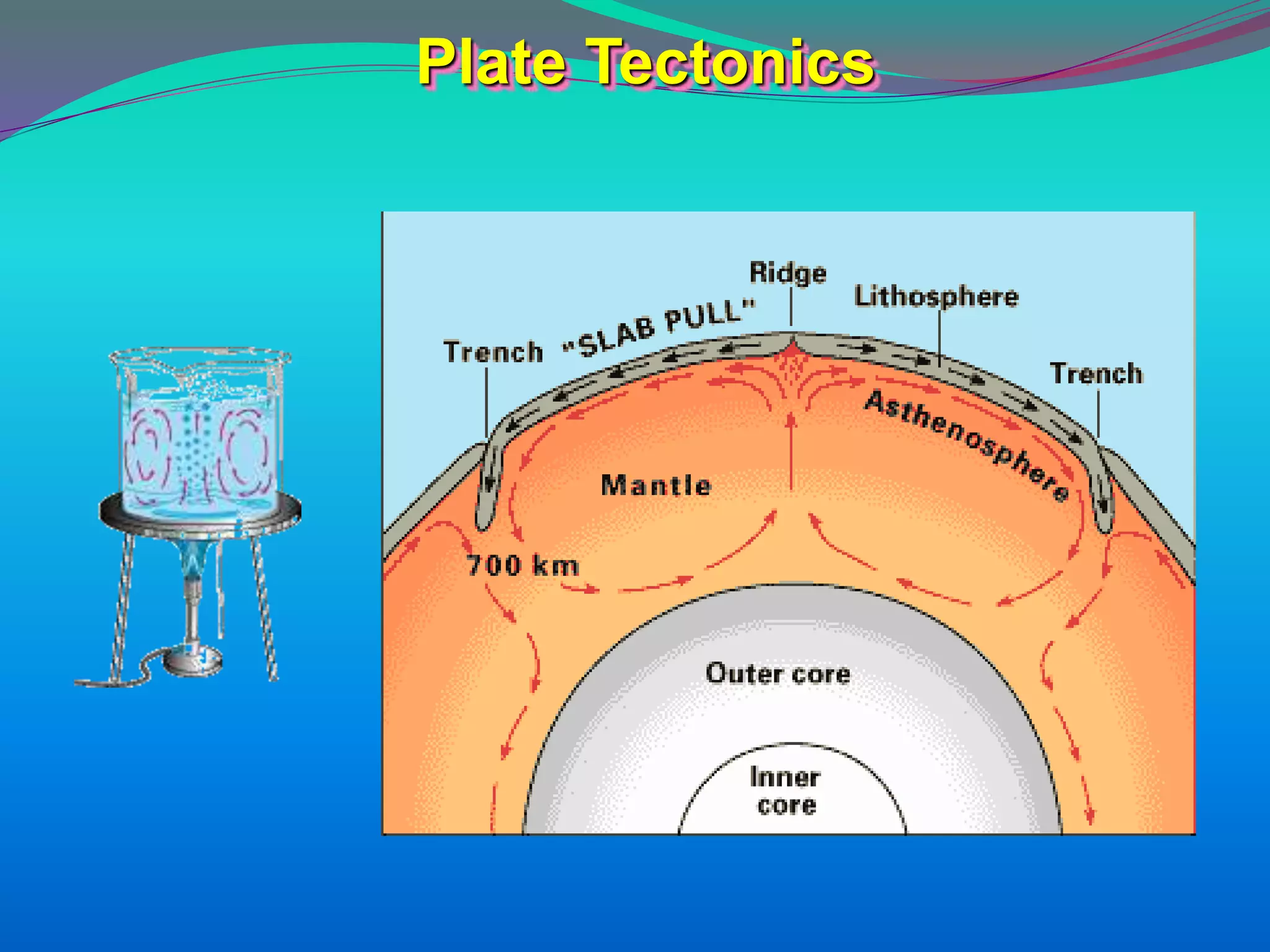
