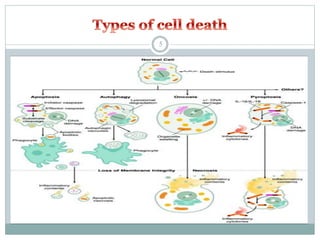
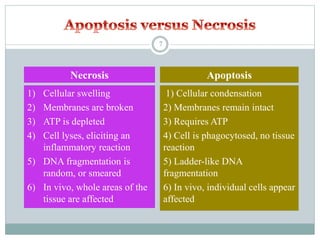
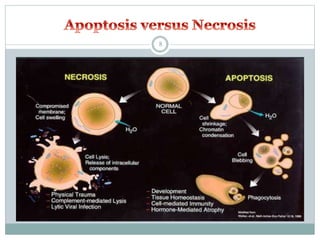
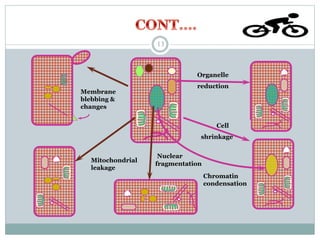
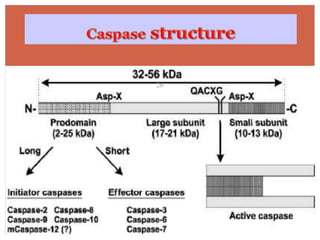
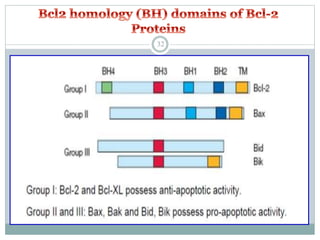
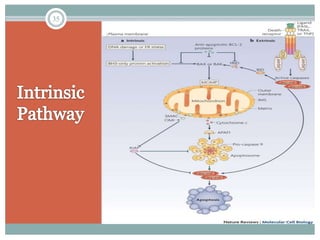
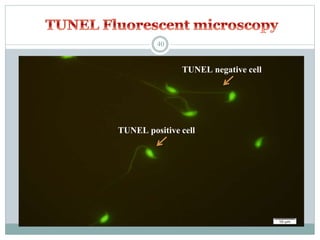
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is an important physiological process that eliminates unwanted or damaged cells. There are two main pathways that trigger apoptosis - the extrinsic or death receptor pathway, and the intrinsic or mitochondrial pathway. The extrinsic pathway involves death receptors and ligands that activate caspase enzymes. The intrinsic pathway occurs in response to cellular stress and involves mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and the release of proteins like cytochrome c. This forms the apoptosome complex and activates caspase-9 and caspase-3, leading to apoptosis. Apoptosis is a highly regulated process involving Bcl-2 family proteins, caspase enzymes, and characteristic morphological changes including cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, and membrane blebbing. Assays to detect