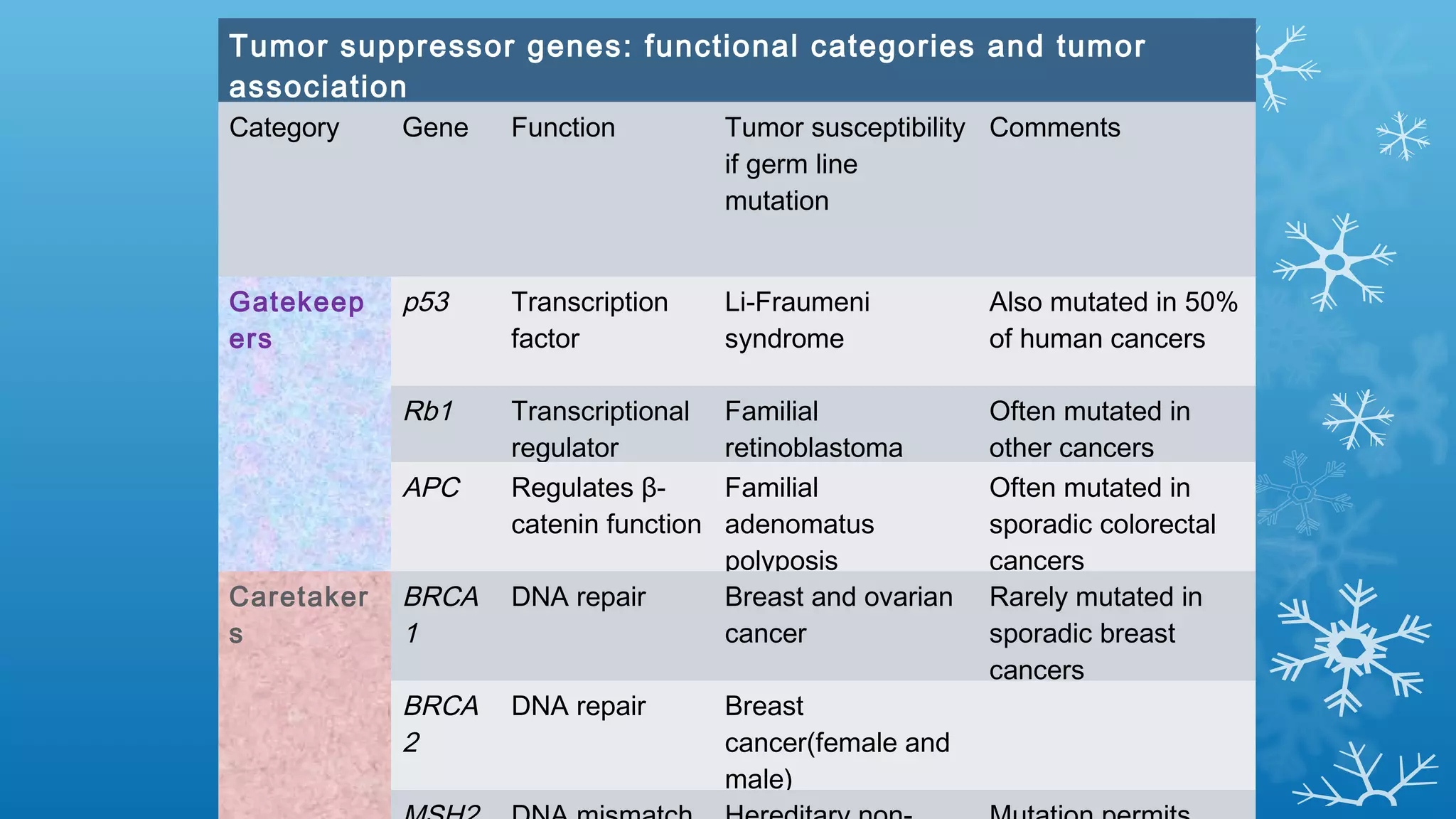
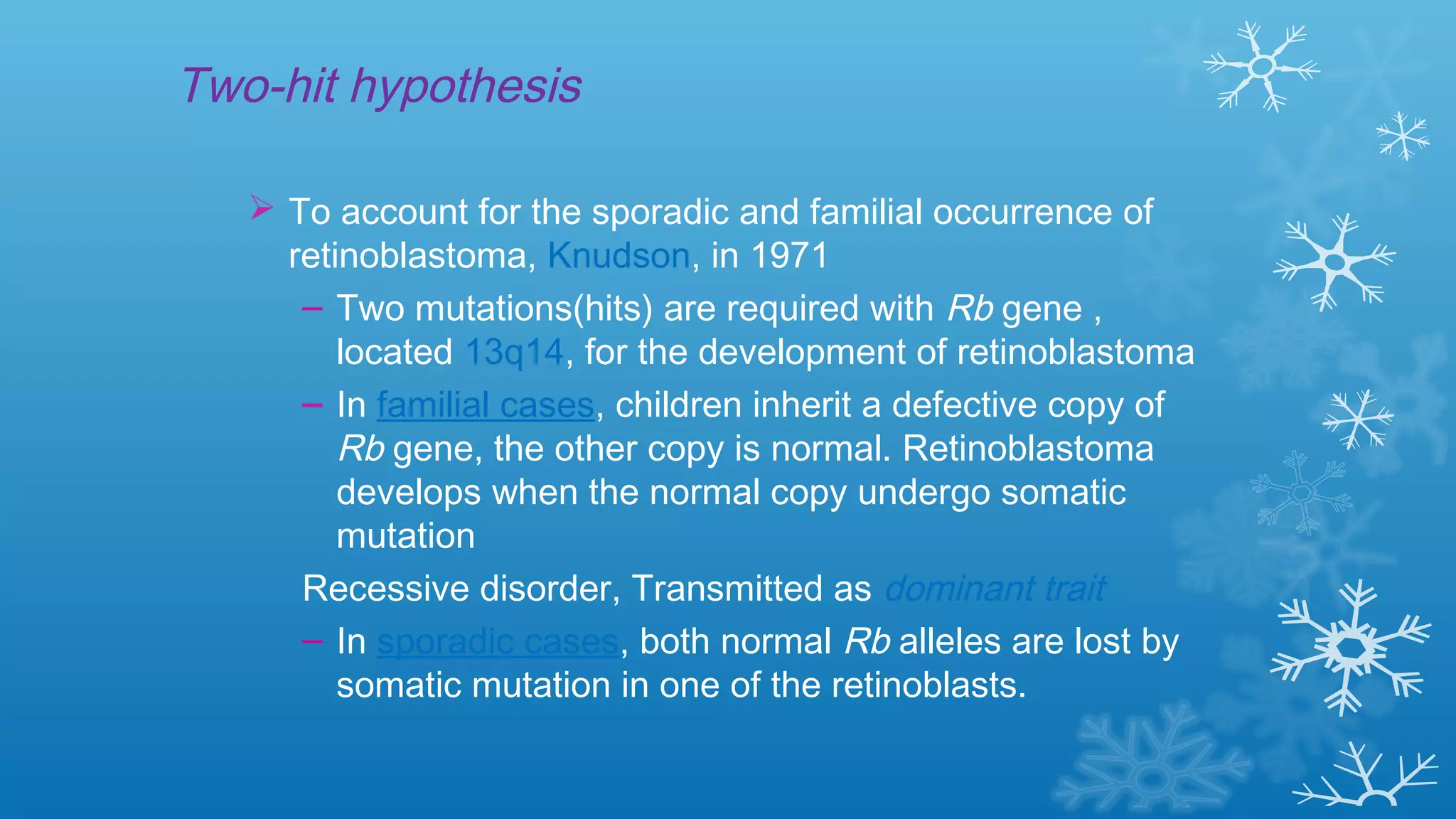
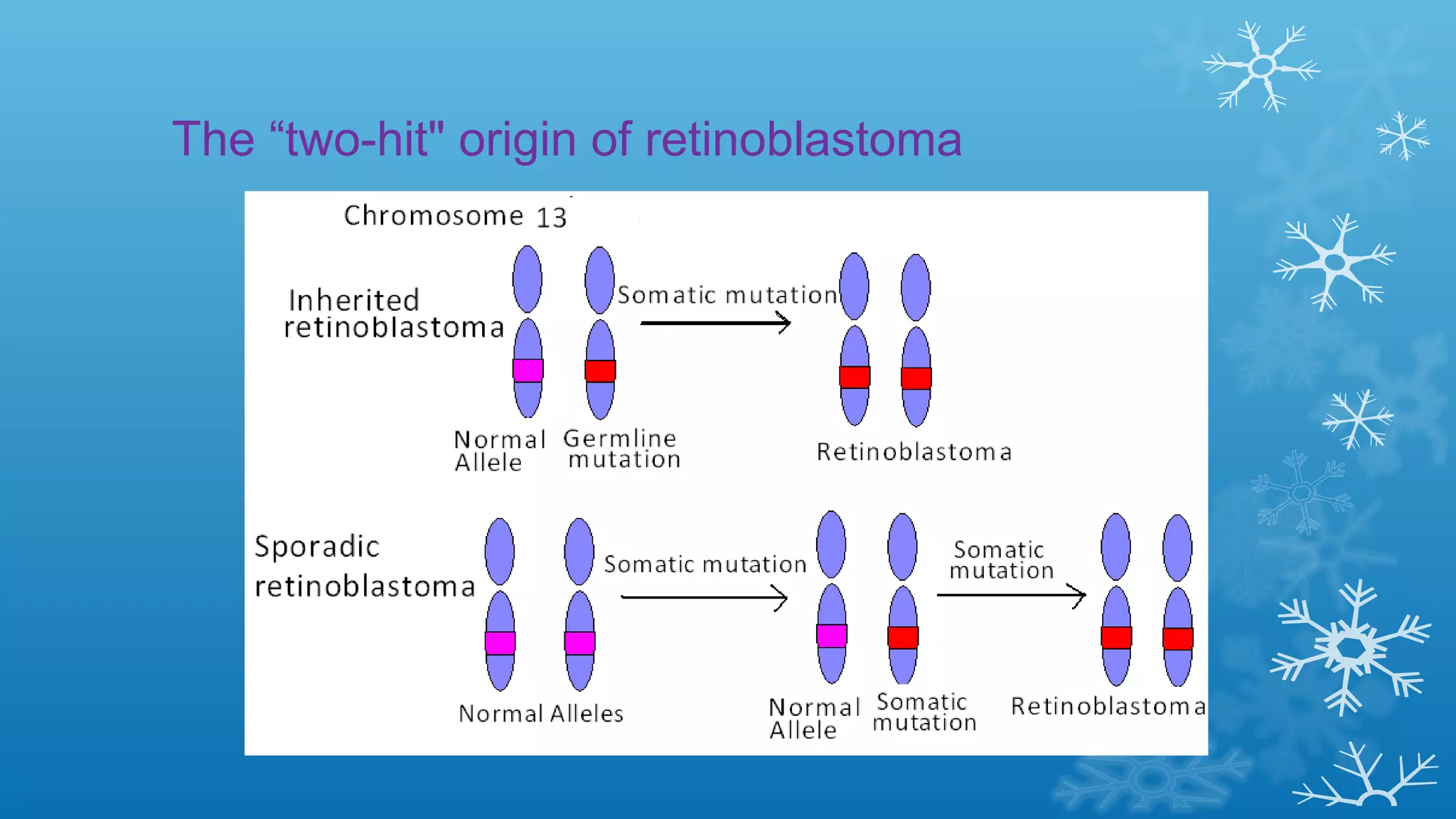
