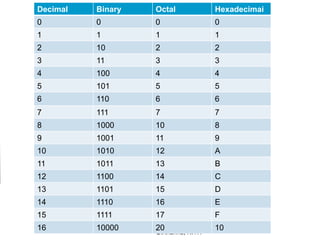
1. The document discusses different number representation systems like binary, octal, hexadecimal and their conversions to decimal numbers.
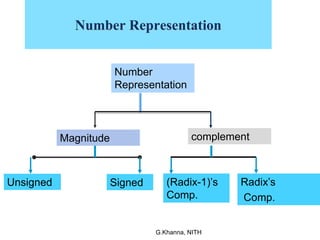
2. It explains various methods for representing signed numbers like signed magnitude representation, 1's complement and 2's complement methods. The 2's complement method allows representing numbers in the range of -(2n-1) to +(2n-1-1).
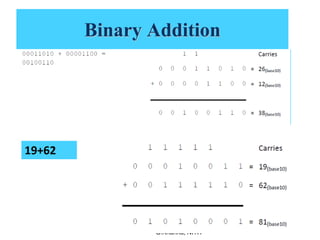
3. Binary addition and subtraction algorithms are covered along with examples. Radix complement method is discussed for subtraction which involves converting the number to its radix-1's complement before addition.