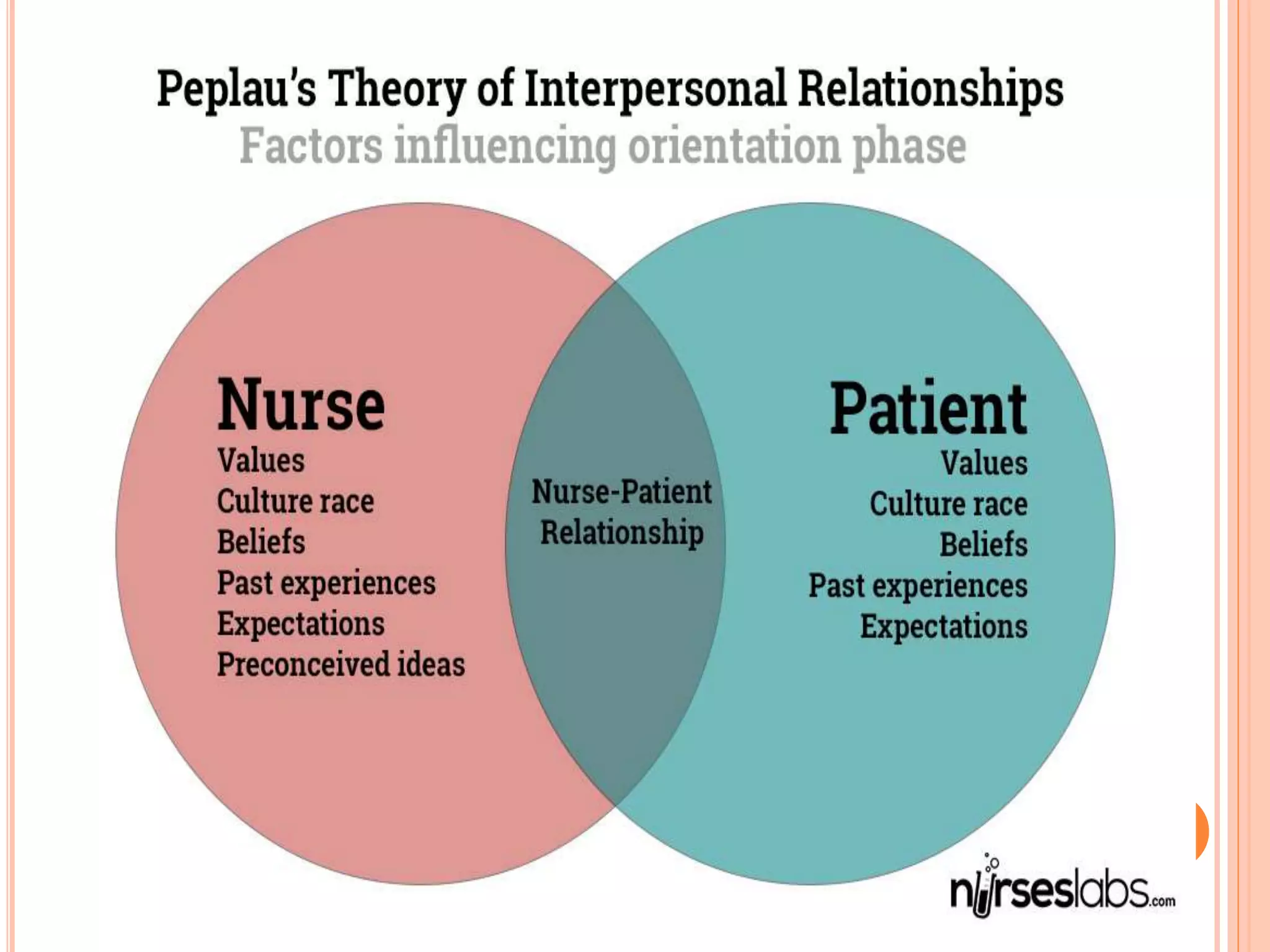
Hildegard Peplau developed the Interpersonal Relations Theory, which focuses on the nurse-patient relationship and identifies phases and roles in that relationship. The theory outlines four phases - orientation, identification, exploitation, and resolution - and seven nursing roles - stranger, resource, teacher, counselor, surrogate, leader, and colleague. Proper application of the theory helps nurses understand patients' needs, facilitate problem-solving, and ensure the relationship progresses appropriately towards termination.