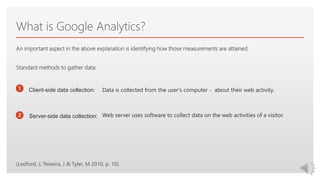
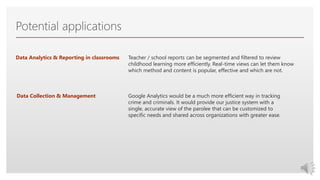
Google Analytics is a software program that collects and reports website data. It measures how many people visit a site, how they find it, and what they do while there. Data is collected through JavaScript code on the site which tracks user behavior and sends this information back to Google Analytics. This raw data is then processed into useful metrics and reports. Businesses can use these metrics and reports to improve site performance, track marketing campaigns, and enhance the user experience. Potential future applications of analytics technology include more personalized content, tracking robot and space activities, and uses in healthcare and bio-technology.