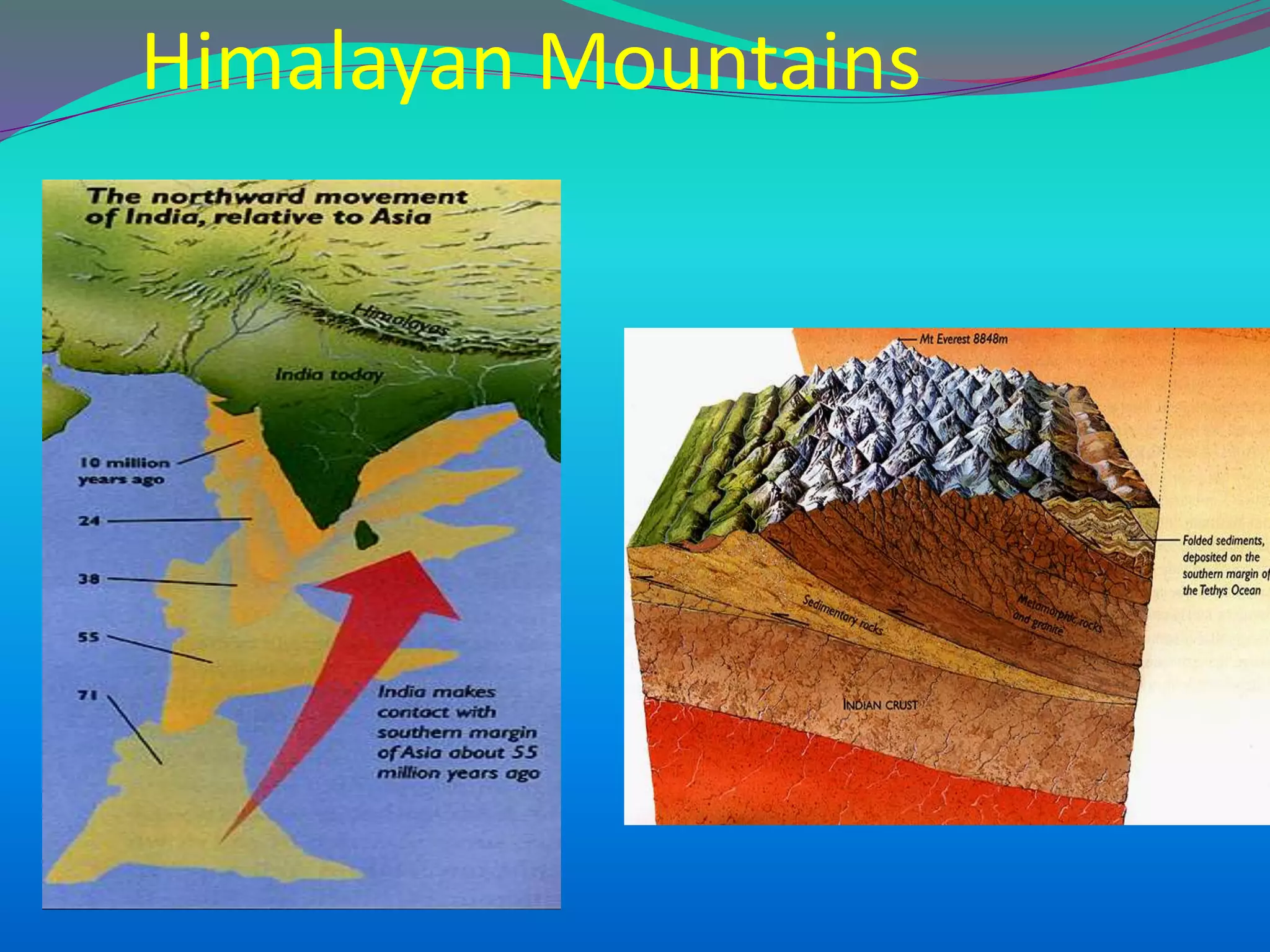
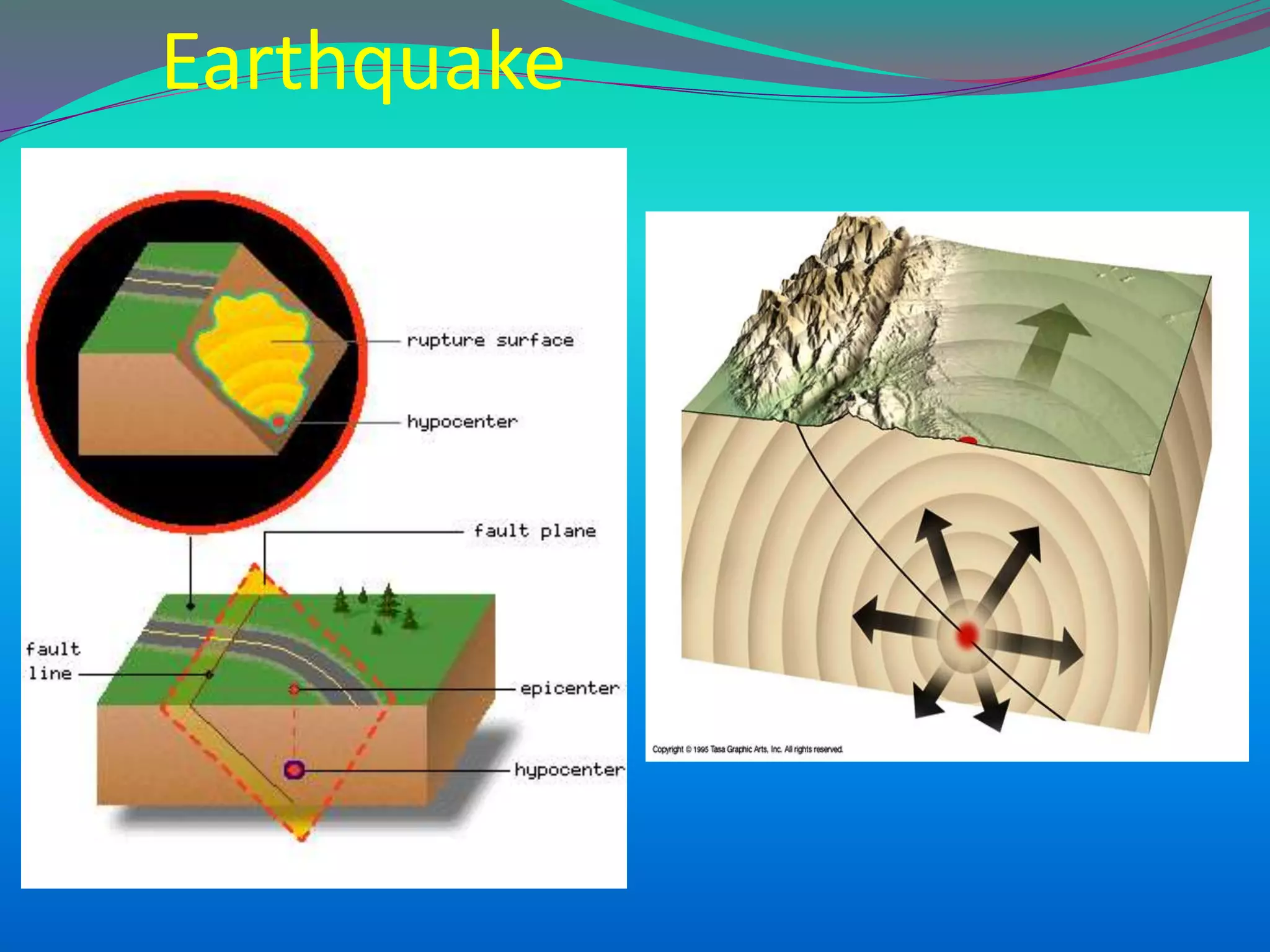
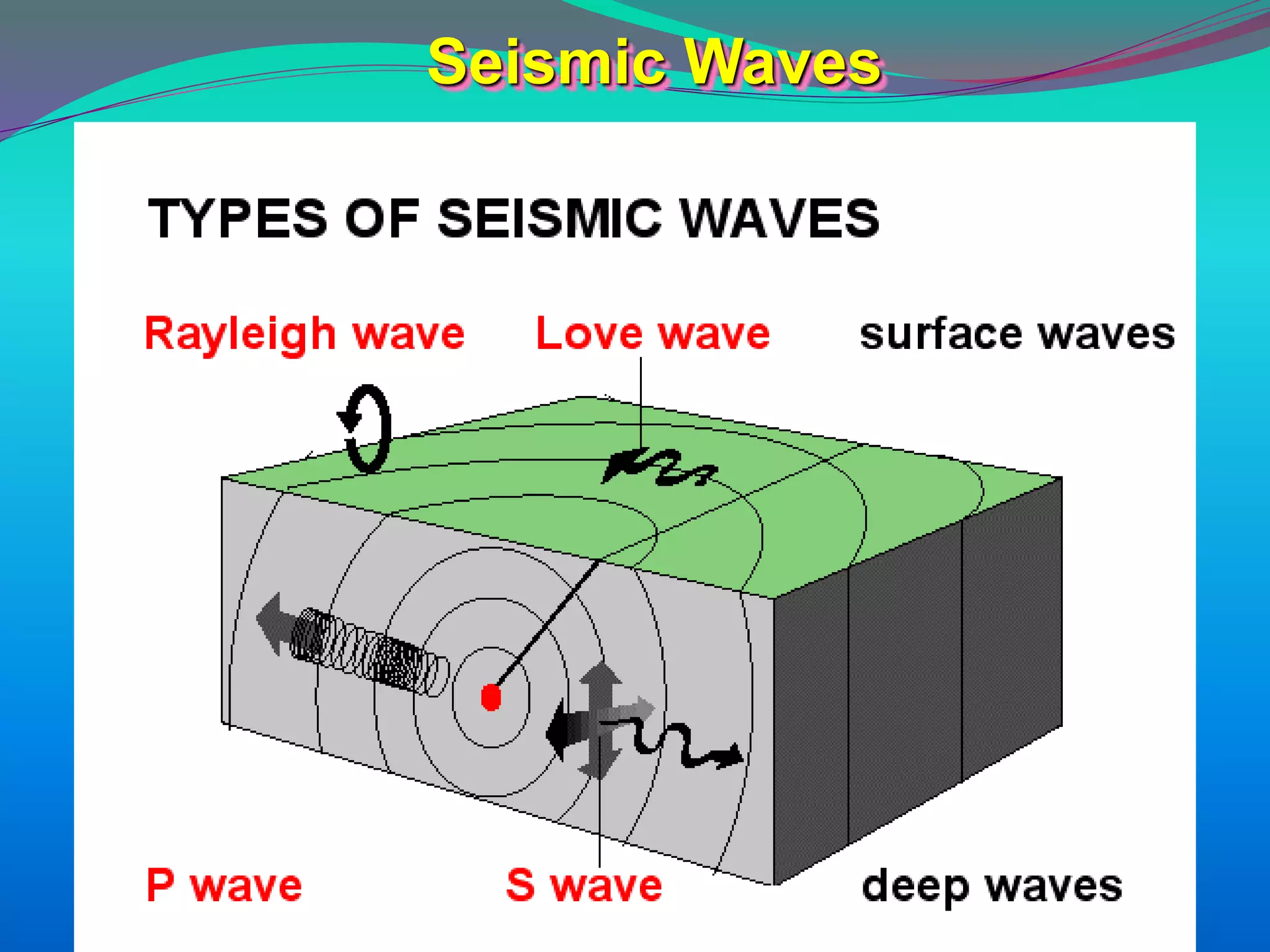
