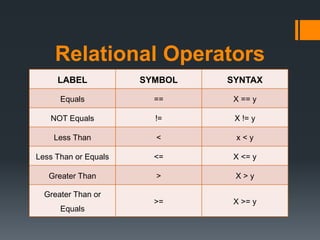
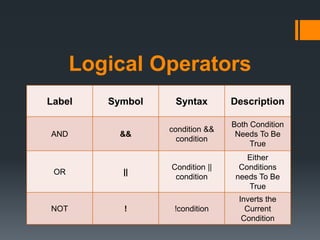
The document discusses conditional statements in Java programming. It describes if-else, if-else-if-else statements and nested conditional statements. It also covers relational operators like ==, !=, <, <=, >, >= and logical operators like &&, ||, ! that are used to evaluate conditions. Examples are provided to demonstrate how to use if, if-else, if-else-if-else statements to run certain code blocks based on conditional expressions. The equals function is also introduced to compare string values more efficiently.