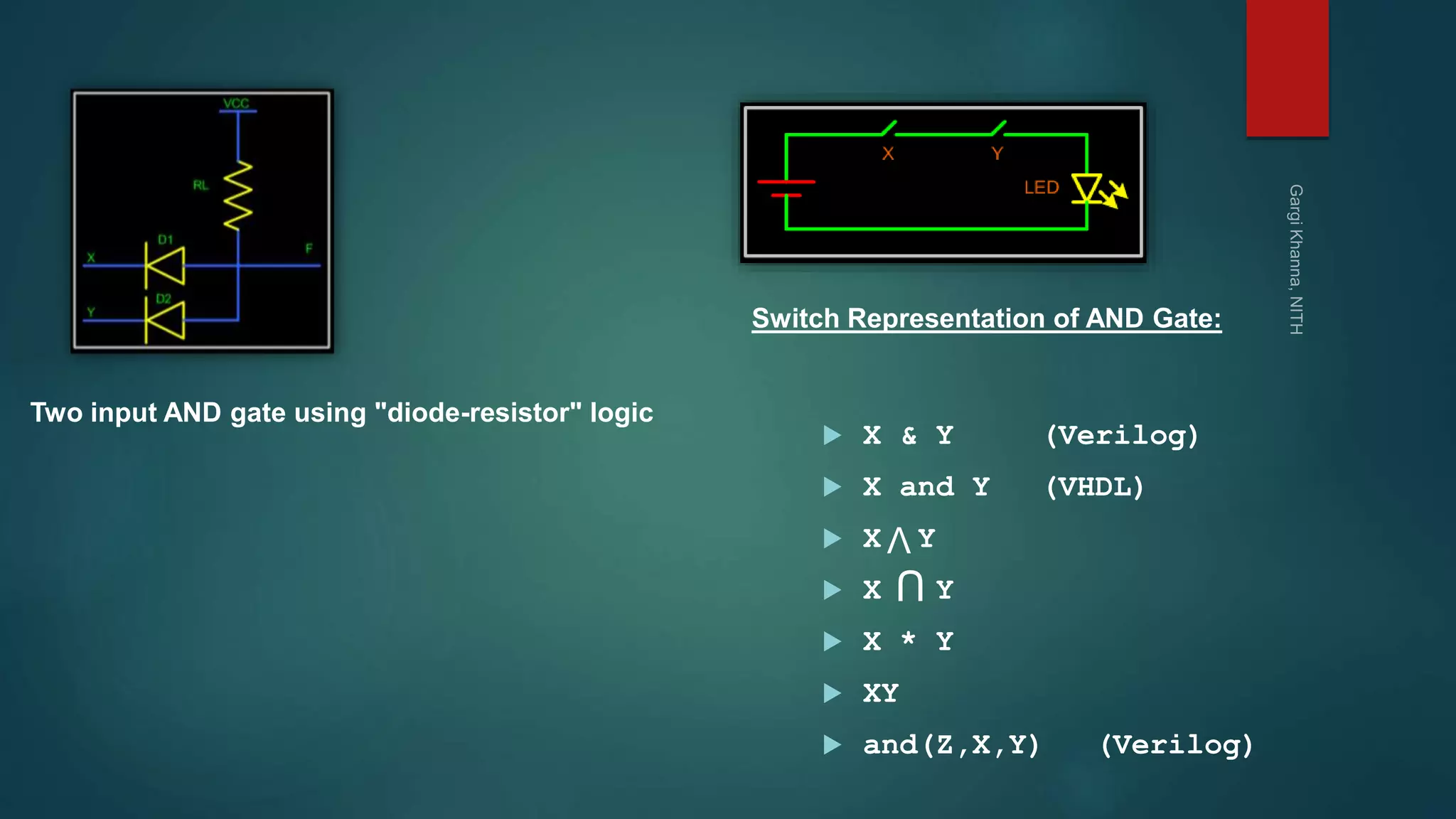
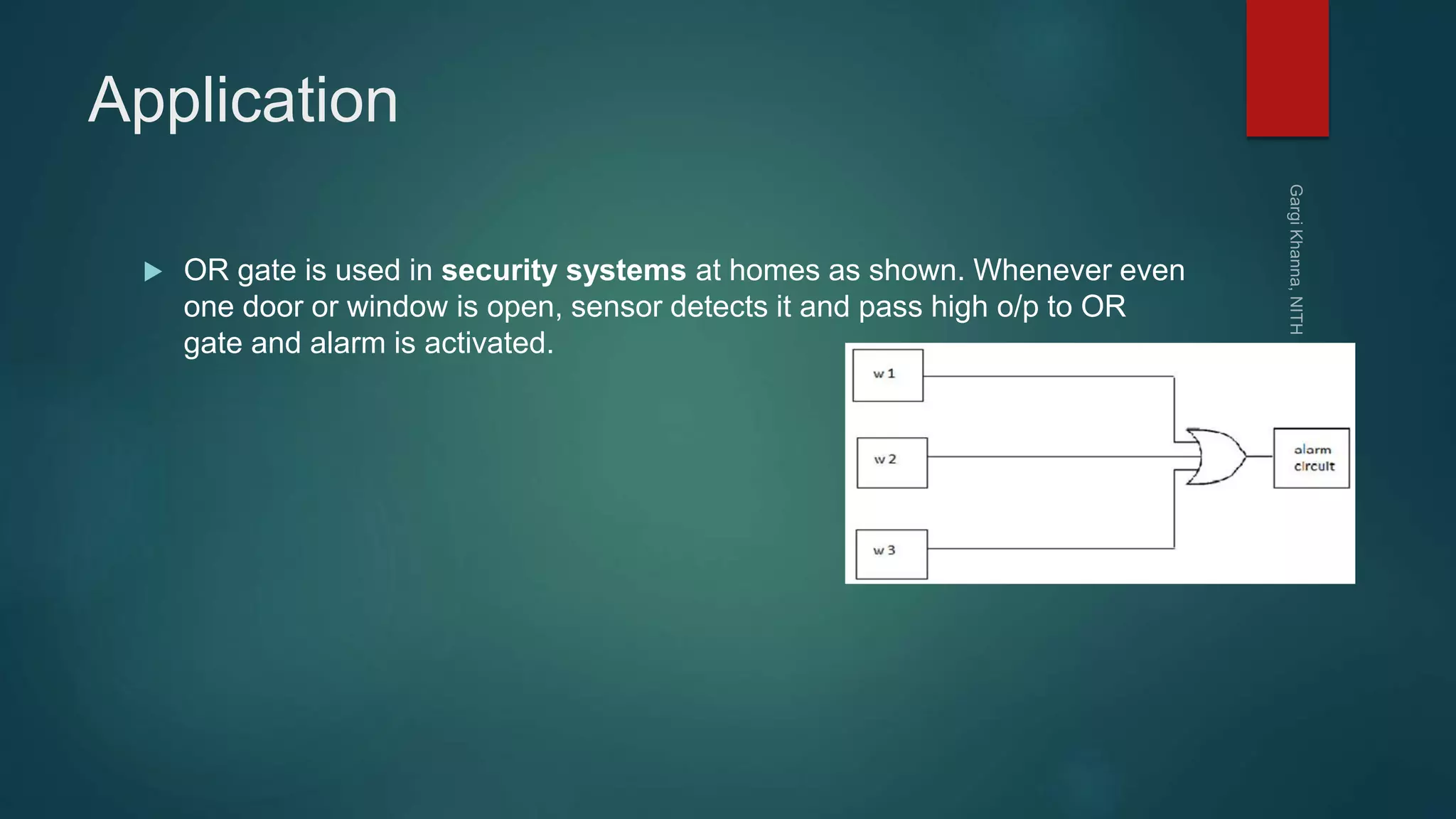
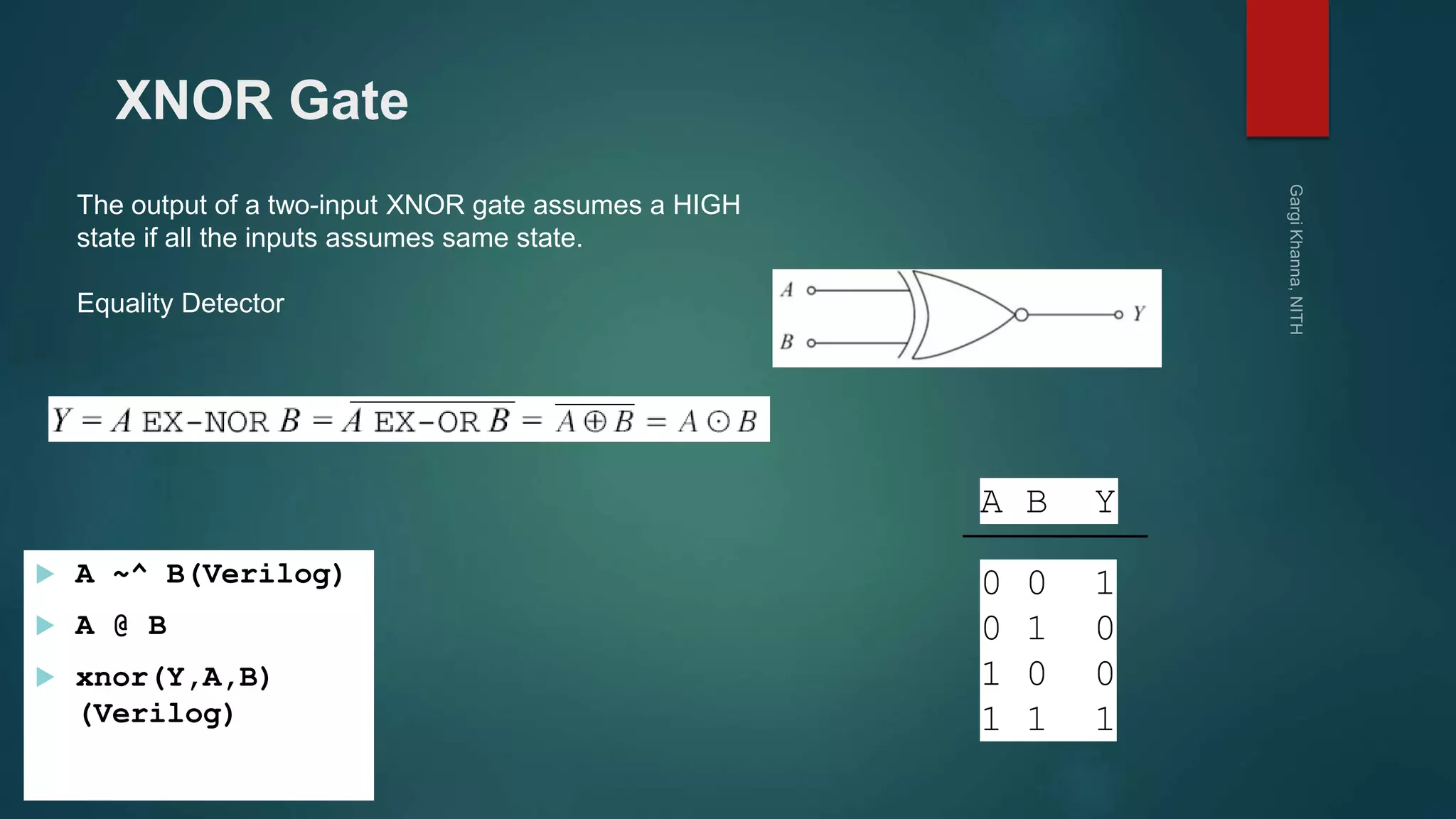
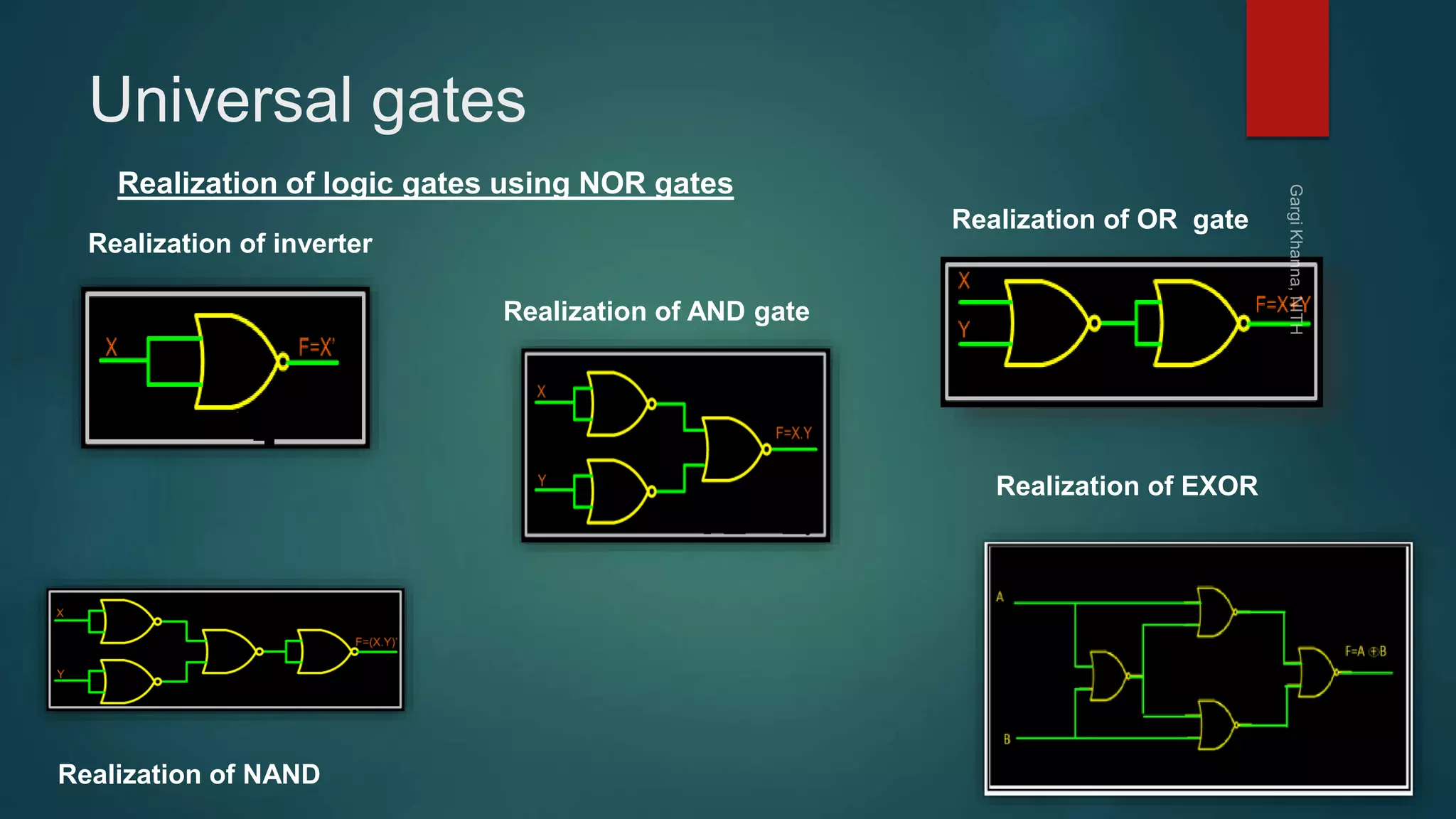
