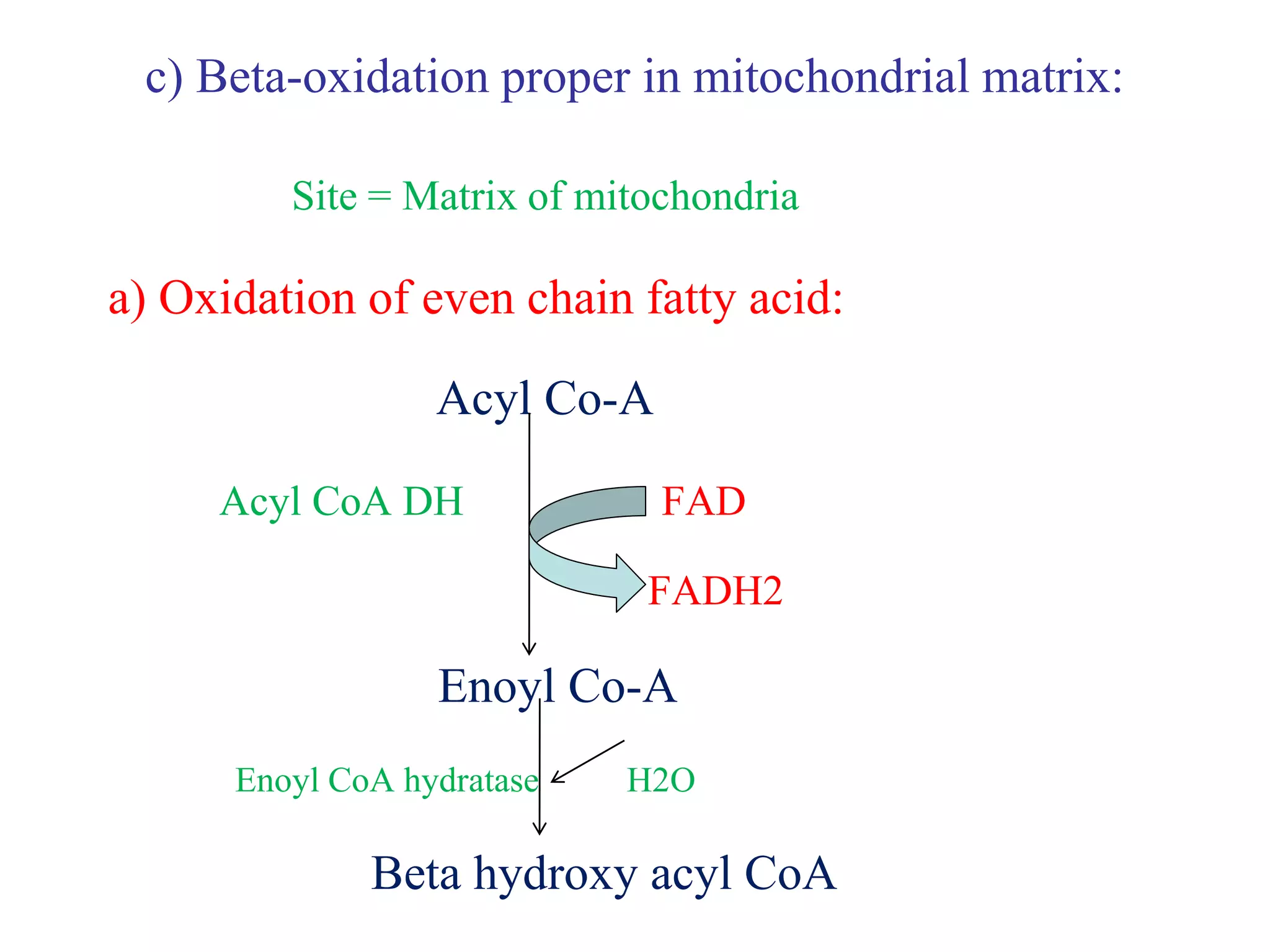
This document summarizes fatty acid oxidation (beta-oxidation) which occurs in three steps: activation in the cytosol, transport from cytosol to mitochondria via carnitine, and beta-oxidation in the mitochondrial matrix. Carnitine transports long-chain fatty acyl-CoA from cytosol to mitochondria for beta-oxidation. Oxidation of palmitic acid through 7 cycles produces 129 ATP. Disorders of fatty acid oxidation include carnitine deficiency and sudden infant death syndrome due to defects in medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase.