This document discusses linear programming (LP) models, including how to formulate, solve, and interpret them. Key points covered include:
- The steps to develop an LP model are formulation, solution, and interpretation with sensitivity analysis.
- LP models seek to maximize or minimize an objective function subject to constraints. They include alternatives and all equations are linear.
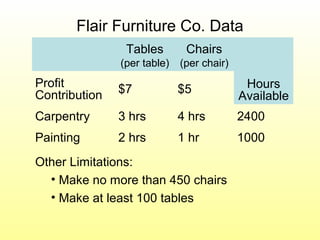
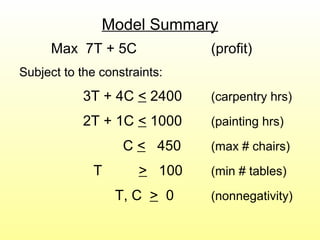
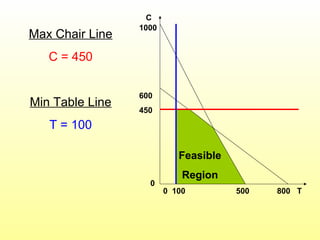
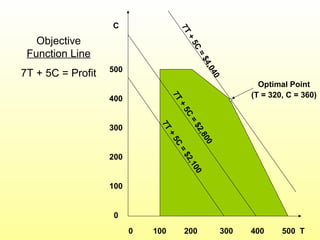
- An example LP model is presented to maximize profit for a furniture company making chairs and tables given resource constraints.
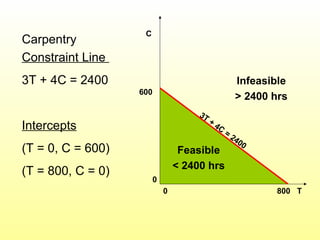
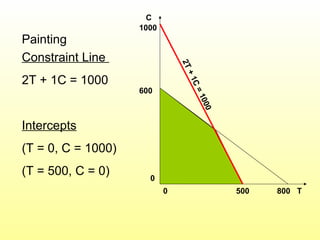
- The graphical solution method is explained to provide insight into LP models and solutions. The optimal solution must occur at a corner point of the feasible region.
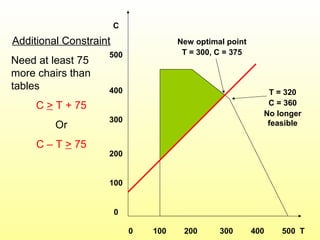
- Special situations in LP like infeasibility, alternate optima, and unbounded