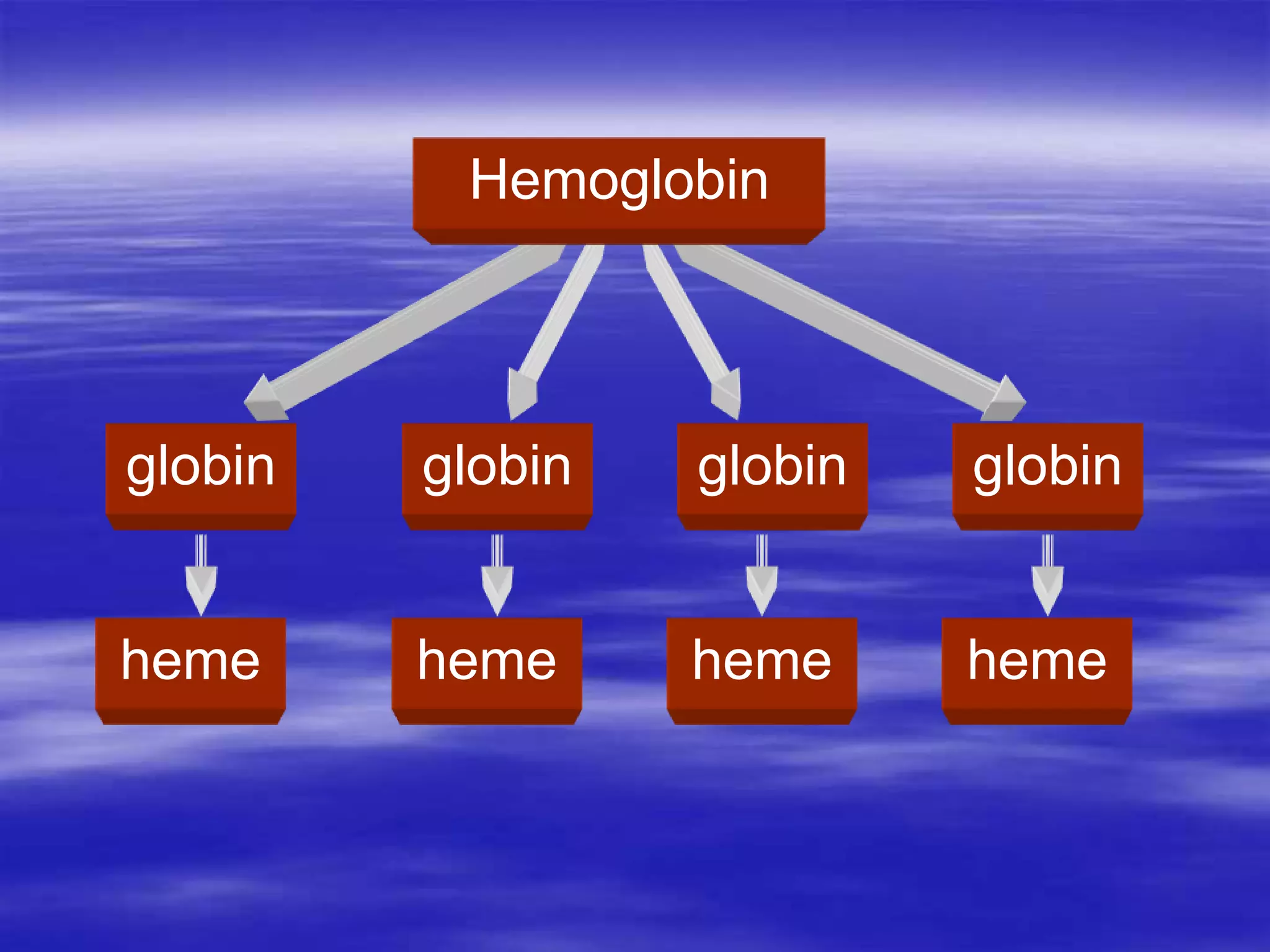
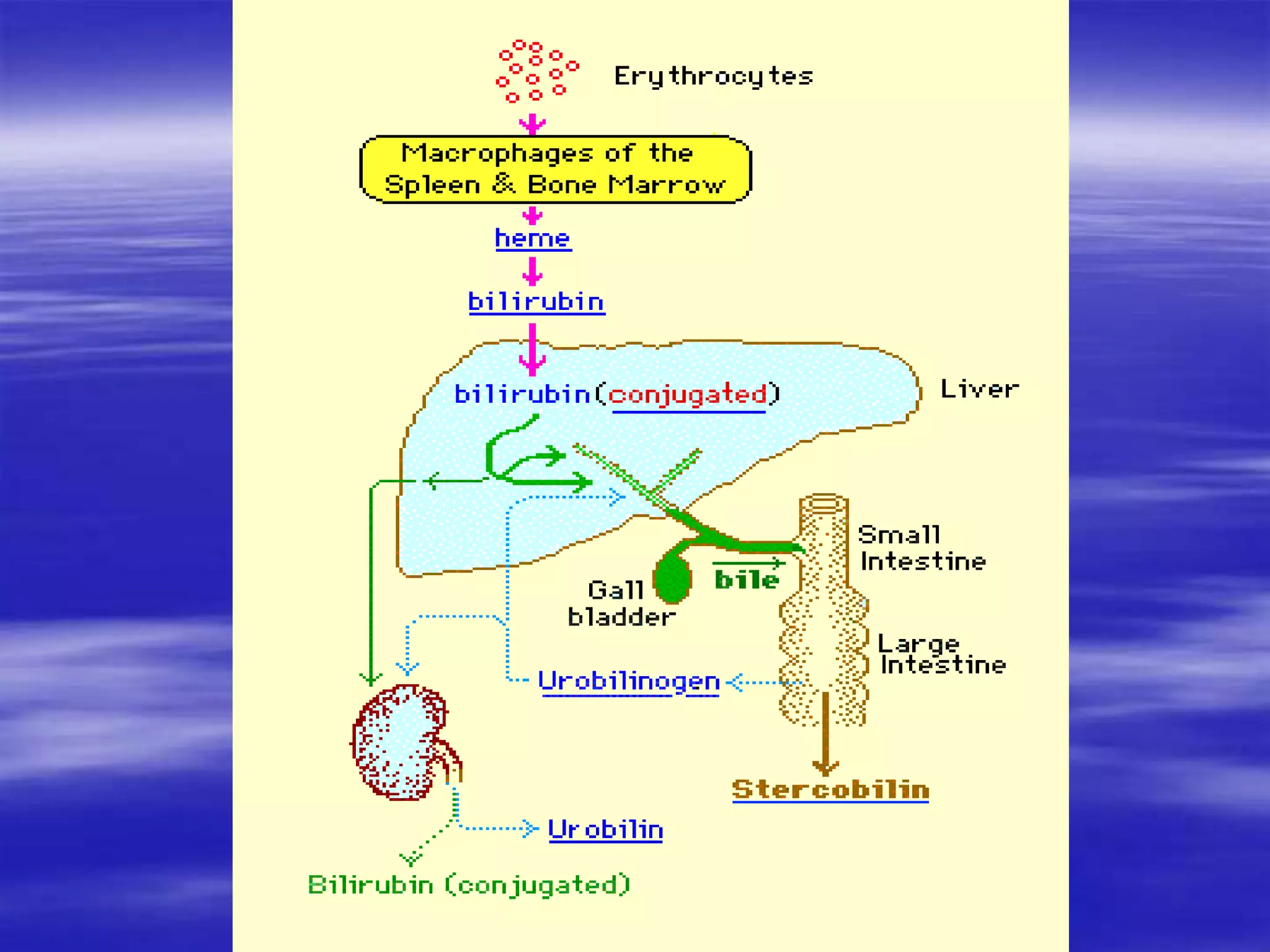
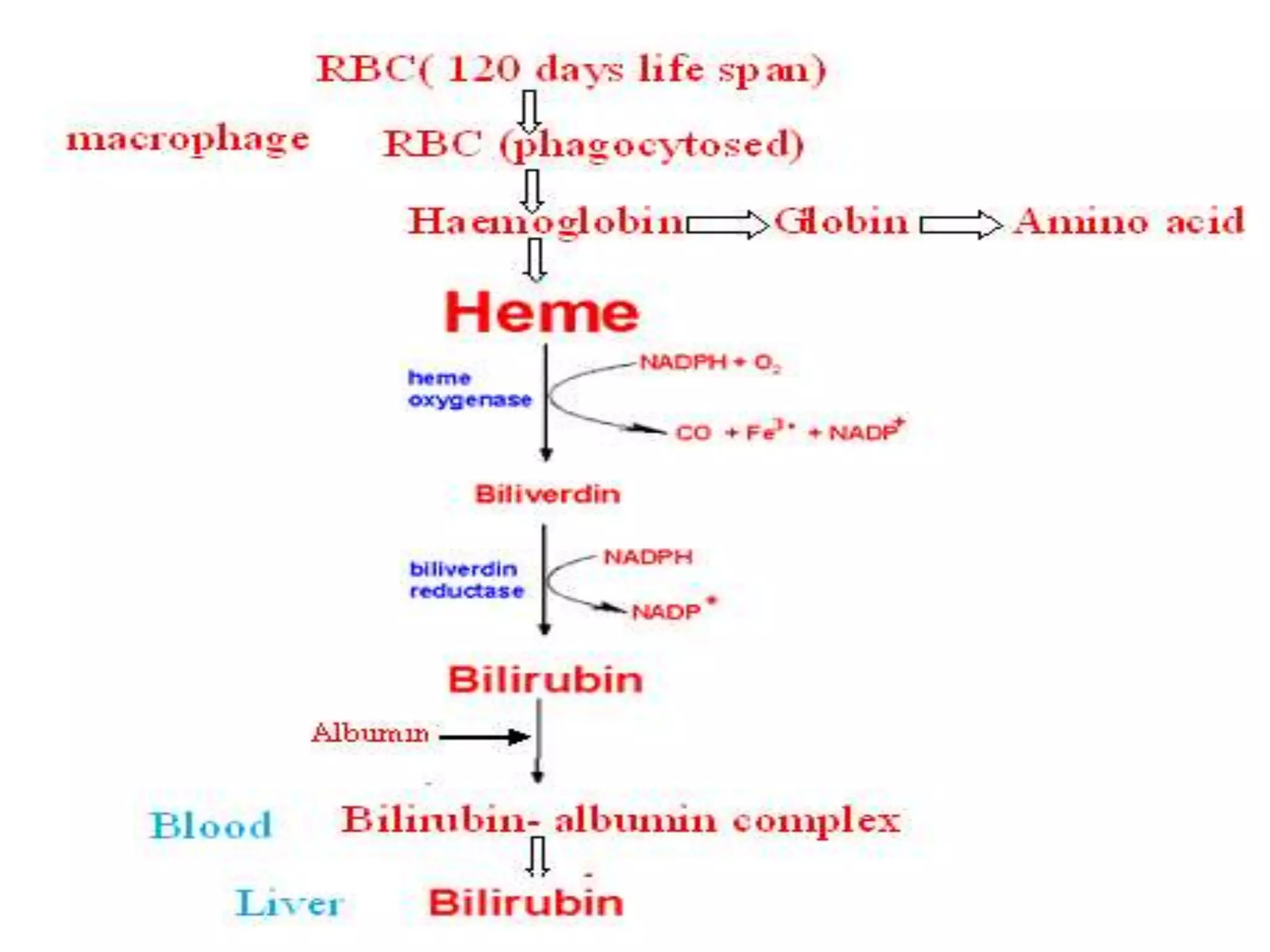
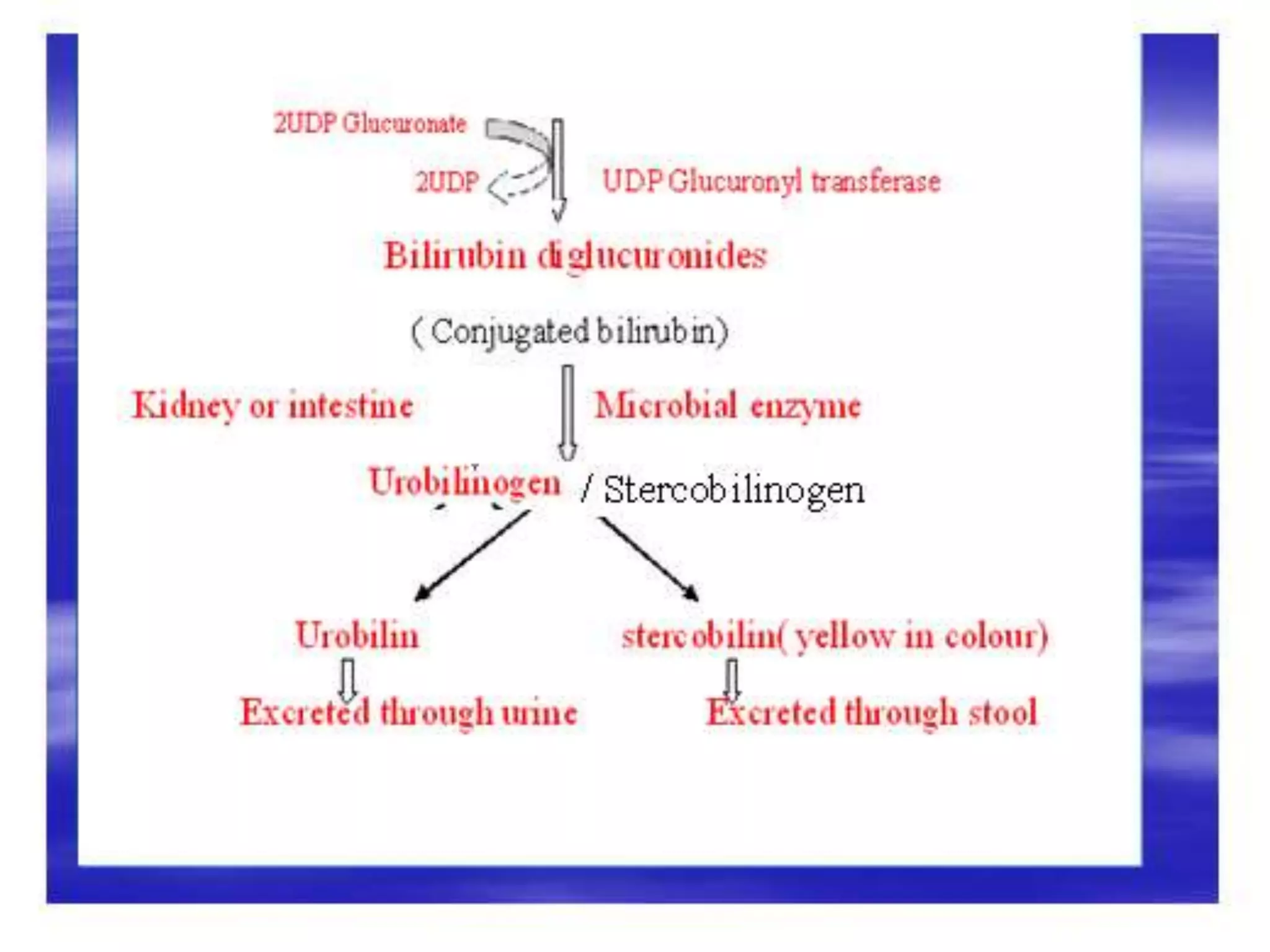