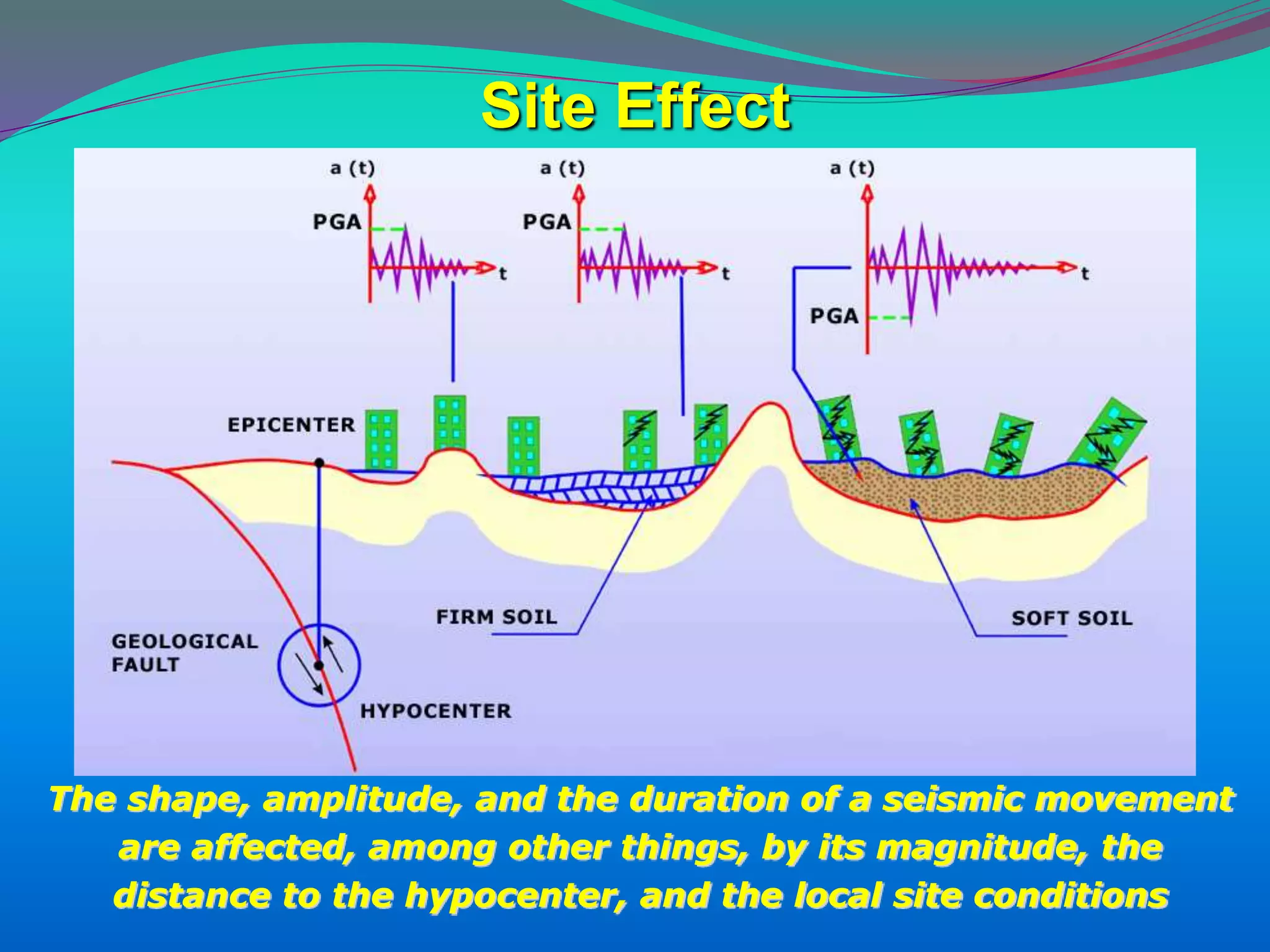
