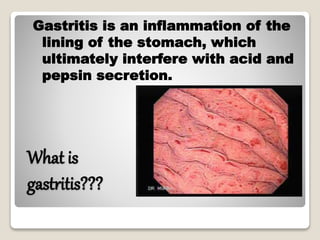
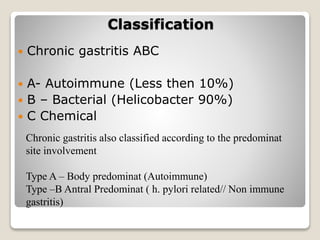
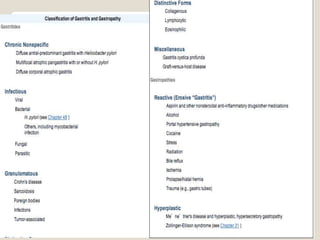
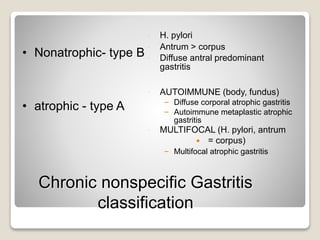
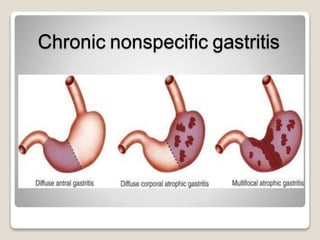
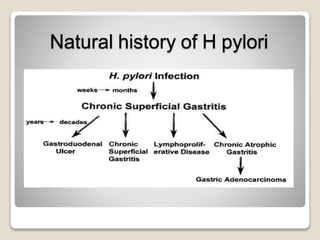
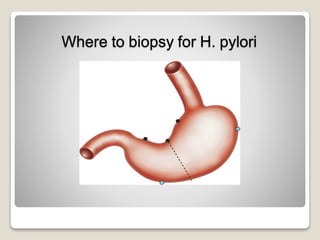
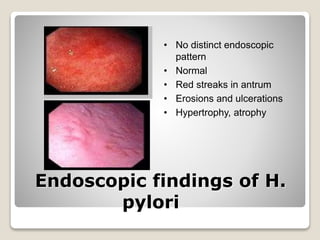
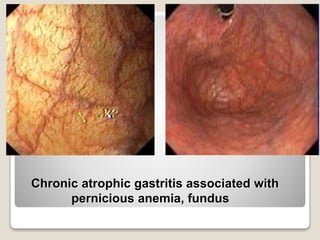
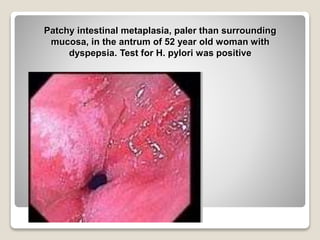
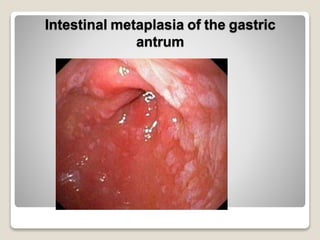
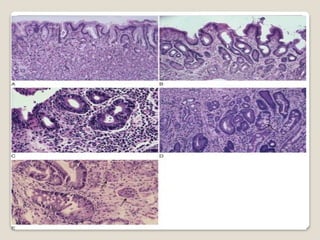
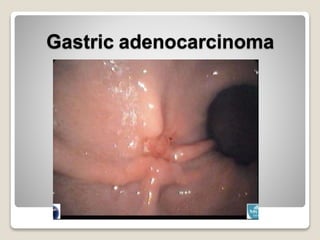
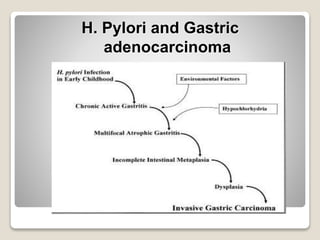
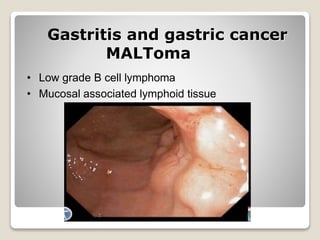
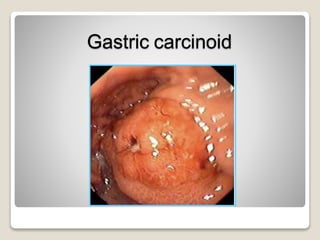
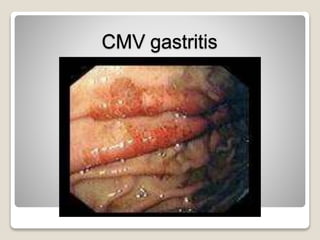
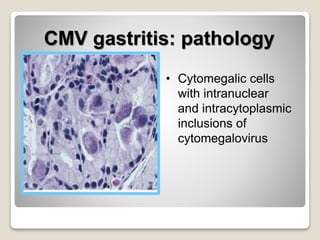
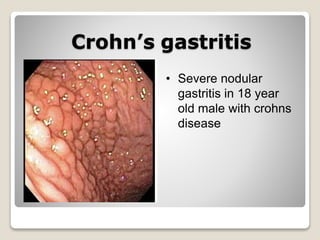
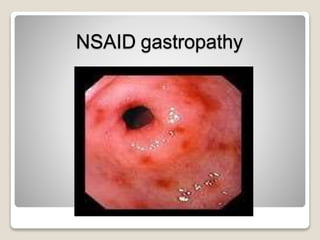
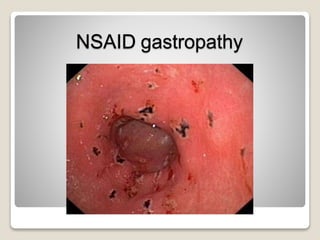
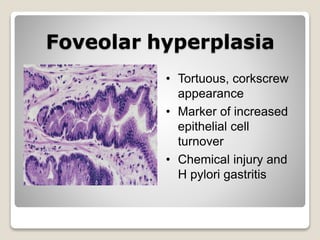
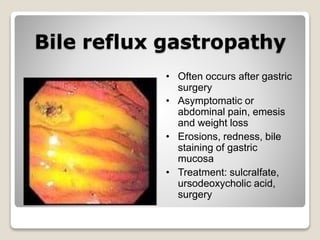
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining that can interfere with acid and pepsin secretion, primarily affecting older adults and those with lifestyle factors like alcohol and smoking. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite, while diagnosis often involves a combination of patient history, laboratory tests, and endoscopy. Treatment may include medications like antiemetics, antacids, and antibiotics, along with dietary adjustments, with a generally good prognosis if patients follow medical advice and lifestyle changes.