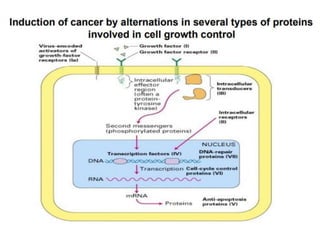
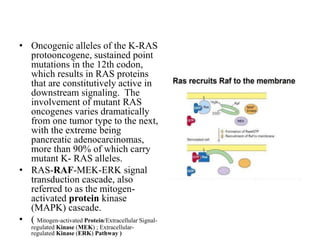
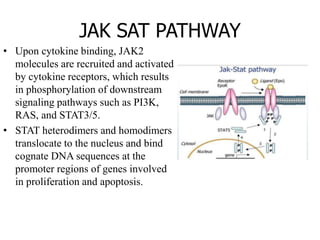
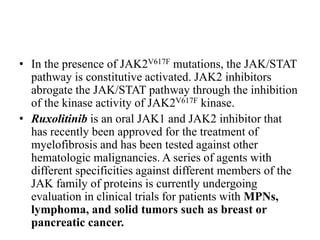
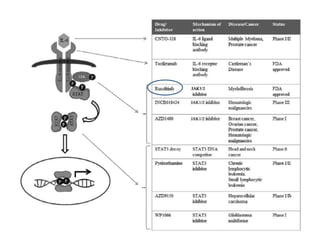
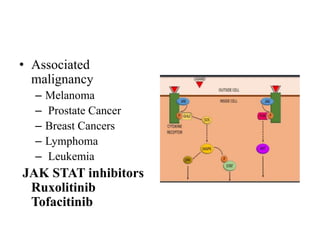
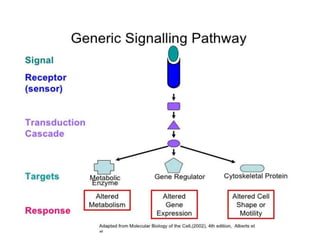
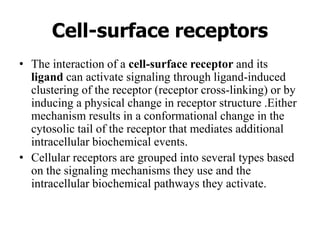
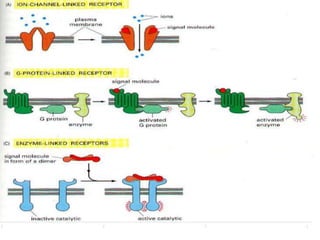
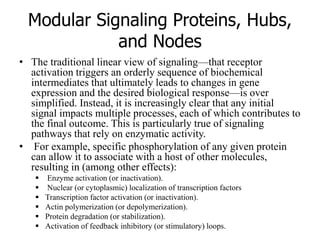
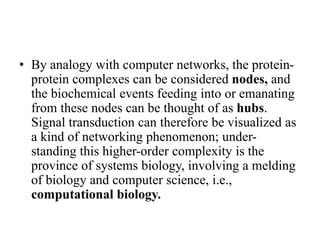
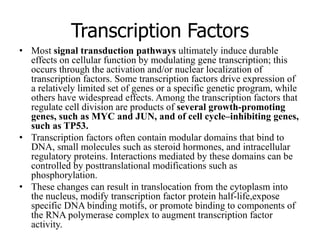
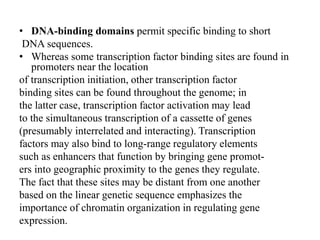
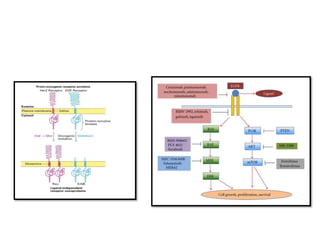
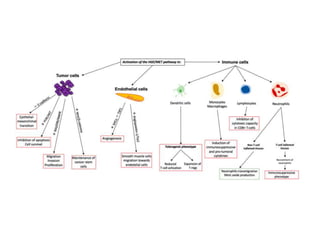
1. Signal transduction is the process by which cells convert extracellular signals into intracellular responses. Growth factors and other ligands bind to cell surface receptors to activate intracellular signaling pathways that regulate processes like cell growth, survival and gene expression.