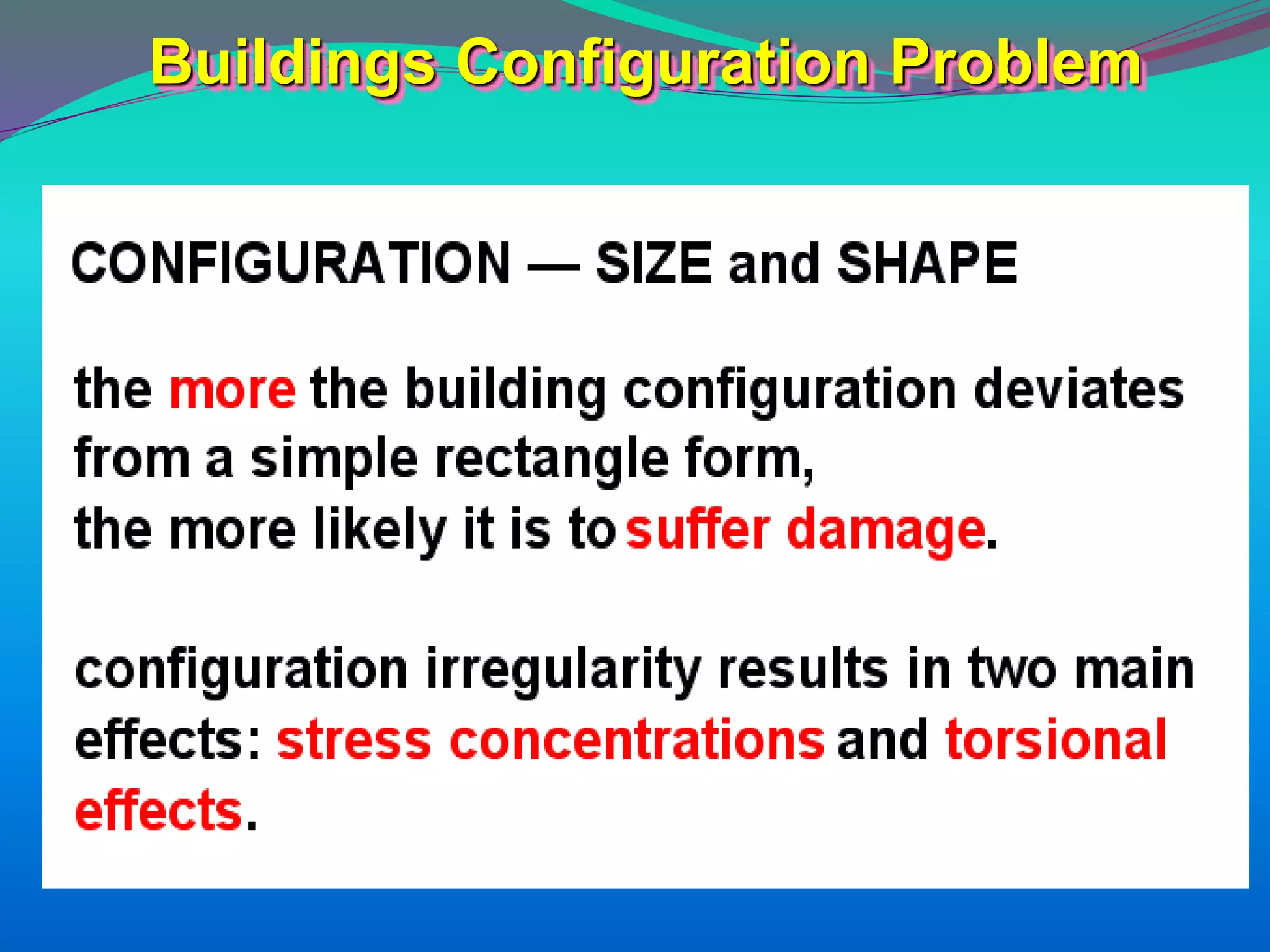
