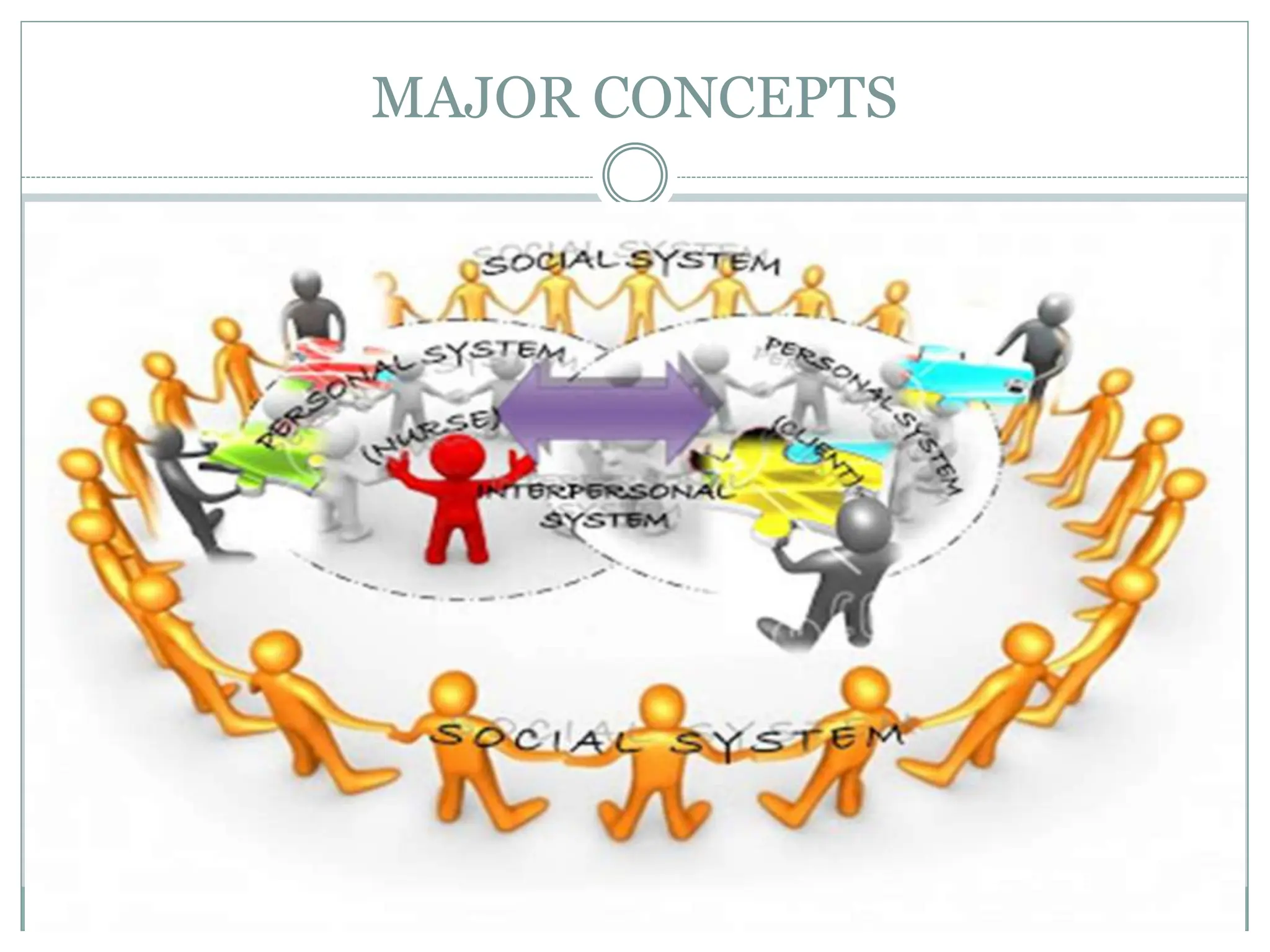
This document provides an overview of Imogene King's Theory of Goal Attainment. It discusses King's background and education. The theory describes nursing as a dynamic interpersonal process where a nurse and client communicate to mutually set and work towards goals. It outlines the theory's major concepts including personal, interpersonal, and social systems. Key concepts for each system like perception, self, roles, and stress are defined. The document also presents the theory's basic assumptions and propositions and examines how the theory relates to the nursing process.