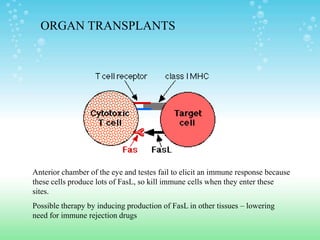
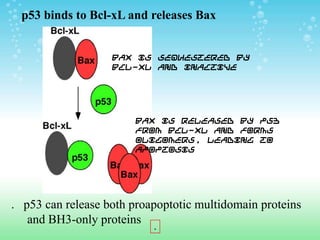
Caspases are cysteine-dependent aspartate specific proteases that cleave target proteins after aspartic acid residues. They exist as inactive zymogens called procaspases in cells and initiate a proteolytic cascade when activated. This leads to cleavage of key proteins and characteristic apoptosis morphology. The Bcl-2 family of proteins regulate apoptosis at the mitochondrial membrane, with pro-apoptotic proteins like Bax activating apoptosis and anti-apoptotic proteins like Bcl-2 inhibiting apoptosis. Many cancers acquire mutations in genes encoding proteins that regulate apoptosis, allowing cancer cells to evade cell death signals and continue uncontrolled proliferation. Targeting apoptosis pathways is a promising strategy for cancer treatment.