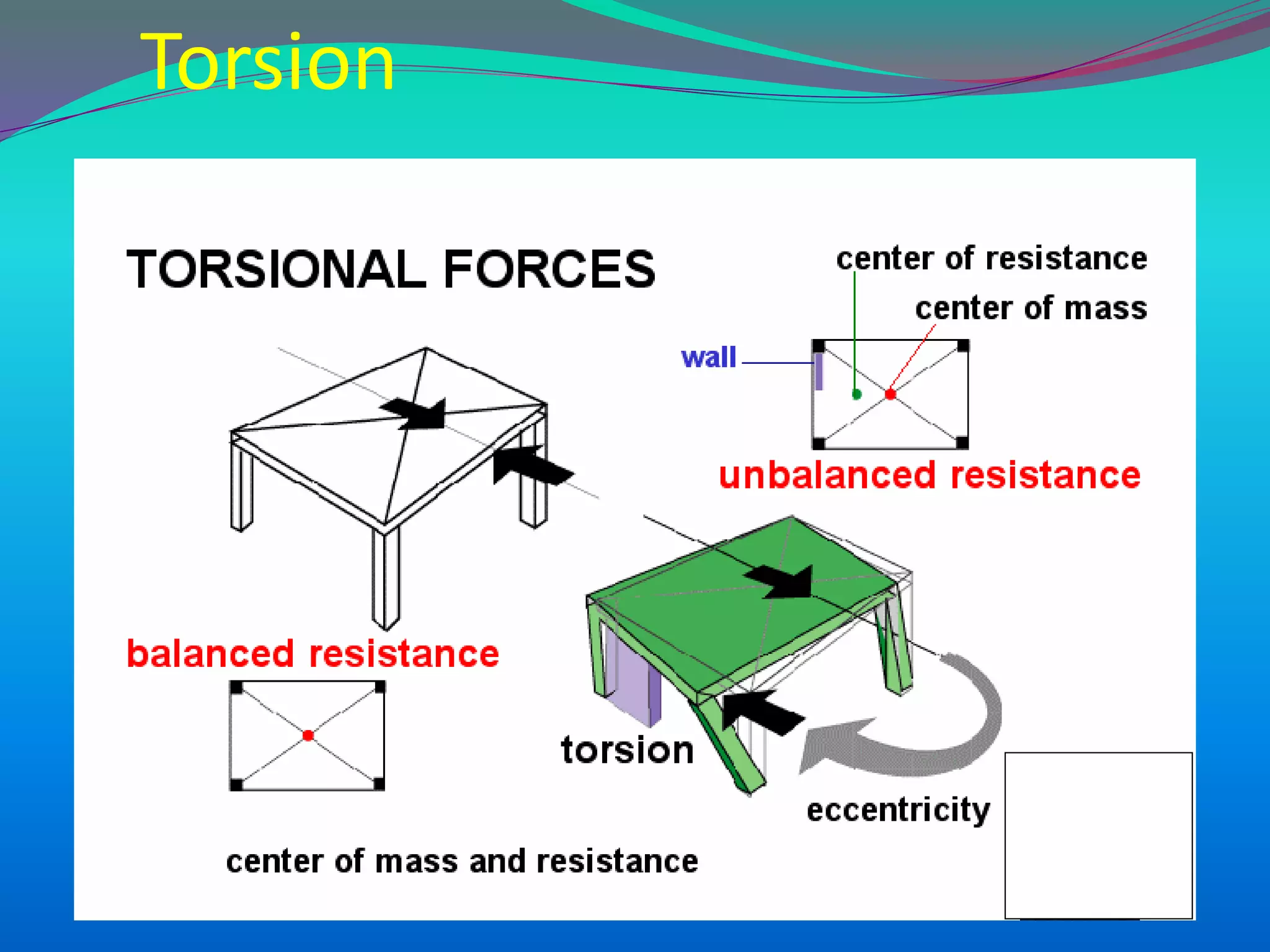
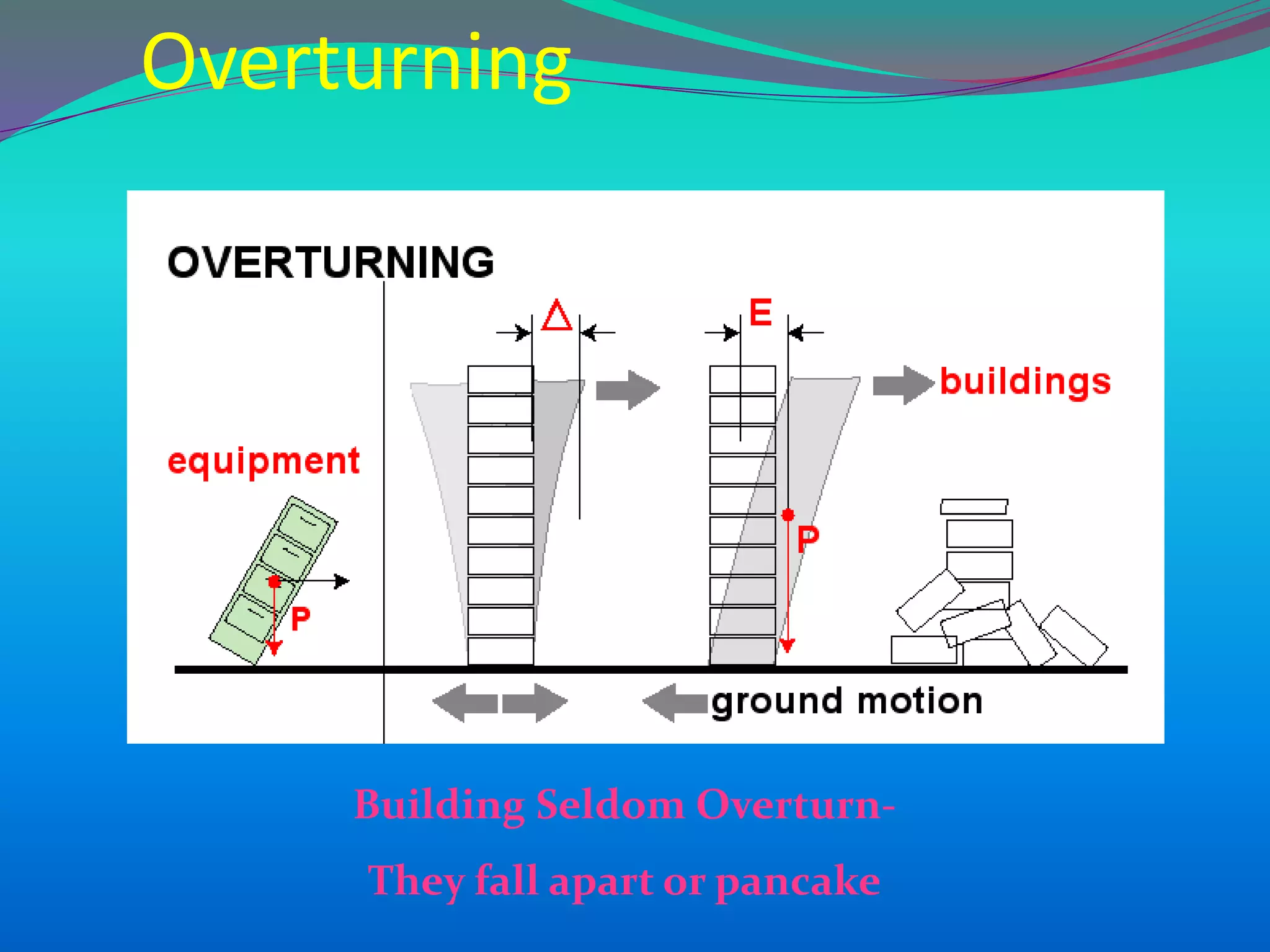
