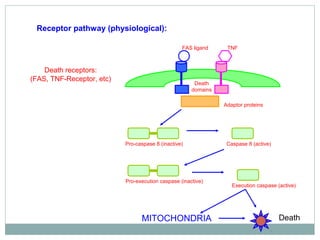
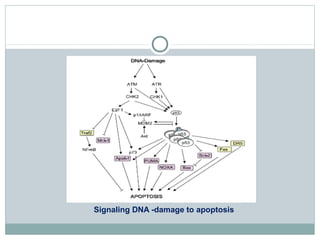
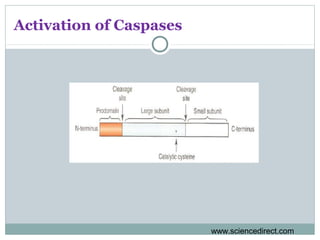
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is regulated by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic pathway involves mitochondria releasing cytochrome c which activates caspase proteases, leading to DNA fragmentation and cell death. The extrinsic pathway involves death receptors activating caspase-8 through adaptor proteins. Caspases are cysteine proteases that cleave other proteins and dismantle the cell in apoptosis. The Bcl-2 family and inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins also regulate apoptosis. Dysregulation of apoptosis contributes to diseases like cancer and neurodegeneration.