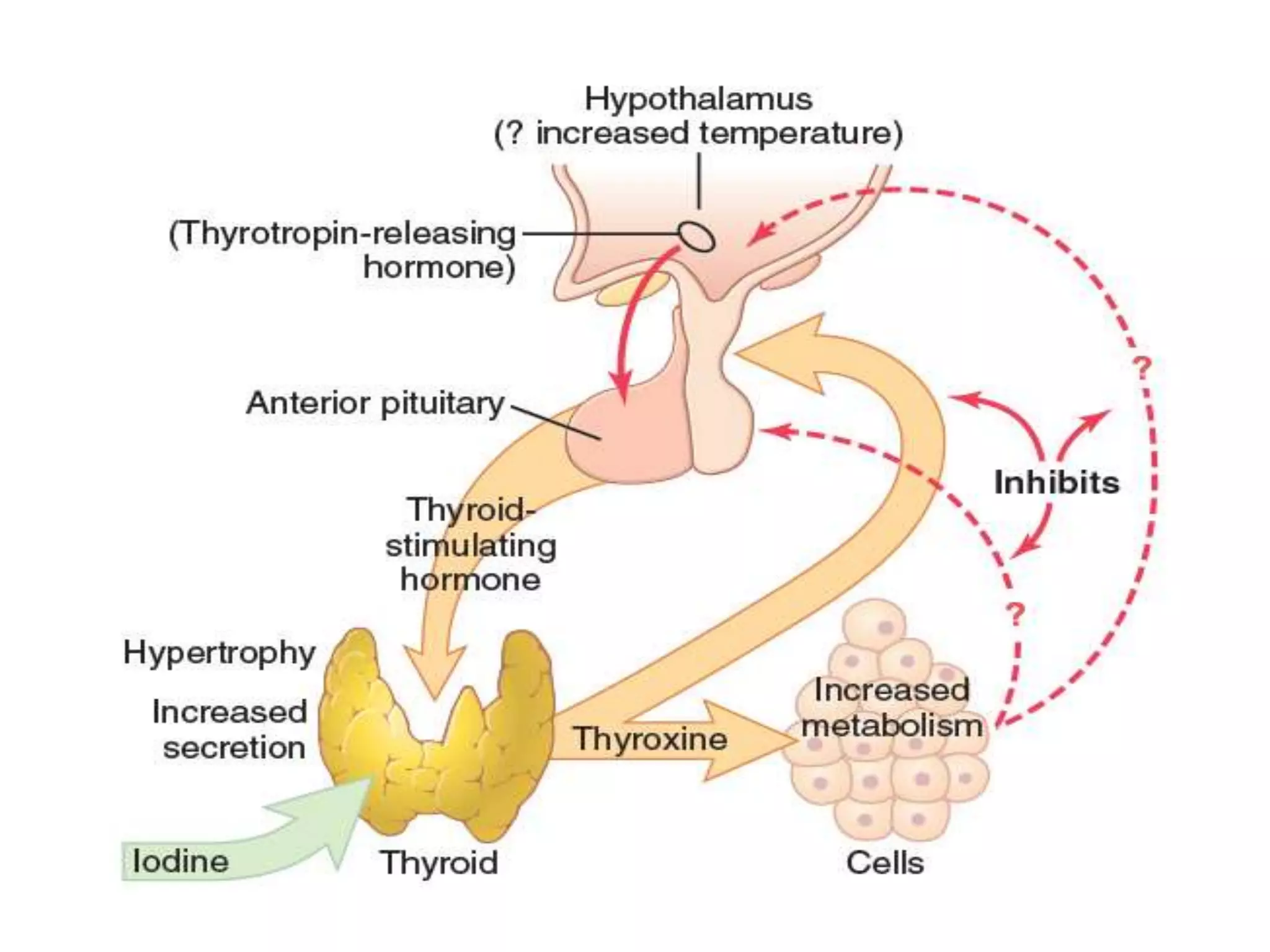
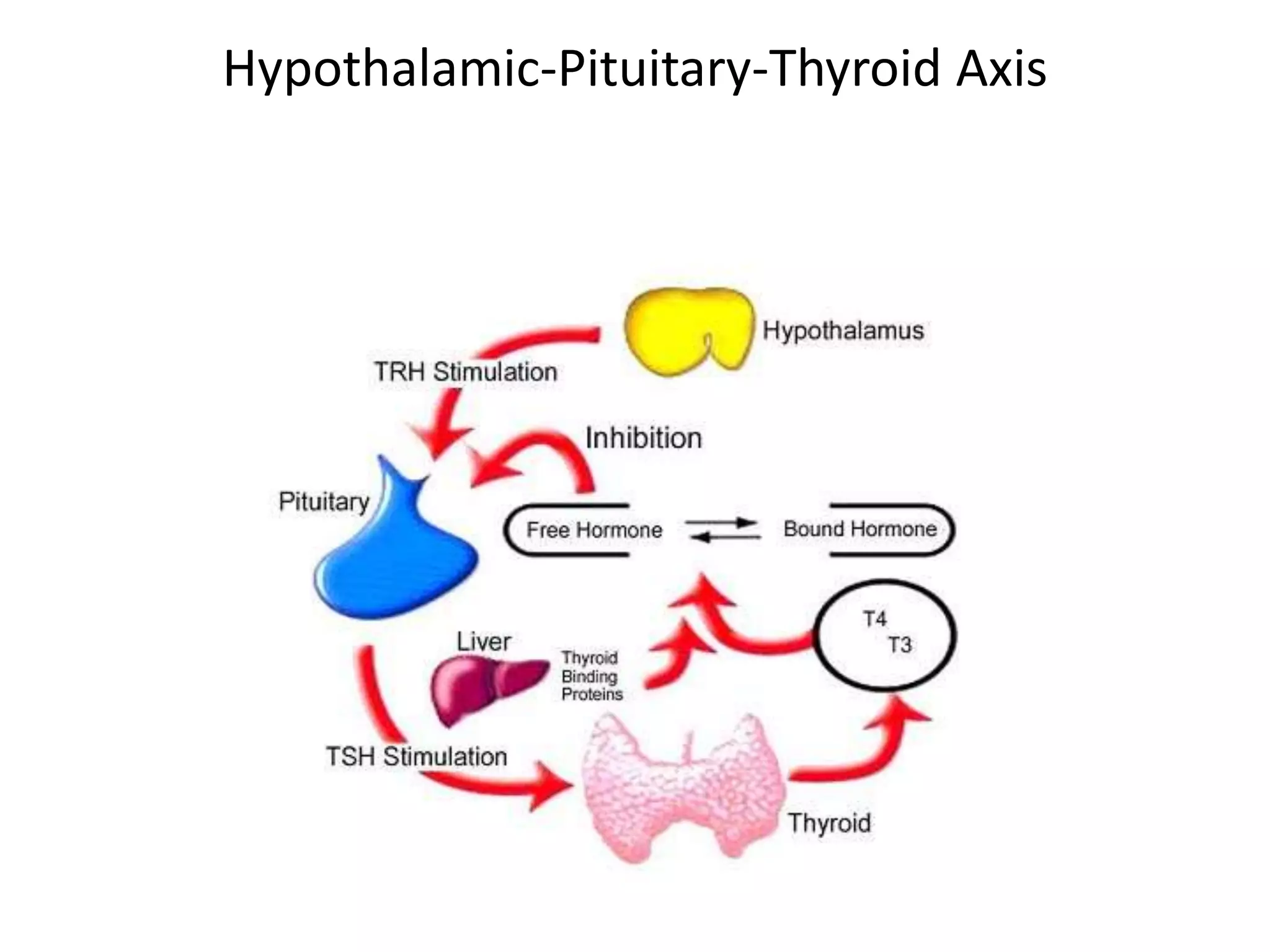
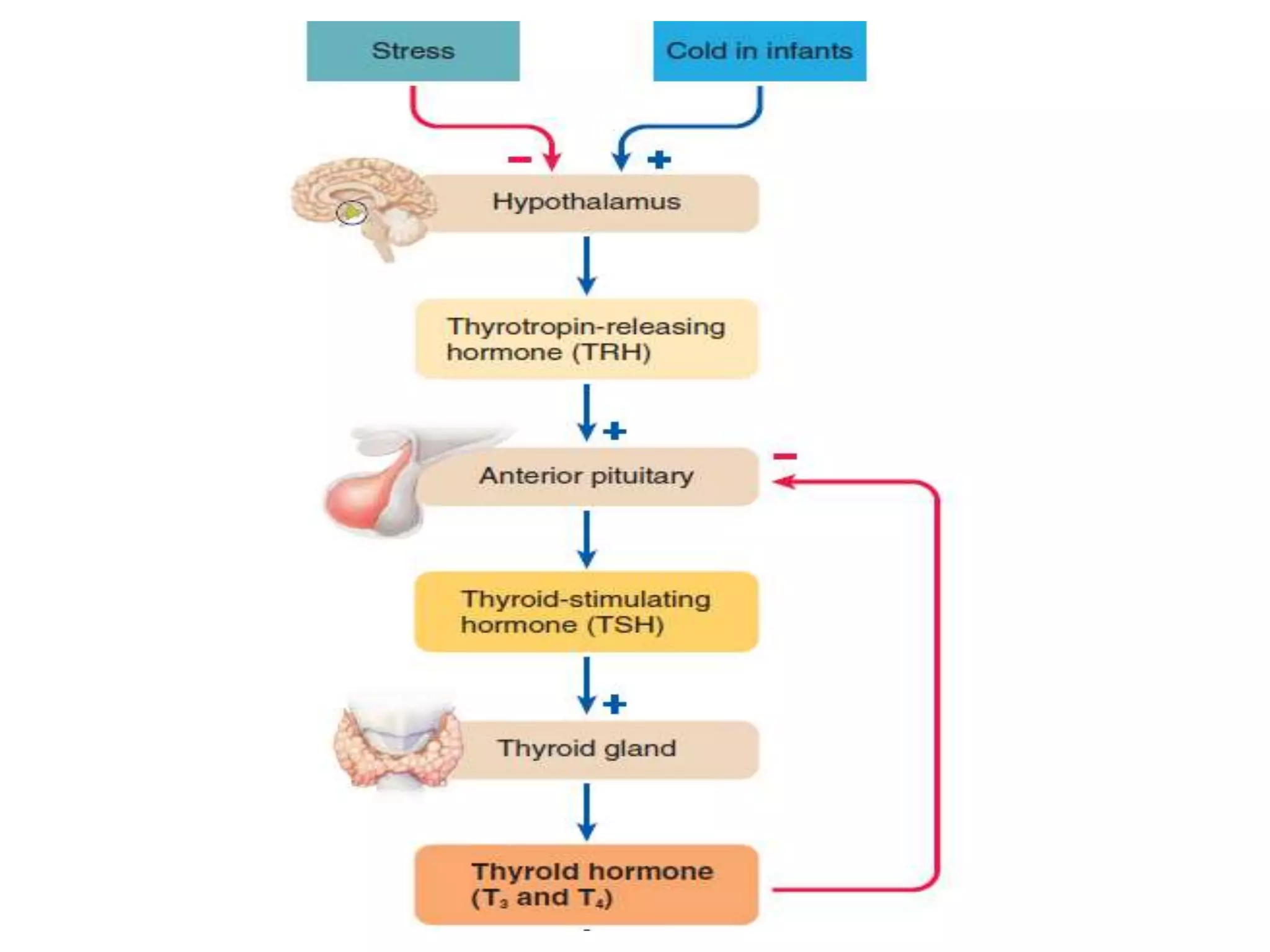