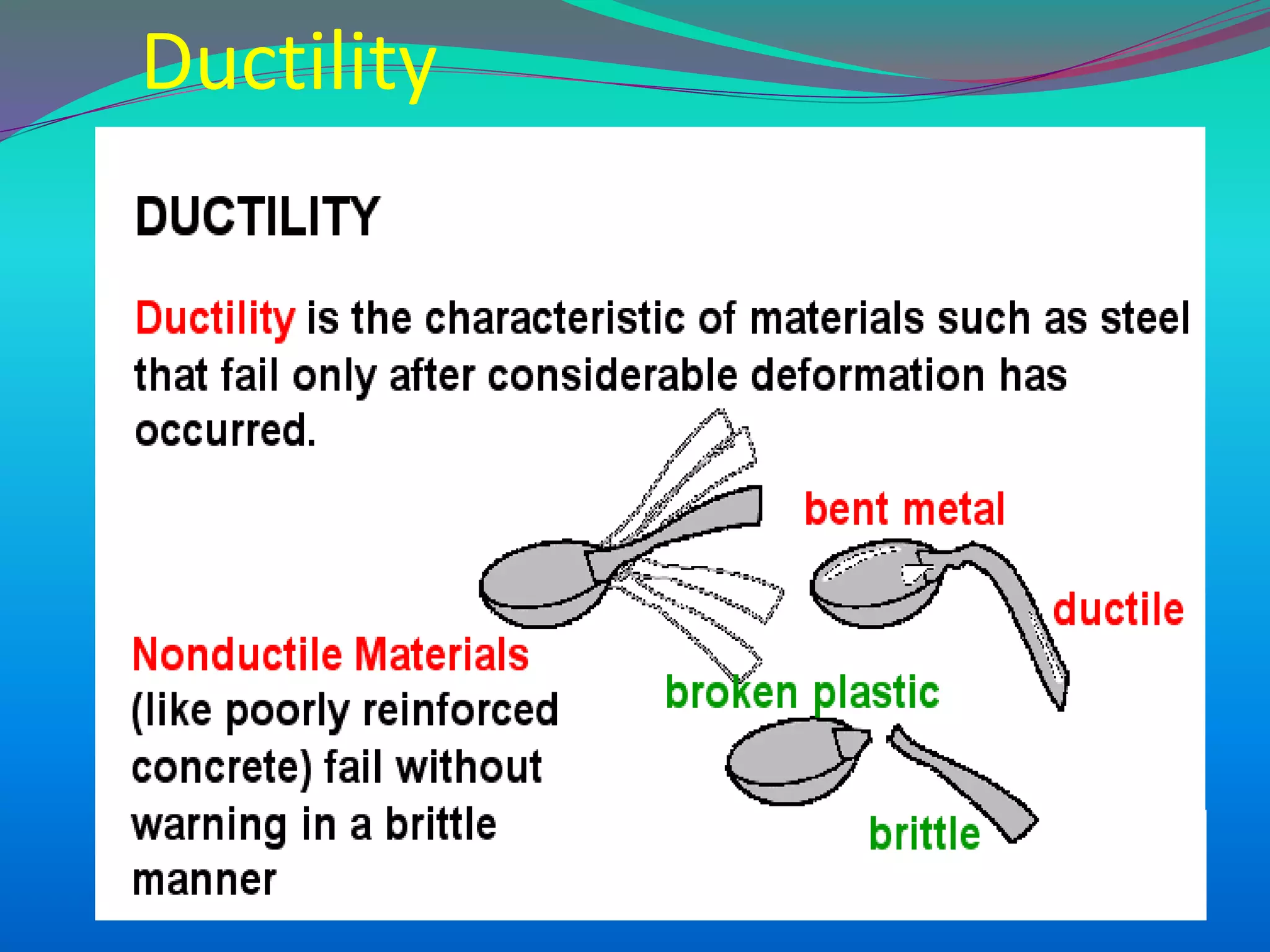