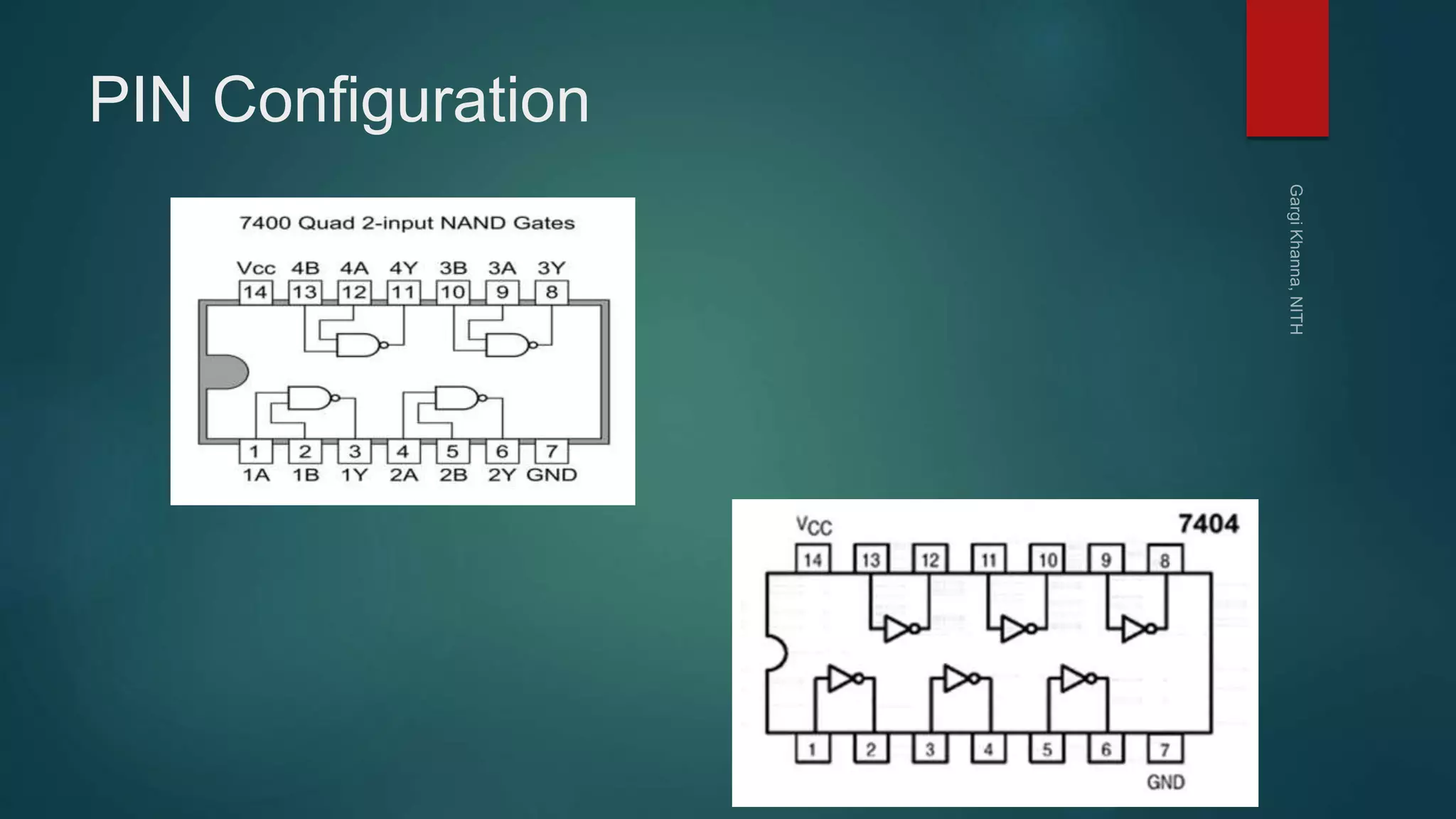
Dr. Gargi Khanna teaches digital electronics and logic design at the National Institute of Technology in Hamirpur. The document defines digital signals as having two discrete levels (HIGH and LOW), and describes the basic logic gates - NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR. It provides truth tables and Boolean equations for each gate, discusses their implementation using transistors and resistors, and gives examples of applications. Universal gates such as NAND and NOR are also covered, as they can be used to realize all other logic functions.