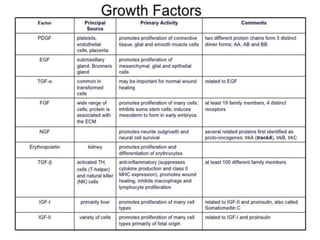
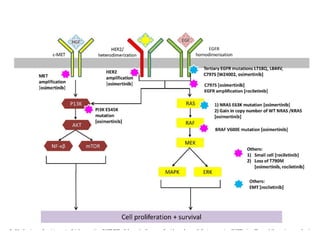
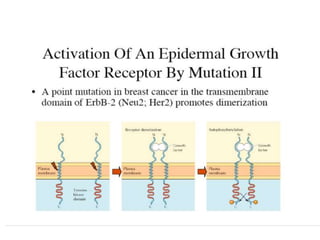
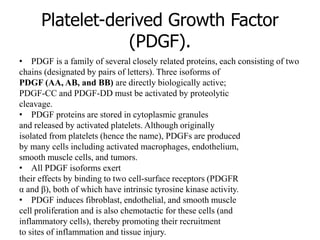
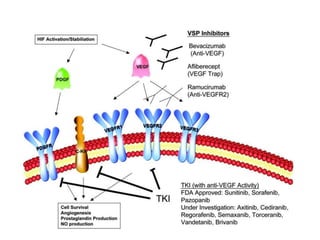
2. Deregulated growth factor signaling can contribute to tumorigenesis by inducing autocrine or paracrine proliferative signaling or by rendering cells hyperresponsive to growth factors. Common growth factors involved include EGF, HGF, PDGF, VEGF and FGF.
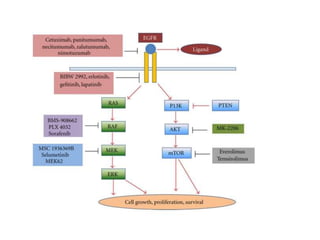
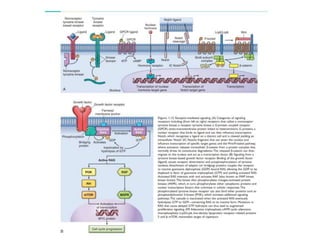
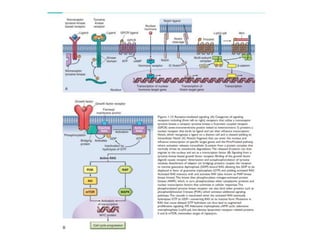
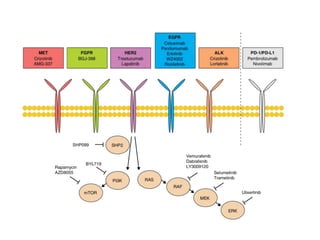
3. Growth factor receptors activate downstream signaling cascades like the MAPK and PI3K-AKT pathways through kinase activity. This leads to the activation of transcription factors that modulate gene expression and drive processes like



















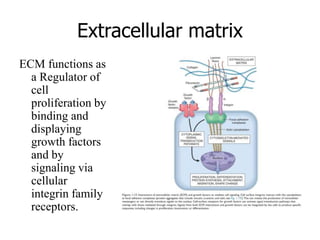
![Adhesive Glycoproteins and
Adhesion Receptors.
• Adhe sive glycoproteins and adhesion receptors are structurally
diverse molecules variously involved in cell-cell, cell-ECM, and
ECM-ECM interactions .Prototypical adhesive glycoproteins
include fibronectin (a major component of the interstitial ECM) and
laminin (a major constituent of basement membrane). Integrins are
representative of the adhesion receptors, also known as cell adhesion
molecules (CAMs); the CAMs also include immunoglobulin family
members, cadherins, and selectins.
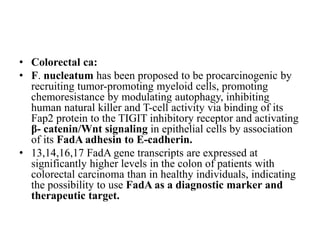
• The product of the NF2 gene, long implicated as a tumor suppressor
because its loss triggers a form of human neurofibromatosis. Merlin,
the NF2 gene product, orchestrates contact inhibition in the
cytoplasm by coupling cell-surface adhesion molecules (e.g., E-
cadherin) to transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases (e.g., the
epidermal growth factor receptor [EGFR]). In so doing, Merlin
strengthens the adhesiveness of cadherin-mediated cell-to-cell
attachments. Additionally, by sequestering such growth factor
receptors, Merlin limits their ability to efficiently emit mitogenic
signals.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/signallingpathwaysintumorigenesis-210309172903/85/Signalling-pathways-in-tumorigenesis-41-320.jpg)