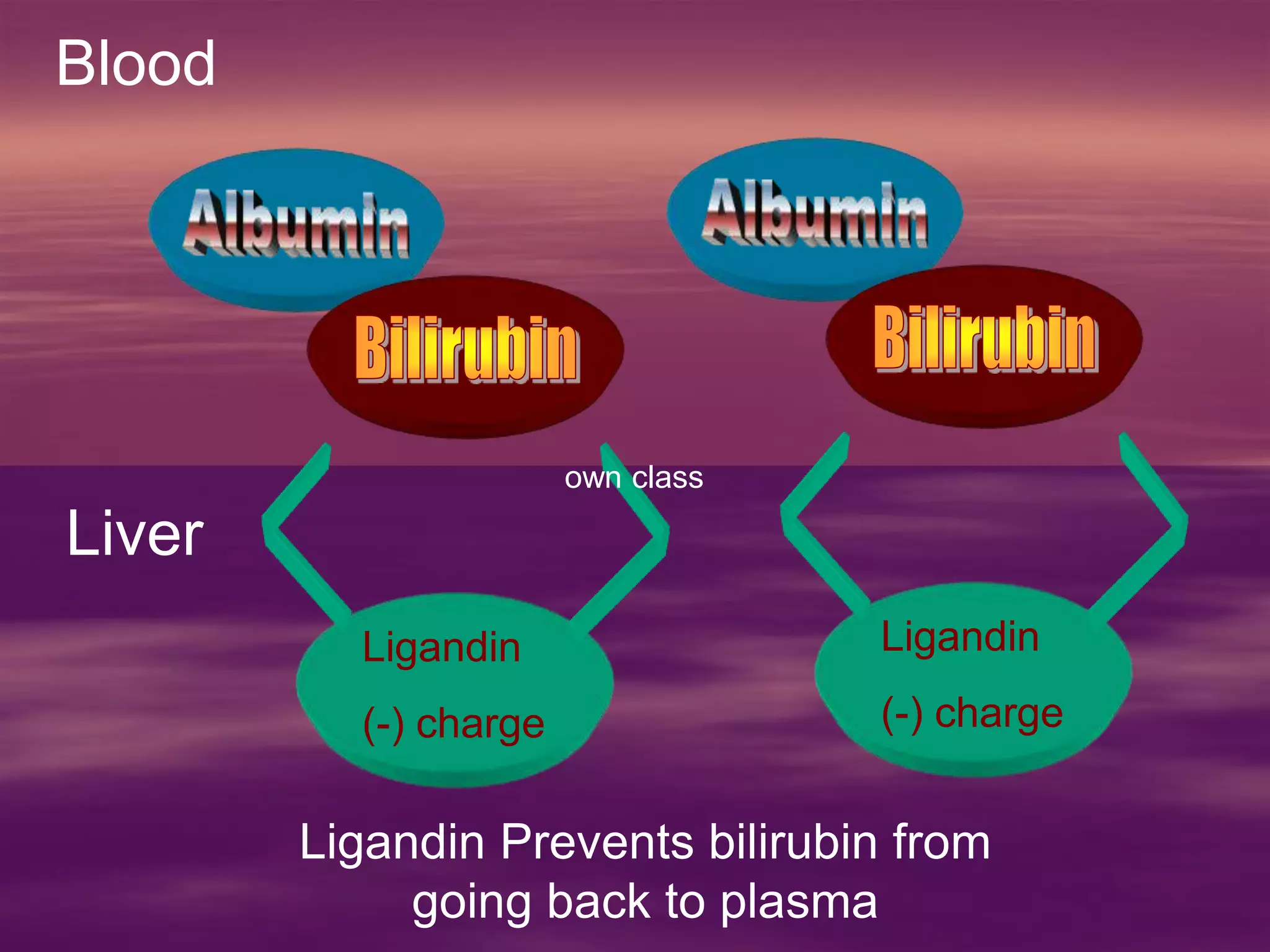
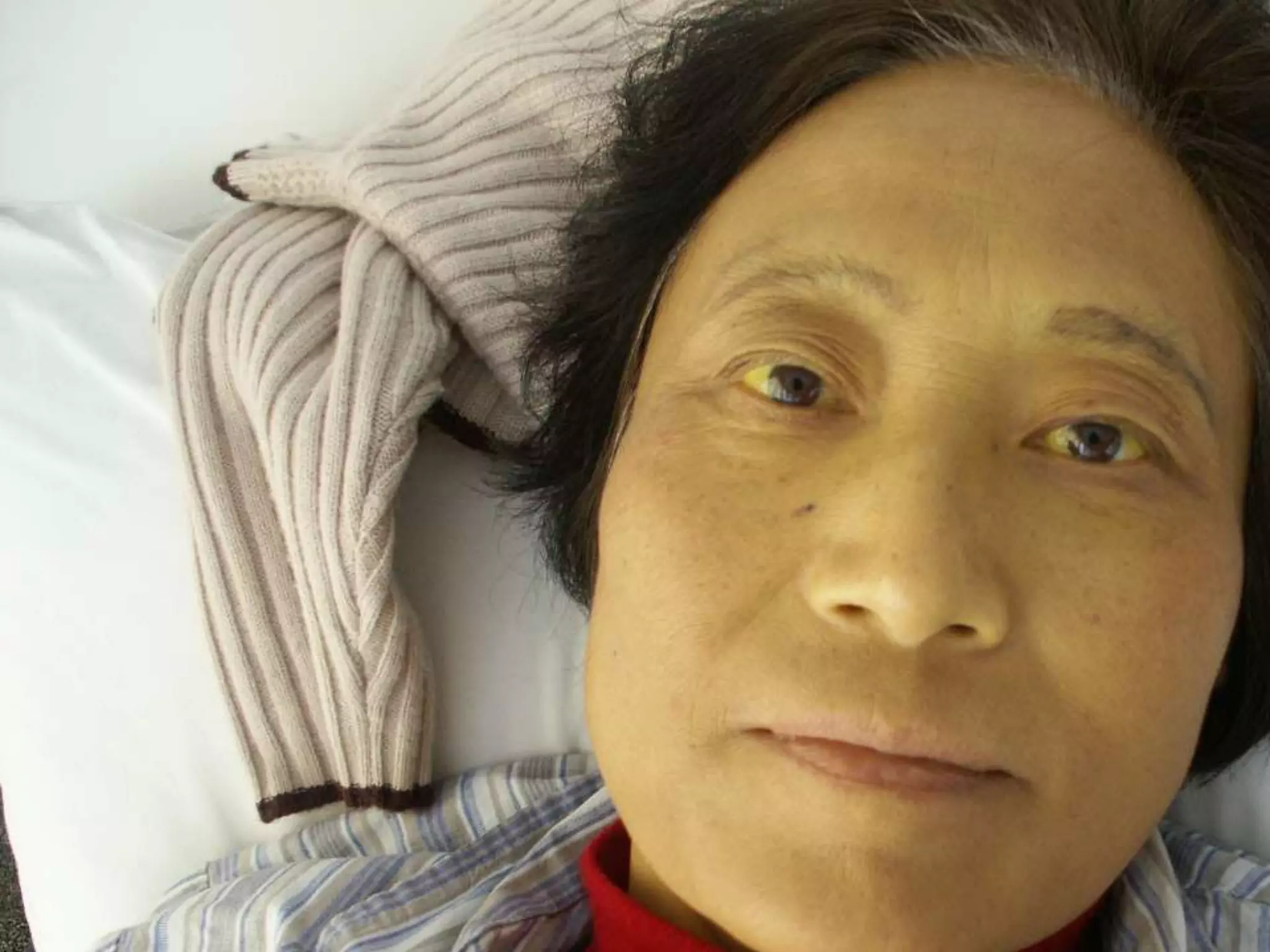
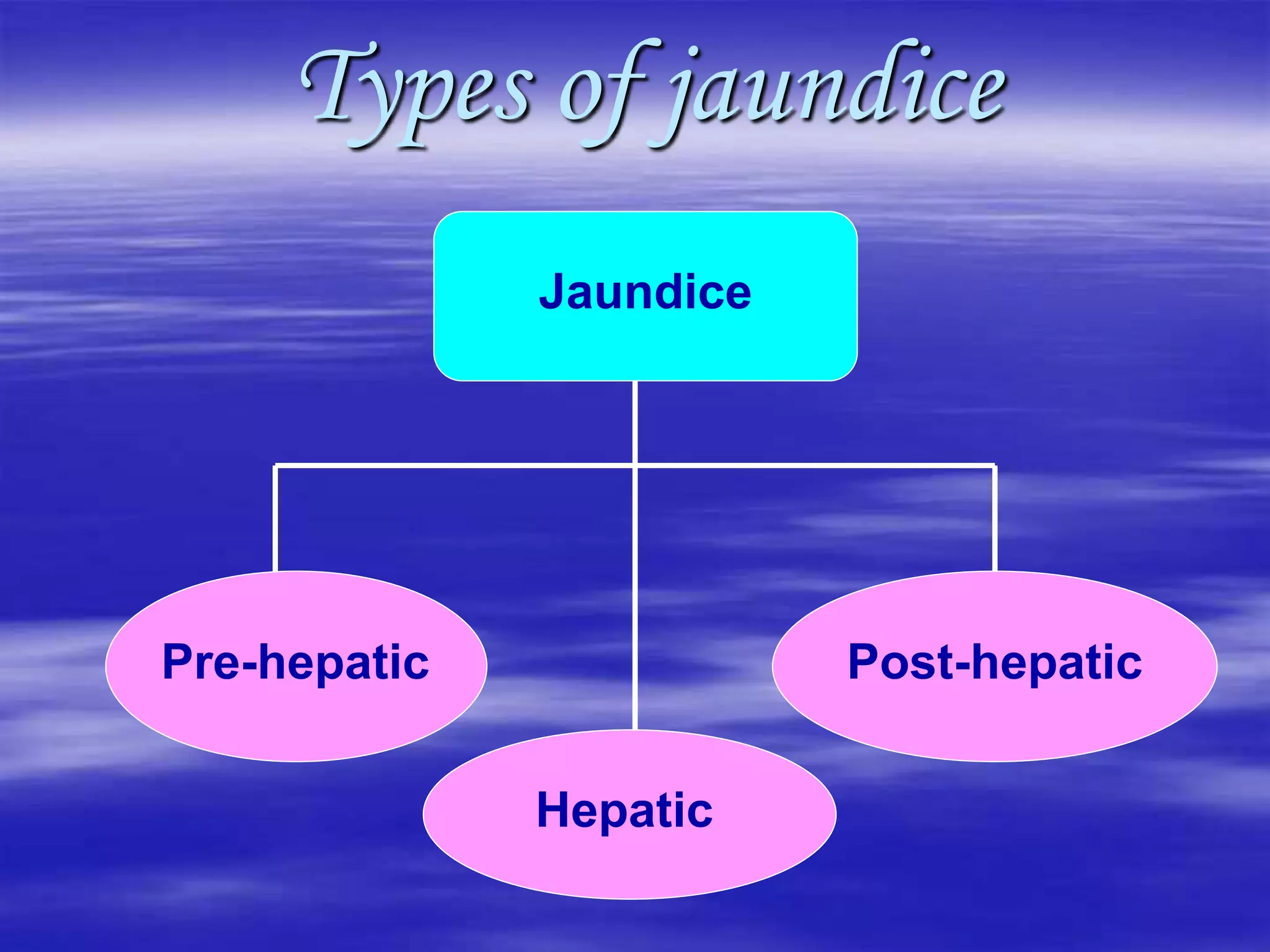