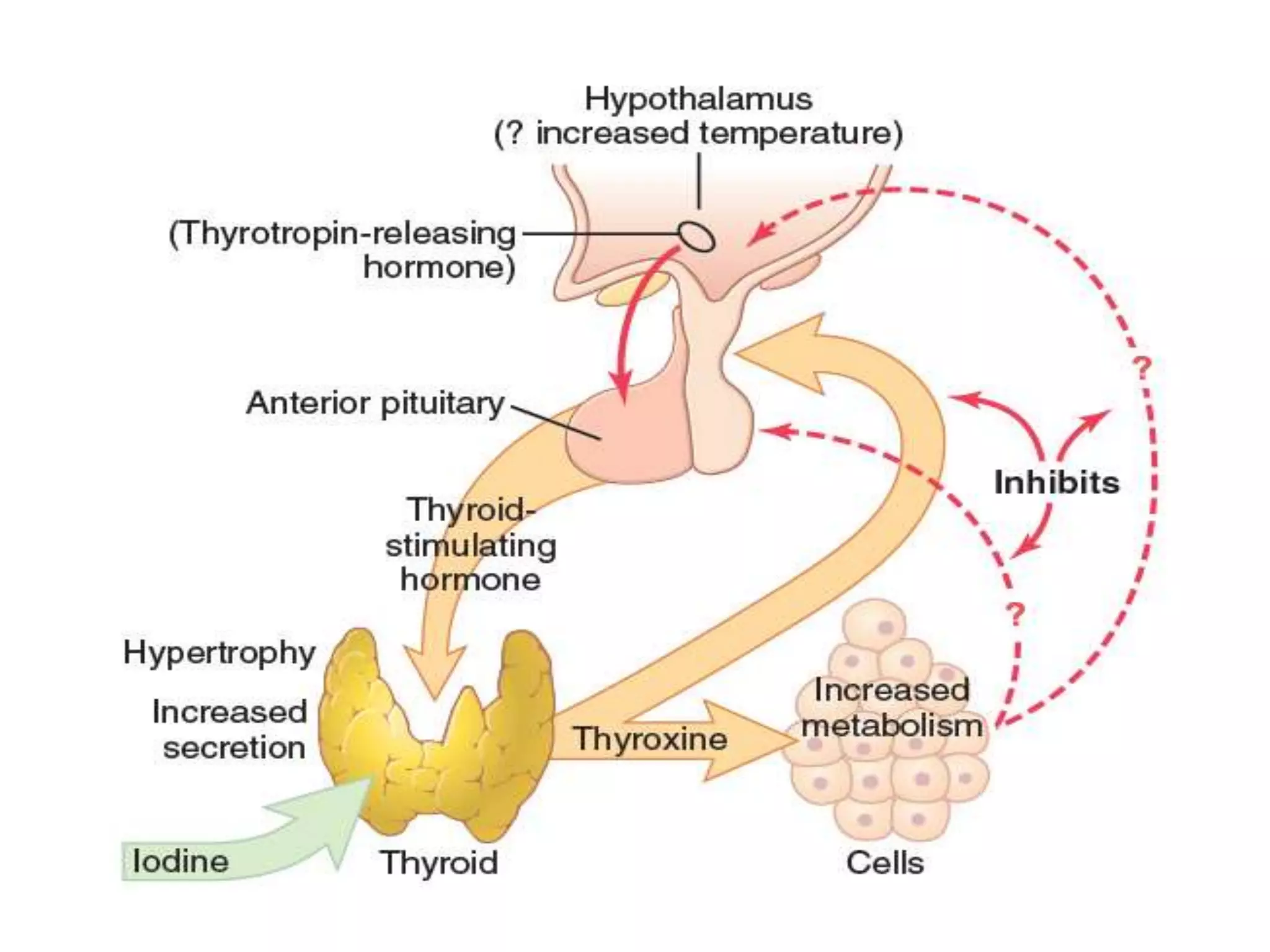
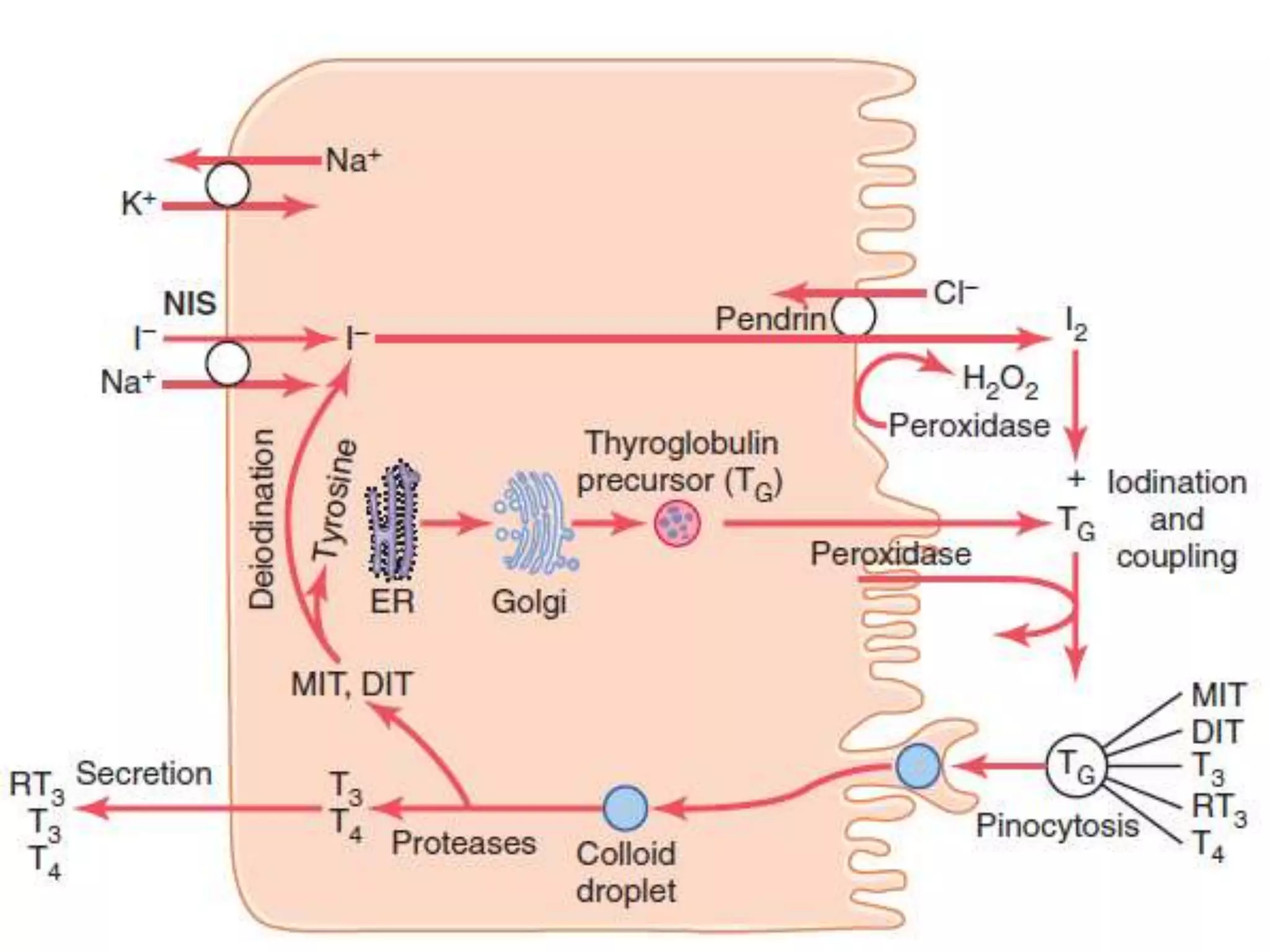
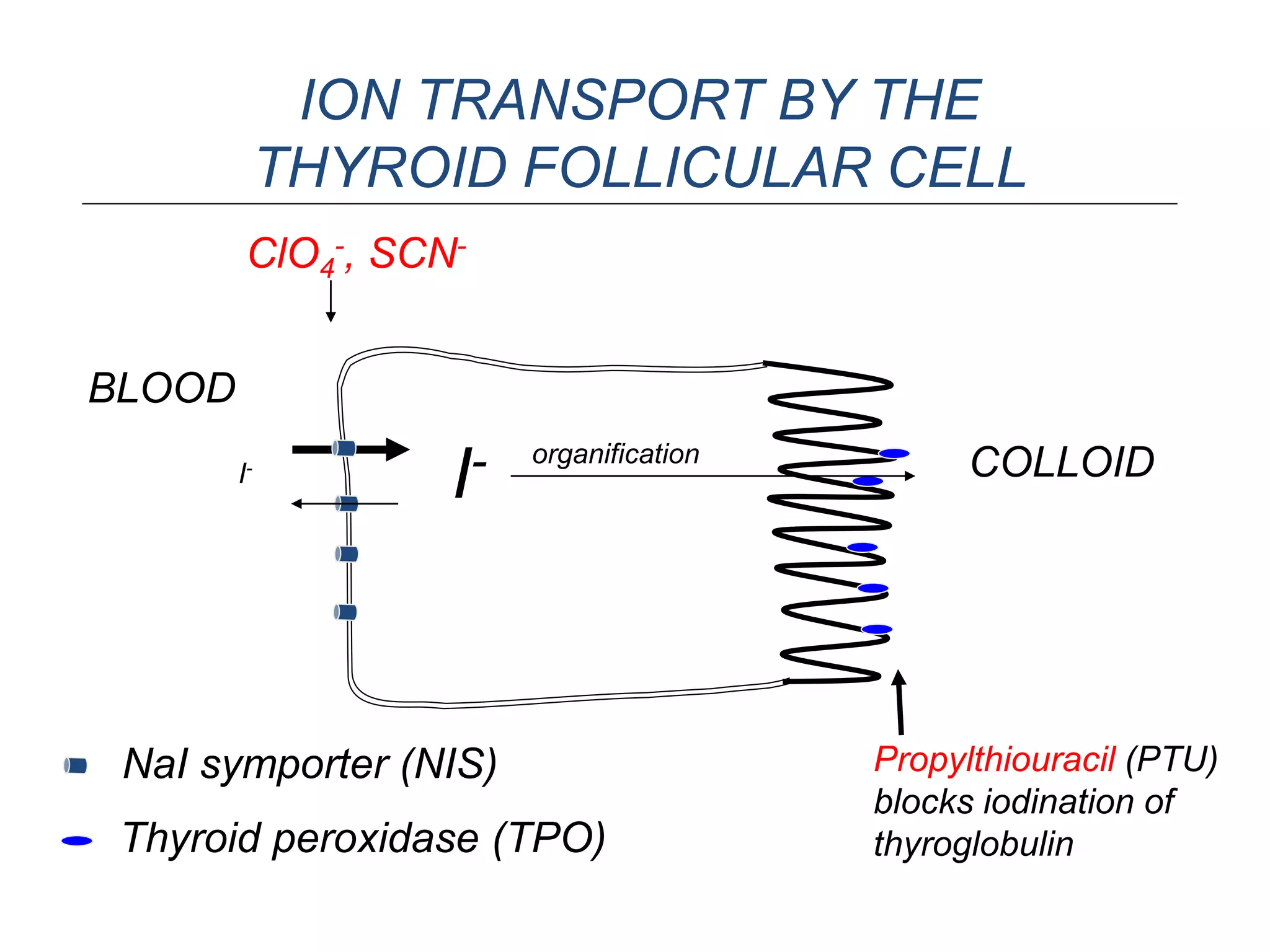
The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis regulates thyroid hormone production and secretion. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary increases thyroid activity, including iodine uptake and hormone synthesis. TSH levels are controlled by negative feedback from thyroid hormones. When thyroid hormone levels drop, TSH secretion increases to stimulate the thyroid to increase hormone production. Antithyroid drugs like thiocyanate and propylthiouracil decrease thyroid function by inhibiting iodine uptake or hormone synthesis.