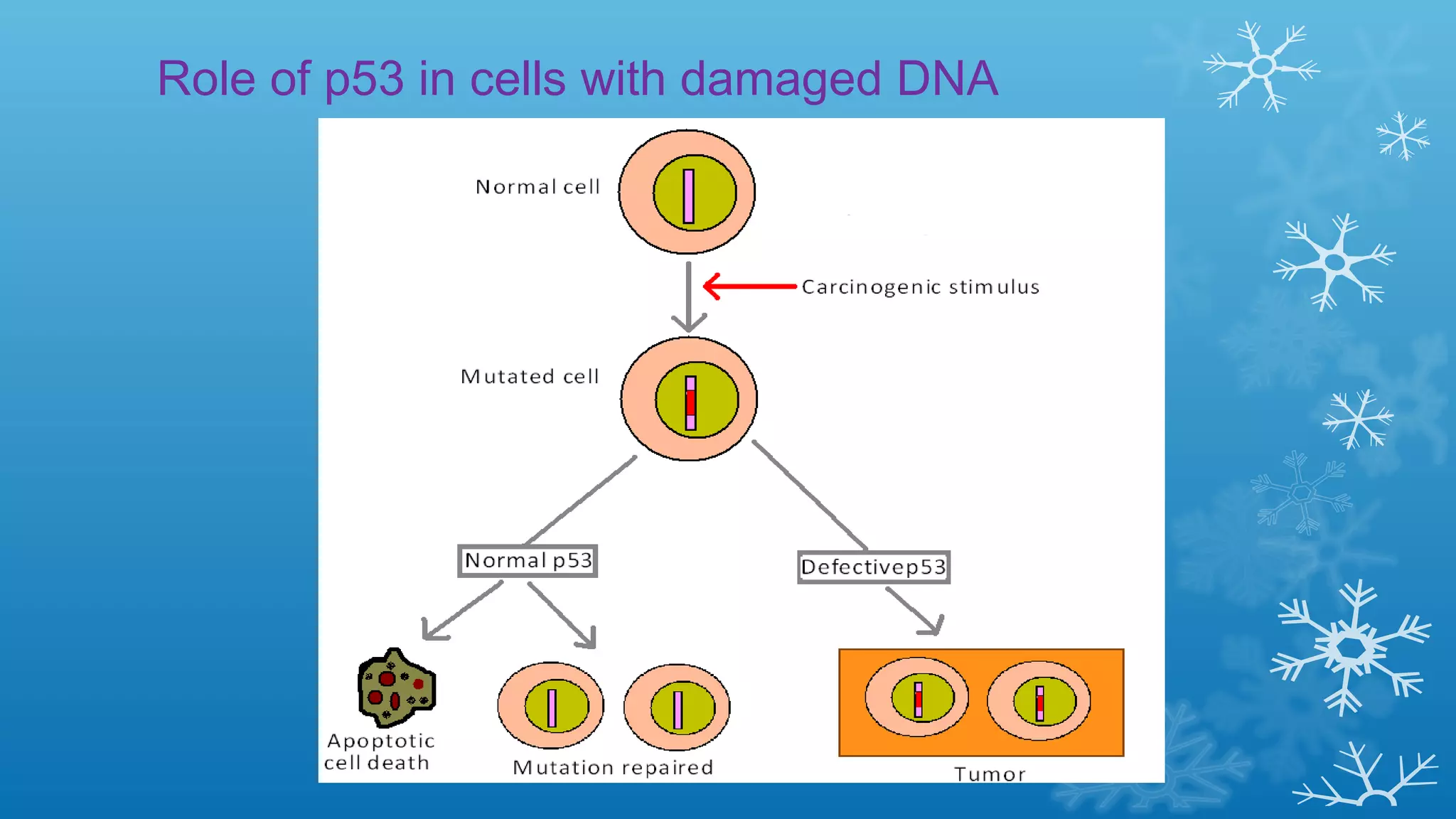
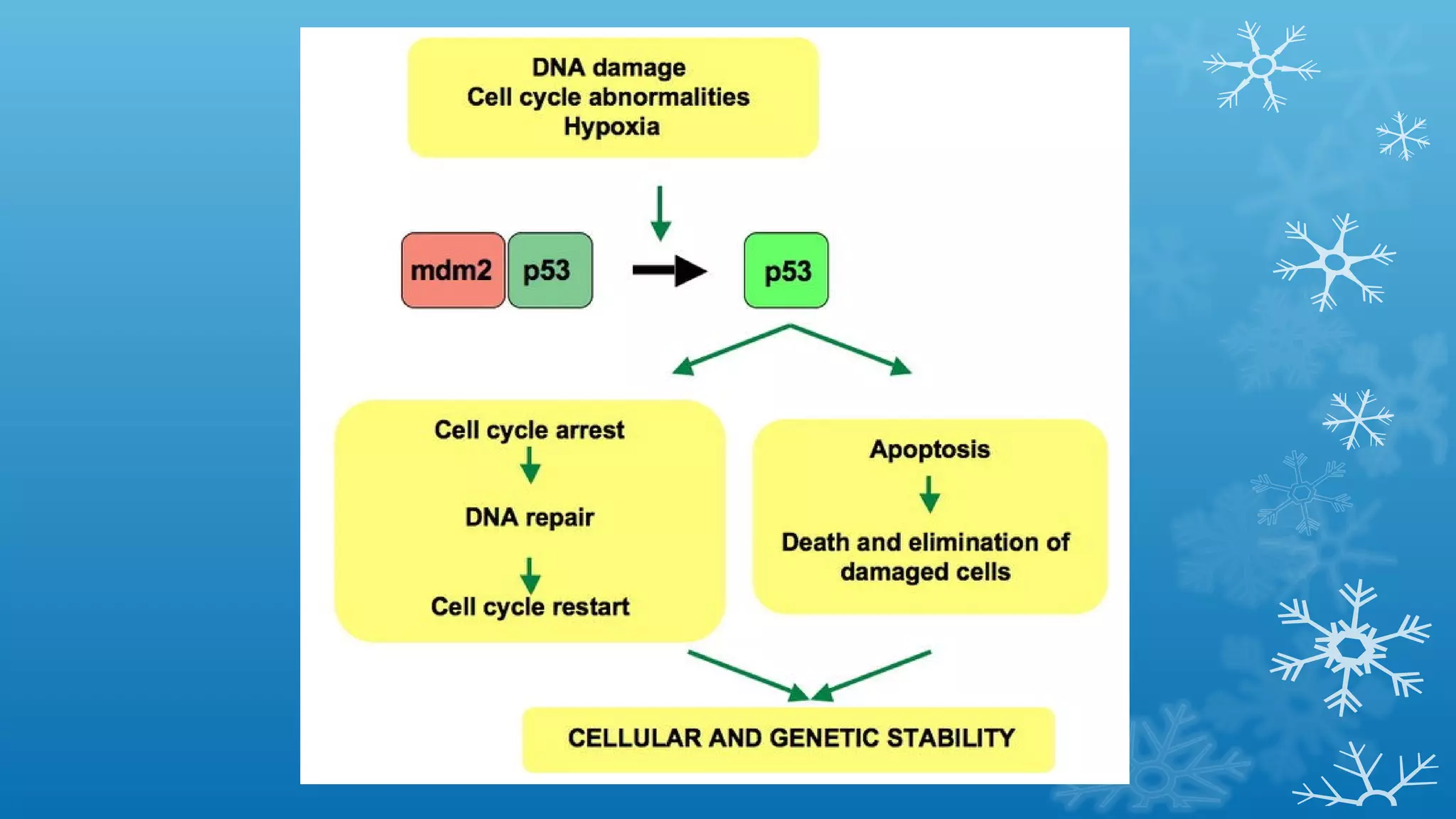
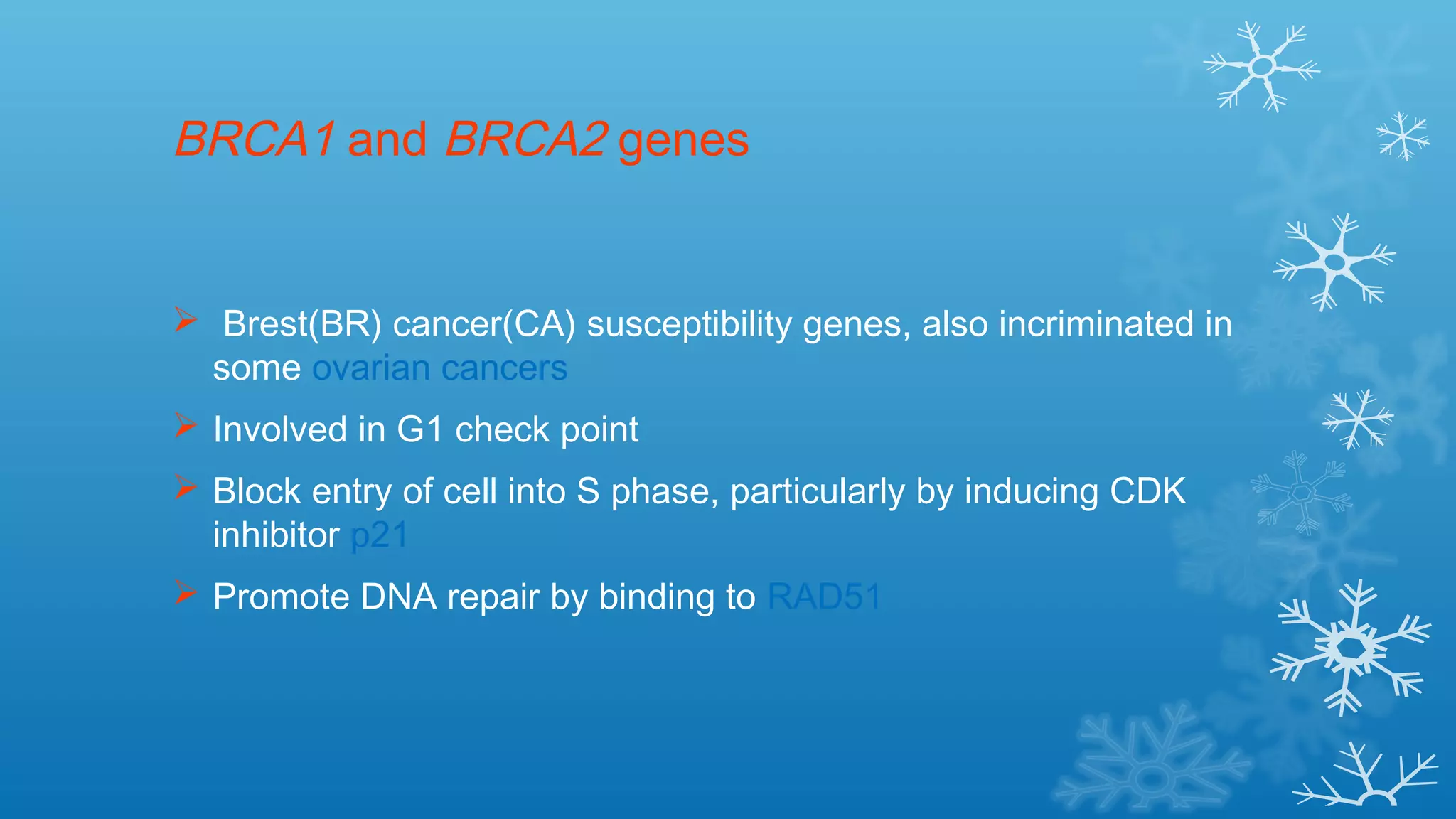
Tumor suppressor genes help repair damaged DNA and inhibit cell proliferation and cancer growth. They fall into two categories: caretaker genes that maintain genome integrity through DNA repair, and gatekeeper genes that inhibit proliferation or promote death of cells with damaged DNA. Key tumor suppressor genes include p53, Rb, APC, WT1, NF1, VHL, p15, p16, BRCA1, BRCA2, and PTEN. Mutation of both copies of a tumor suppressor gene, as with the two-hit hypothesis for retinoblastoma, can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer development.