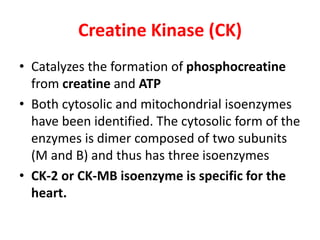
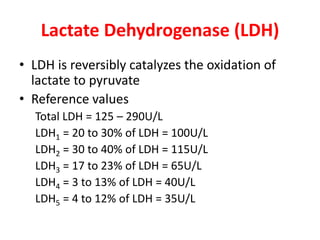
Cardiac markers are proteins and enzymes released when heart muscle is damaged. They help diagnose acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and other heart conditions. Key markers include creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), troponins, and myoglobin. Troponins and myoglobin rise earliest after AMI onset (1-8 hours) while CK and LDH levels peak later (12-72 hours). Troponins remain elevated the longest (5-10 days) making them the most specific indicators of heart damage. Together, cardiac markers provide a timeline of injury and are crucial for accurate diagnosis.