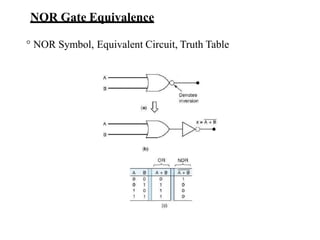
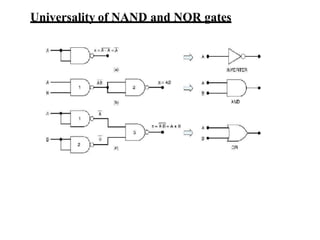
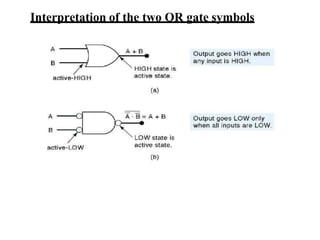
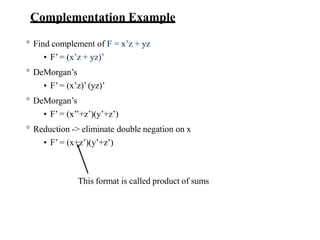
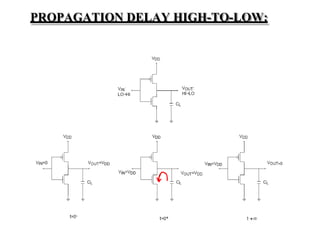
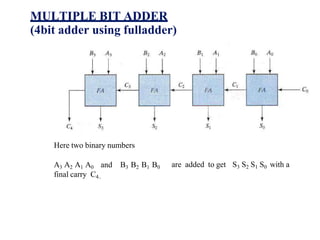
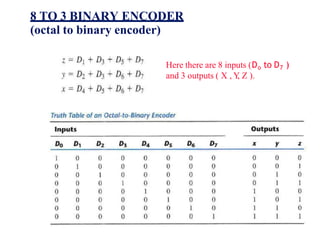
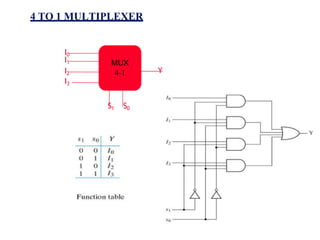
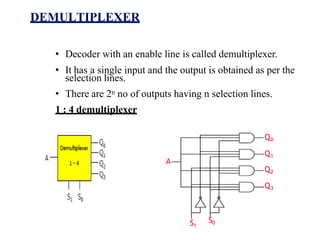
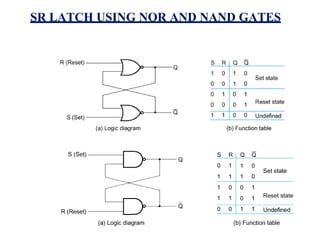
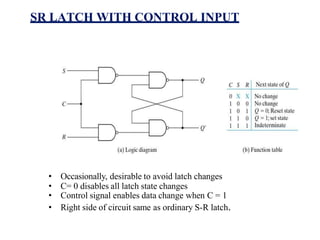
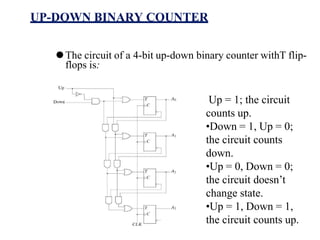
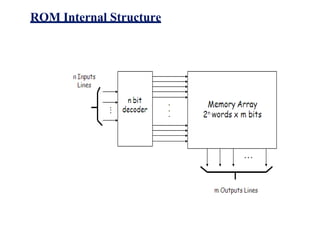
This document provides lecture notes on digital system design. It covers topics like logic simplification, combinational logic design, understanding binary and other number systems, binary operations, and Boolean algebra. The first section discusses decimal, binary, octal and hexadecimal number systems. Later sections explain binary addition, subtraction, multiplication and conversions between number bases. Signed number representations like 1's complement and 2's complement are also introduced. Finally, the document discusses Boolean algebra, logic functions, truth tables, and basic logic gates like AND and INVERTER.





















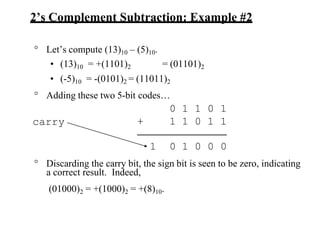
![Two’s Complement
° Algorithm 1 – Simply complement each bit and then add 1 to the
result.
• Finding the 2’s complement of (01100101)2 and of its 2’s
complement…
N = 01100101 [N] = 10011011
10011010 01100100
+ 1
-
10011011
+ 1
01100101
° Algorithm 2 – Starting with the least significant bit, copy all of the bits
up to and including the first 1 bit and then complementing the
remaining bits.
• N
[N]
= 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1
= 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-electronics-221009074643-9bec069c/85/digital-electronics-pptx-22-320.jpg)