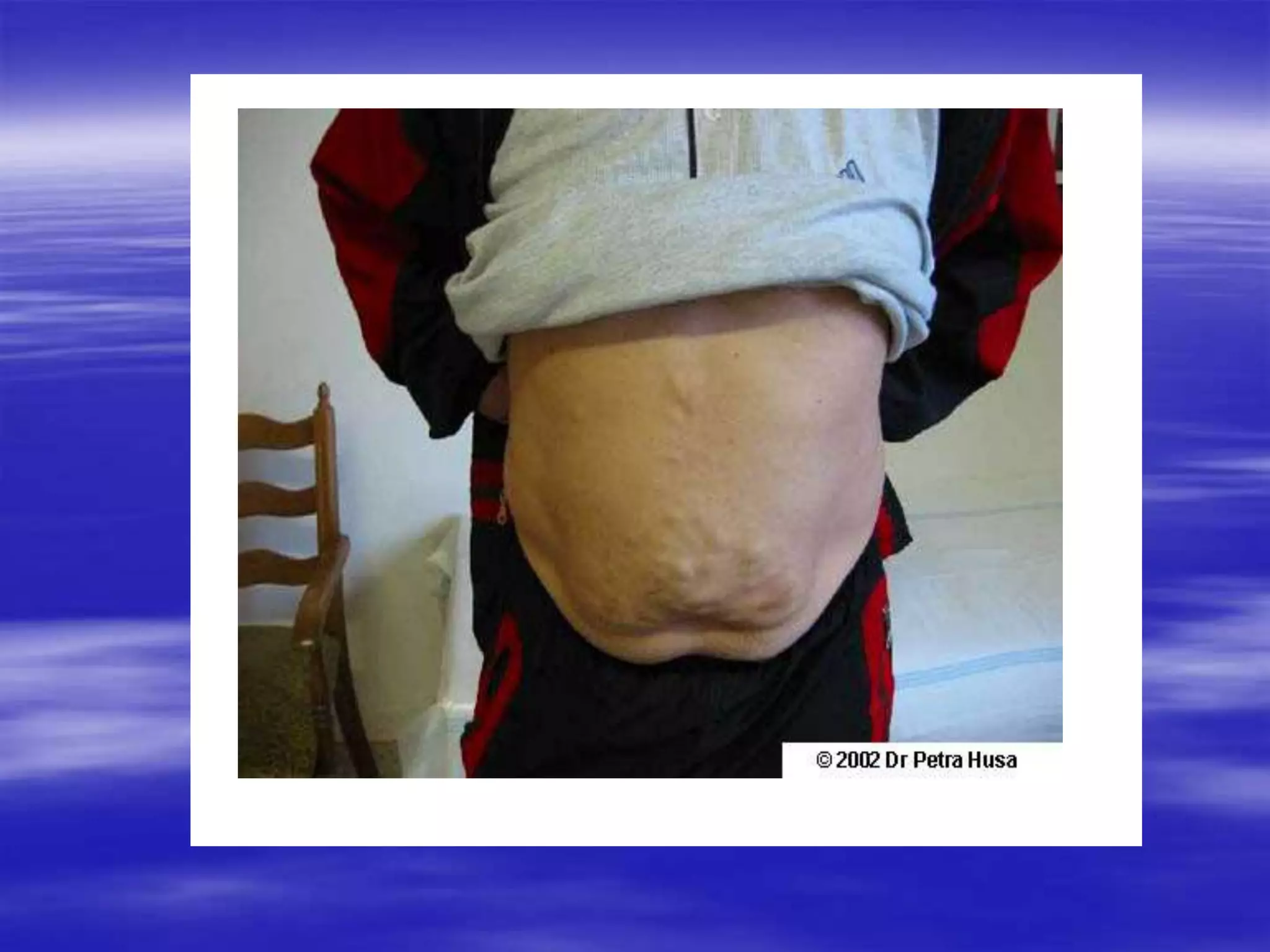
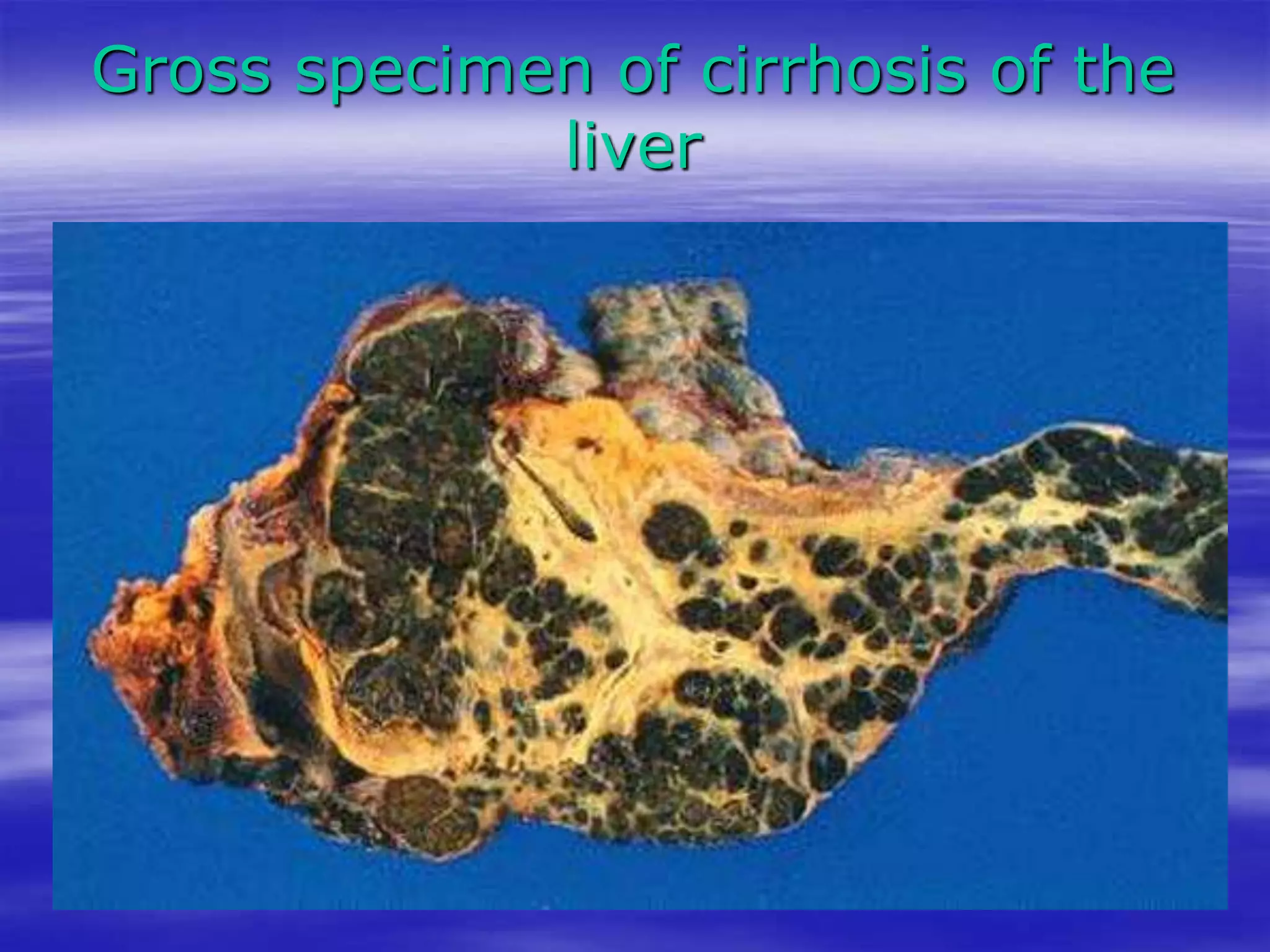
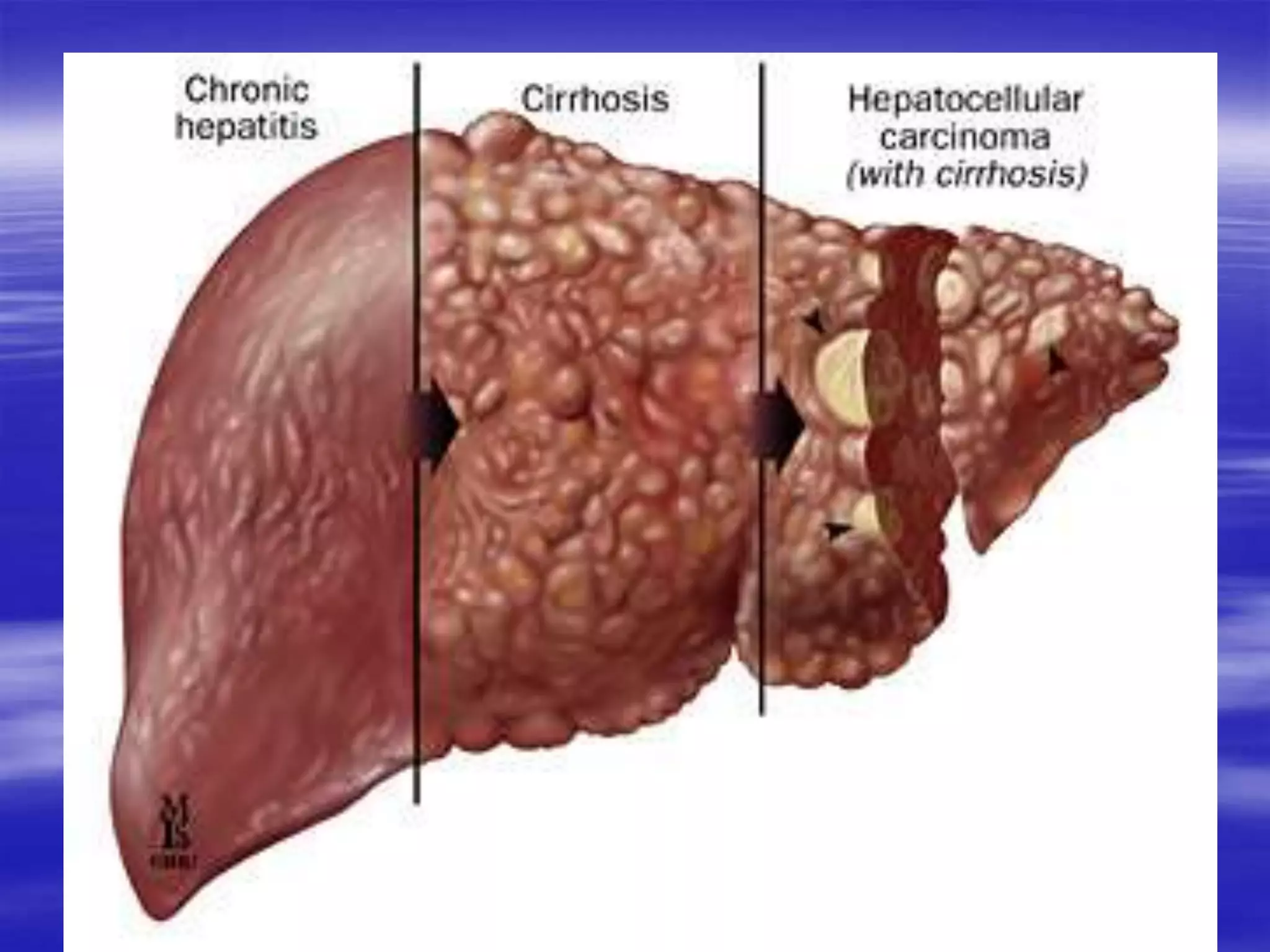
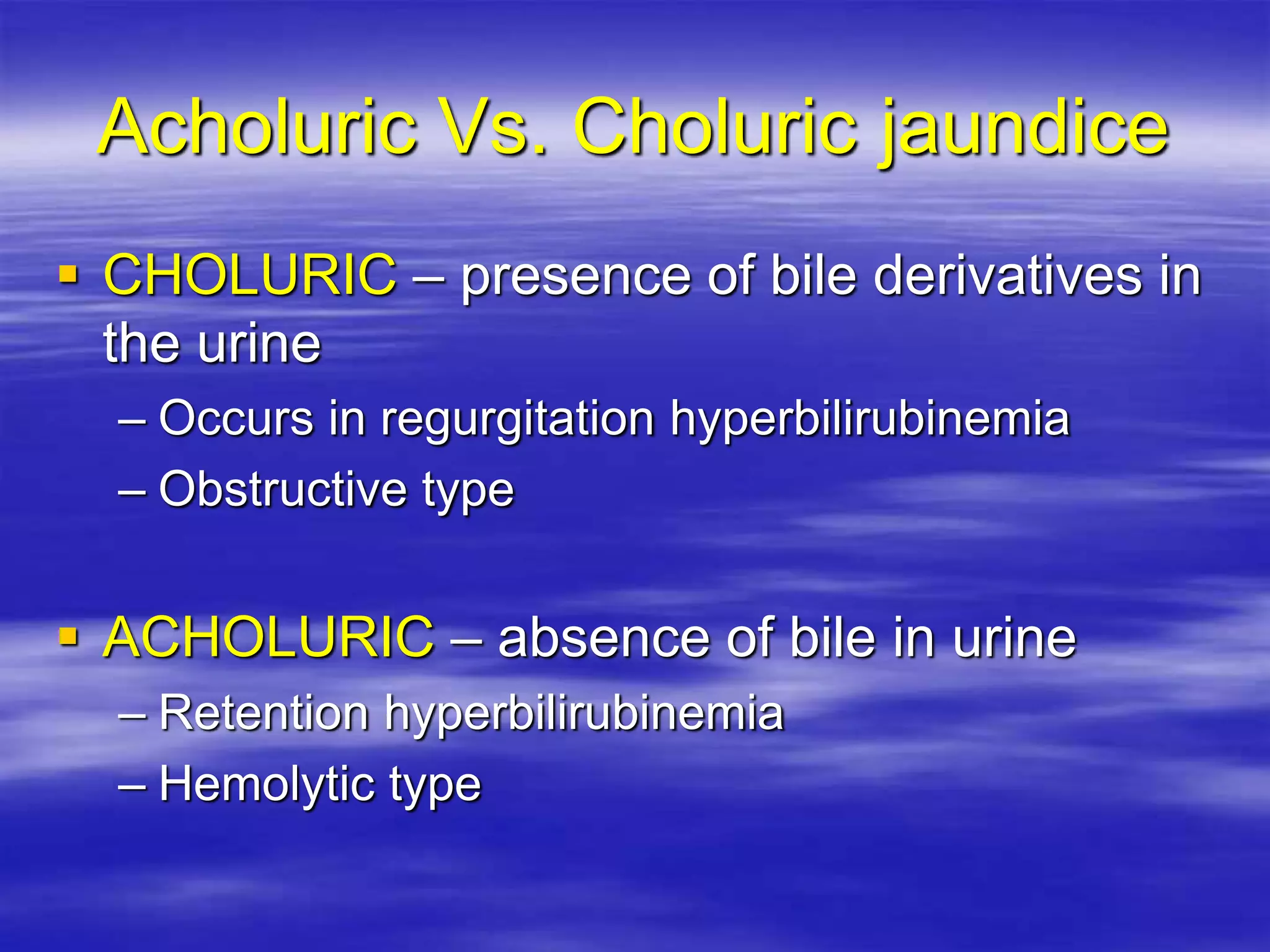
