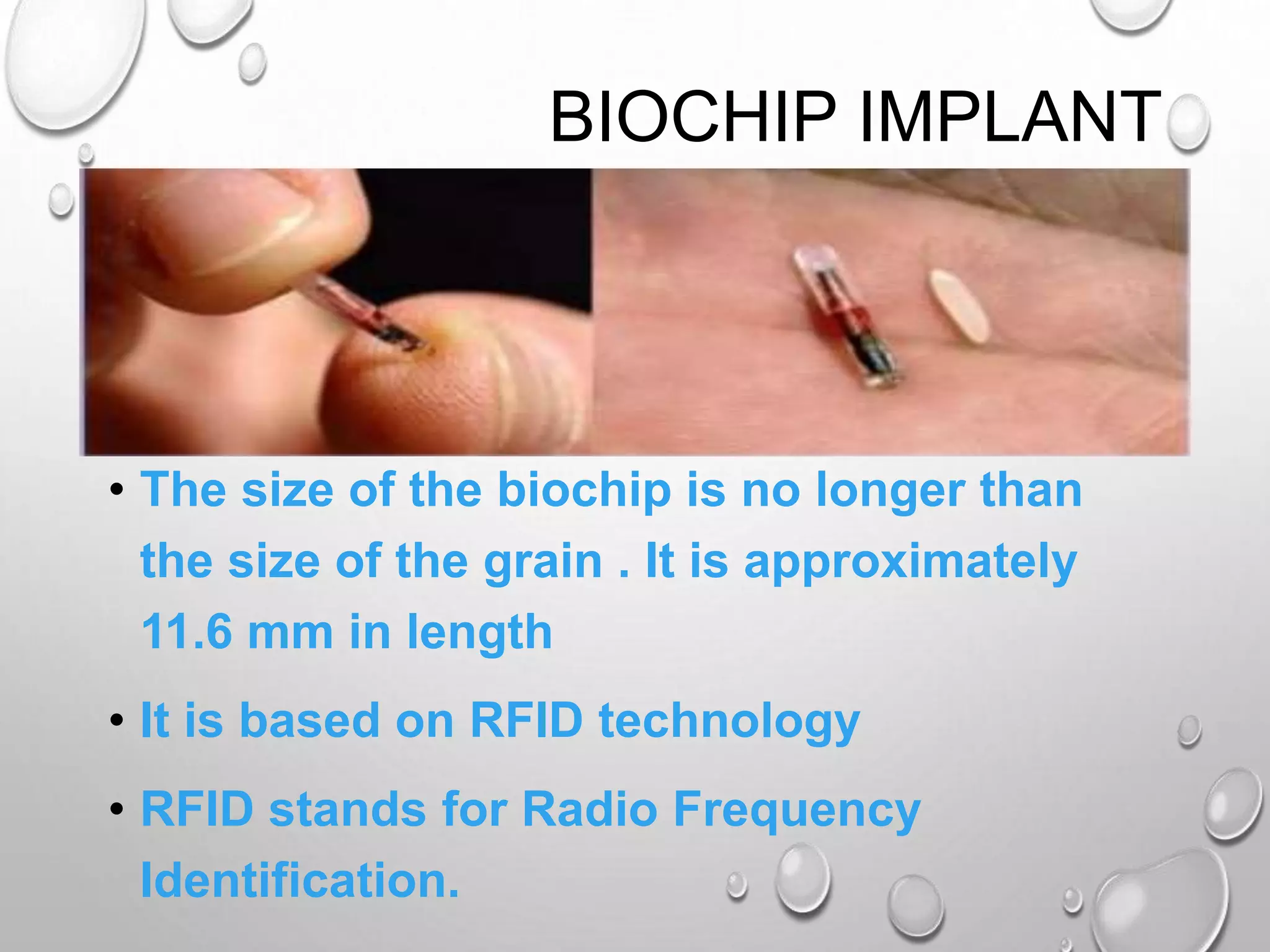
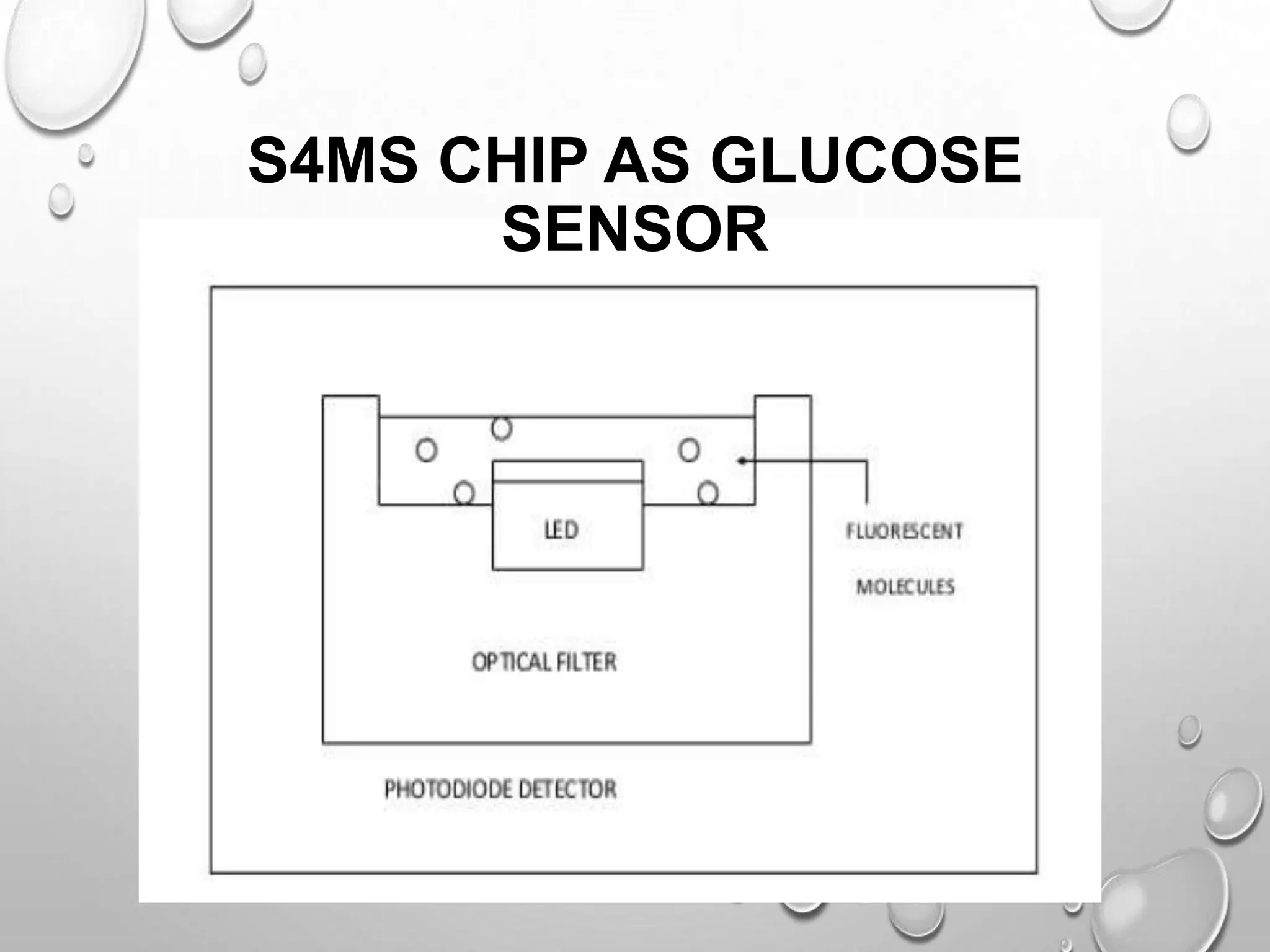
The document discusses biochips, which are microarray devices implanted under the skin that can perform multiple medical tests simultaneously. It provides the history of biochips from their origins in glucose sensors to modern commercial versions. A biochip implant consists of a transponder containing a microchip, antenna coil, and capacitor, encased in biocompatible glass. When activated by a reader, it transmits a unique identification code. Applications include tracking individuals, storing medical/financial information, and monitoring health conditions like glucose levels. While biochips provide benefits for healthcare, they also raise privacy and freedom concerns if used to monitor people without consent.