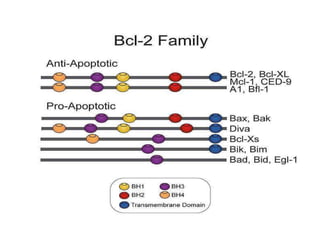
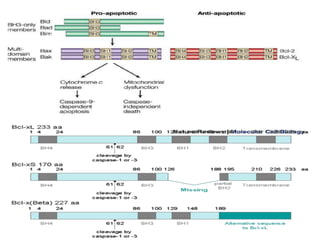
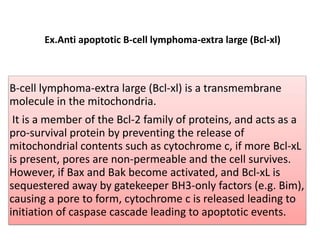
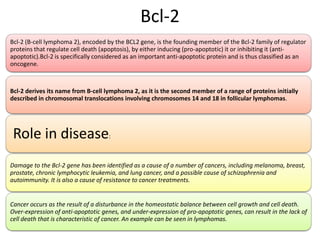
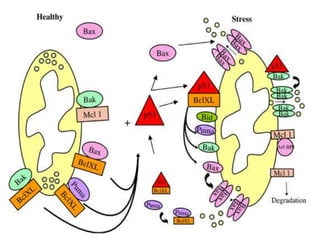
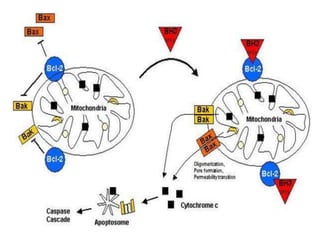
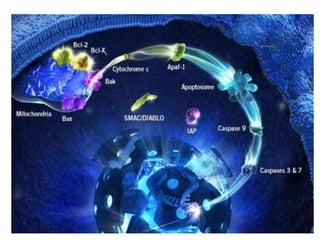
The Bcl-2 family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins that regulate apoptosis by either inducing it (pro-apoptotic) or inhibiting it (anti-apoptotic). There are 25 known genes in the family. They govern mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and the release of cytochrome c. Bcl-2 family proteins contain BH domains and either promote or inhibit apoptosis. Anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-xL prevent pore formation and cytochrome c release, while pro-apoptotic proteins like Bax can form pores, leading to caspase activation and cell death. Targeting specific Bcl-2 proteins may help treat cancers characterized by abnormal apoptosis regulation.