This document provides an introduction to the concept of differentiation in mathematics. It defines differentiation as the limit of the incremental ratio as the increment approaches 0, which represents the derivative or rate of change of a function. The document outlines standard differentiation rules and formulas for common functions such as sums, products, quotients, square roots, exponentials and logarithms. It provides examples of applying the product, quotient and chain rules to differentiate various functions. Finally, it defines the second derivative as taking the derivative of a function a second time to determine the rate of change of the rate of change.

![Unit-IV Basic Differentiation
RAI UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD
Introduction—Let y = f(x) be a given function. Let is a small increment in x and is the
corresponding increment in y. then—
+ = ( + )
∴ = ( + )– ( ) [∵ = ( )]
The limit of the incriminatory ratio when → 0 is called the derivative or differential
coefficient of y with respect to x and it is denoted by .
Thus = → =
( ) ( )
→
The derivative of = ( ) w.r.t. x is also denoted by ( ), , , or [ ( )].
The derivative of = ( ) at = is denoted by ( ) [ ] and it is given by
( ) =
( + ) − ( )
→
The process of finding derivatives is called as differentiation.
Example—Consider : → , ( ) = . suppose we wish to find derivative of f(x) w.r.t. .
Here, ( + ) = ( + ) = + 2 + ( )
( + ) − ( ) = + 2 + ( ) −
= 2 + ( )
= (2 + )
By definition, =
( ) ( )
→
=
( )
→ = (2 + )→ ( ≠ 0)
∴ ( ) = 2
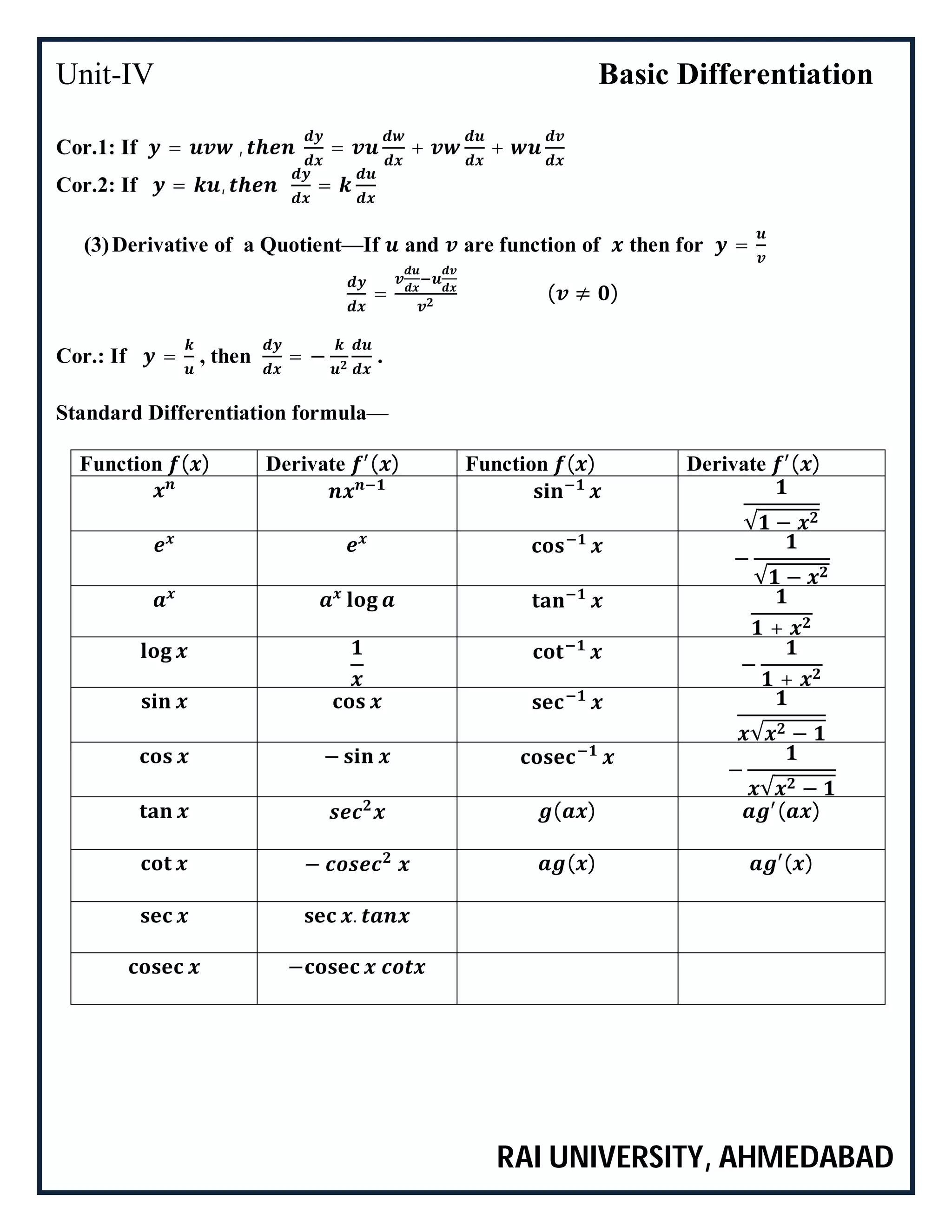
Rules for Differentiation—
(1)Derivative of sum and difference— If and are functions of then for =
±
= ±
(2)Derivative of Product—If and are function of then for =
= +](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcaunit-iv-150111012441-conversion-gate02/75/BCA_MATHEMATICS-I_Unit-IV-2-2048.jpg)