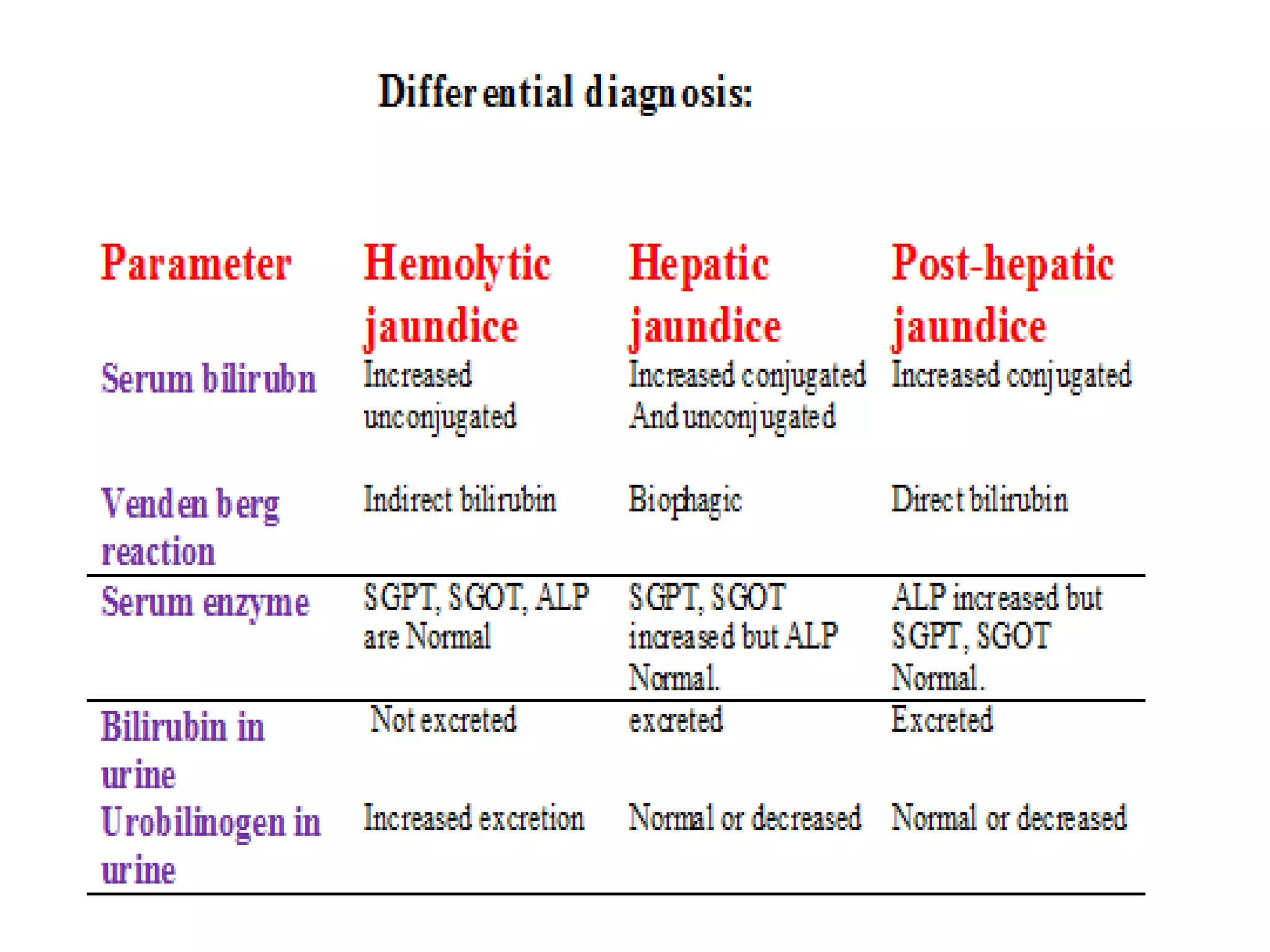
This document discusses bilirubin metabolism and jaundice. It begins by explaining bilirubin formation from heme and its transport and metabolism in the liver, which involves hepatic uptake, conjugation, and biliary excretion. An enterohepatic circulation is also described. Jaundice occurs when bilirubin levels exceed 2 mg/dL and can be pre-hepatic (hemolytic), hepatic, or obstructive in origin. Specific causes and characteristics of each jaundice type are provided. The document also discusses hyperbilirubinemia conditions like Gilbert's syndrome and Crigler-Najjar syndrome. Testing to differentiate jaundice types and clinical features like symptoms and lab findings are summarized