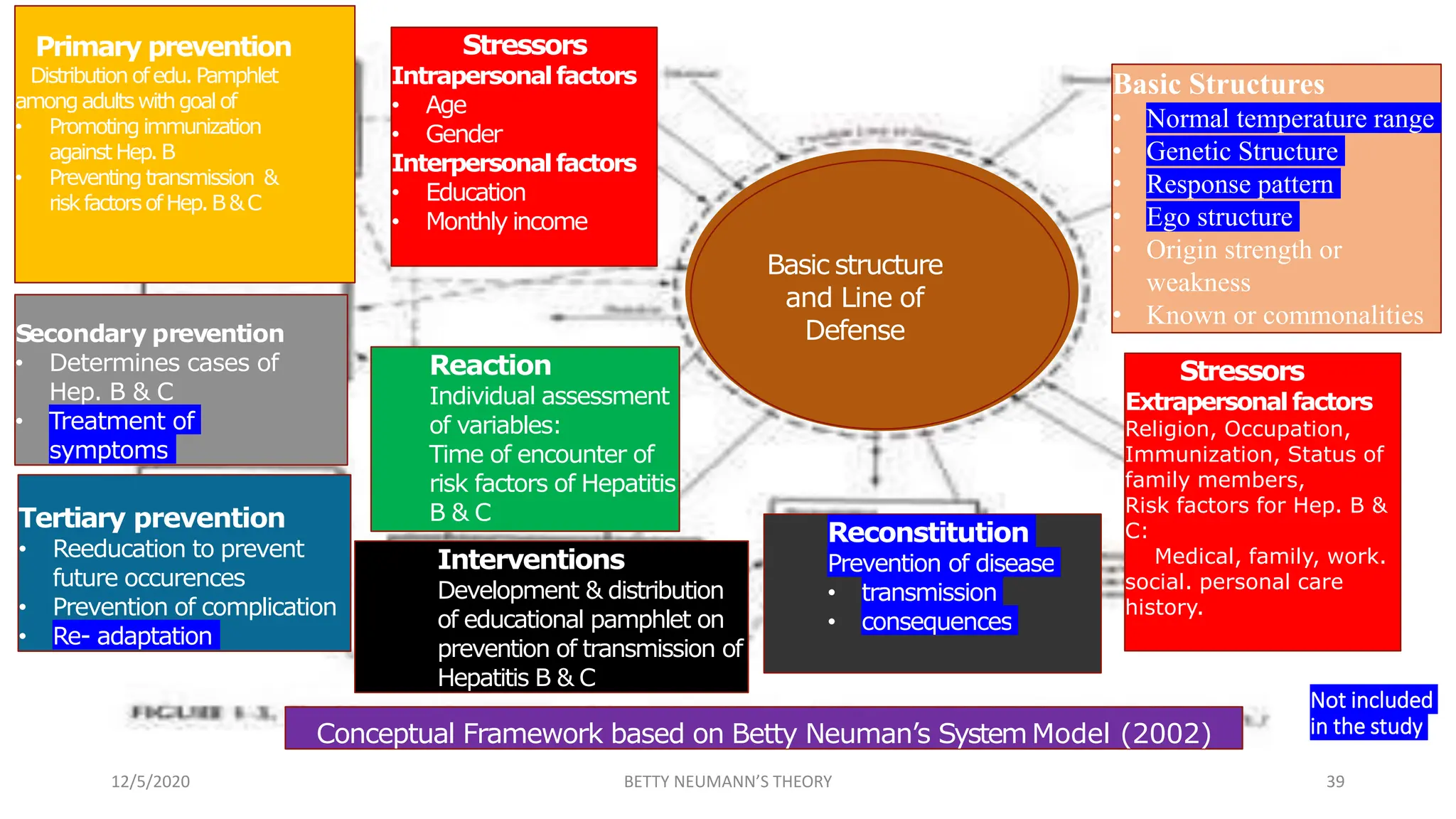
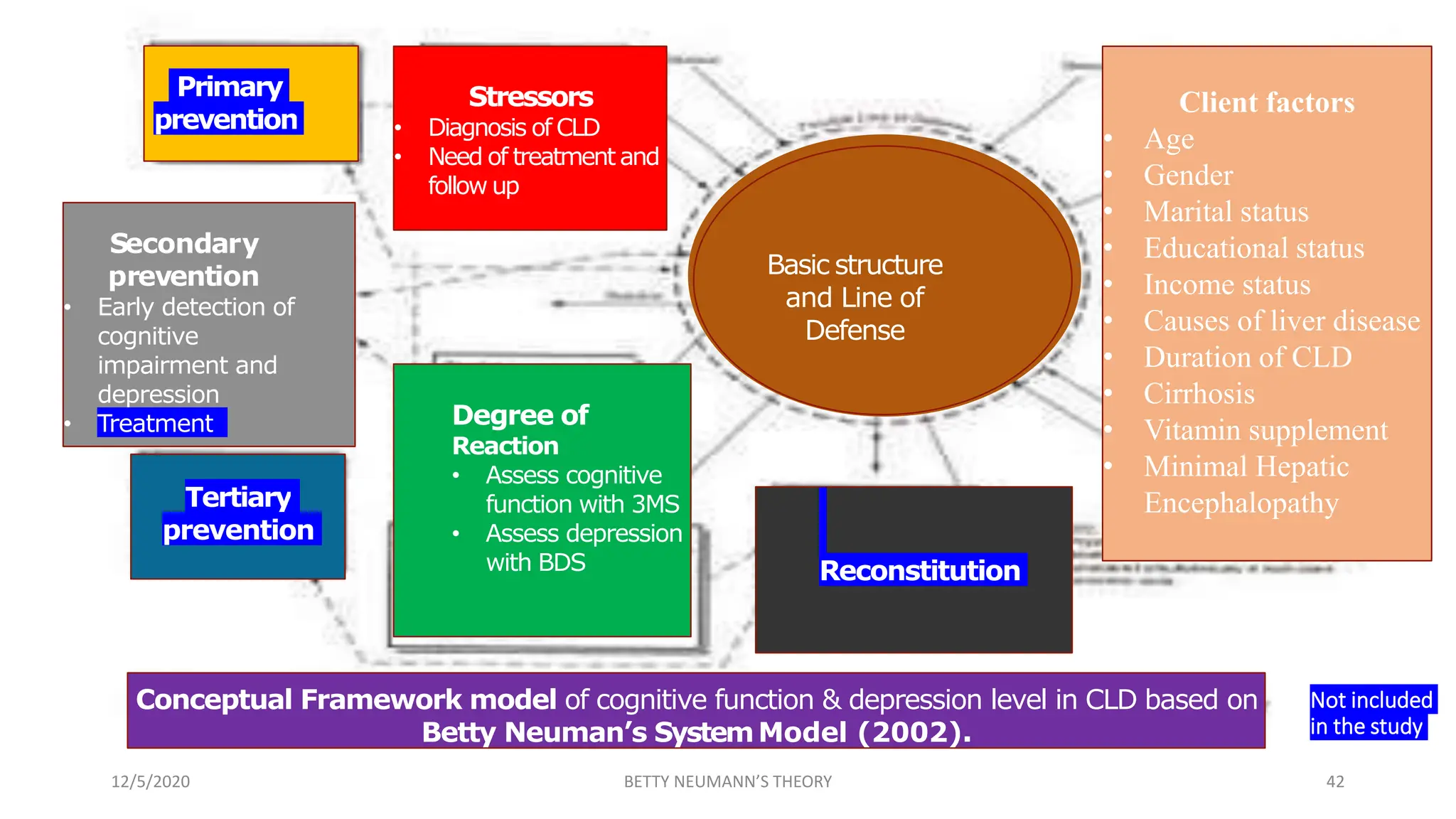
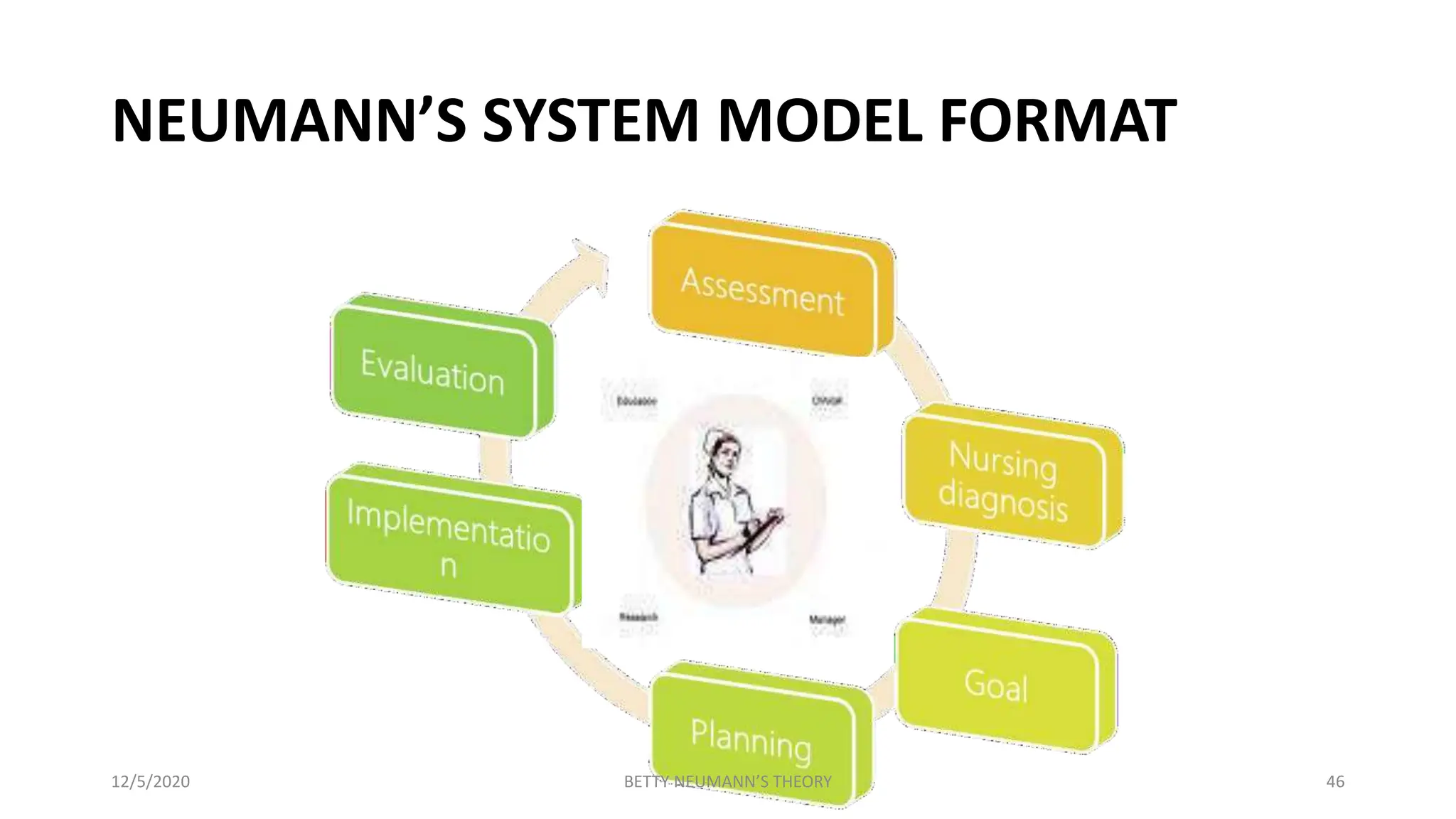
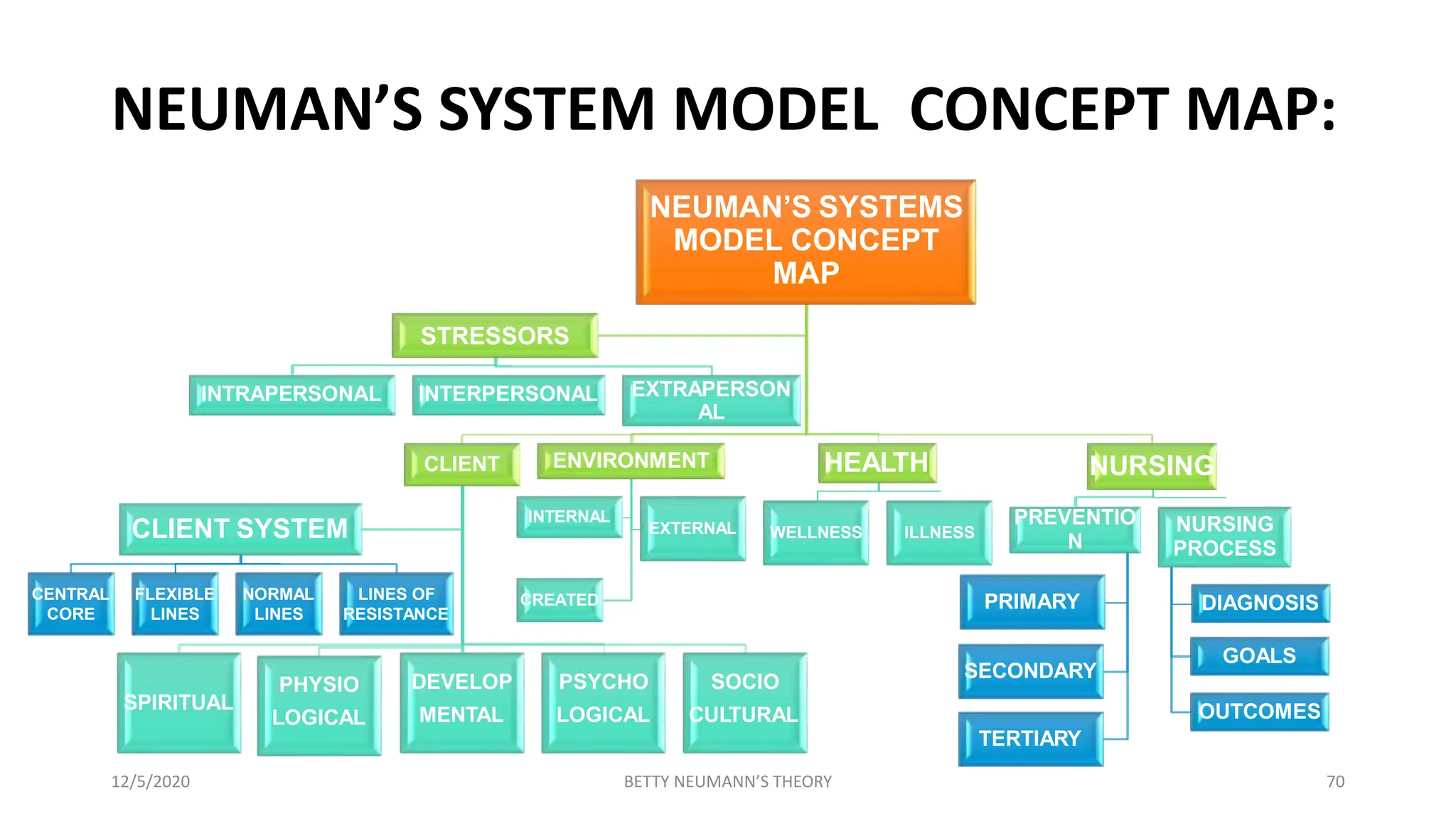
The document presents an overview of Betty Neuman's Systems Model, which is a comprehensive, holistic framework for nursing that addresses the client's response to environmental stressors. It details Neuman's background, the evolution and components of the model, including fundamental concepts of person, environment, health, and nursing, highlighting its application in various nursing practices. Additionally, it includes research examples illustrating the model's effectiveness in health education and nursing diagnoses.