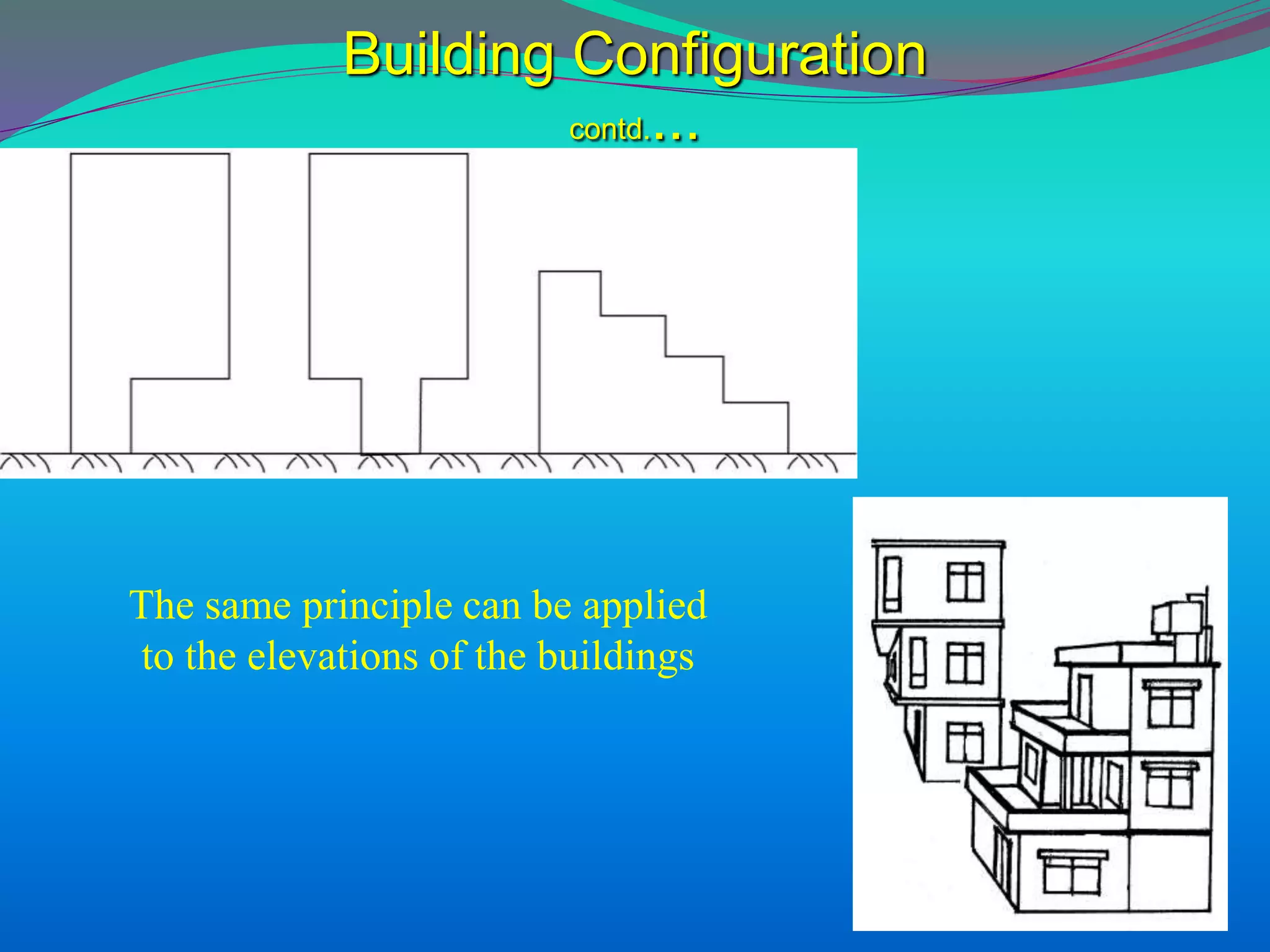
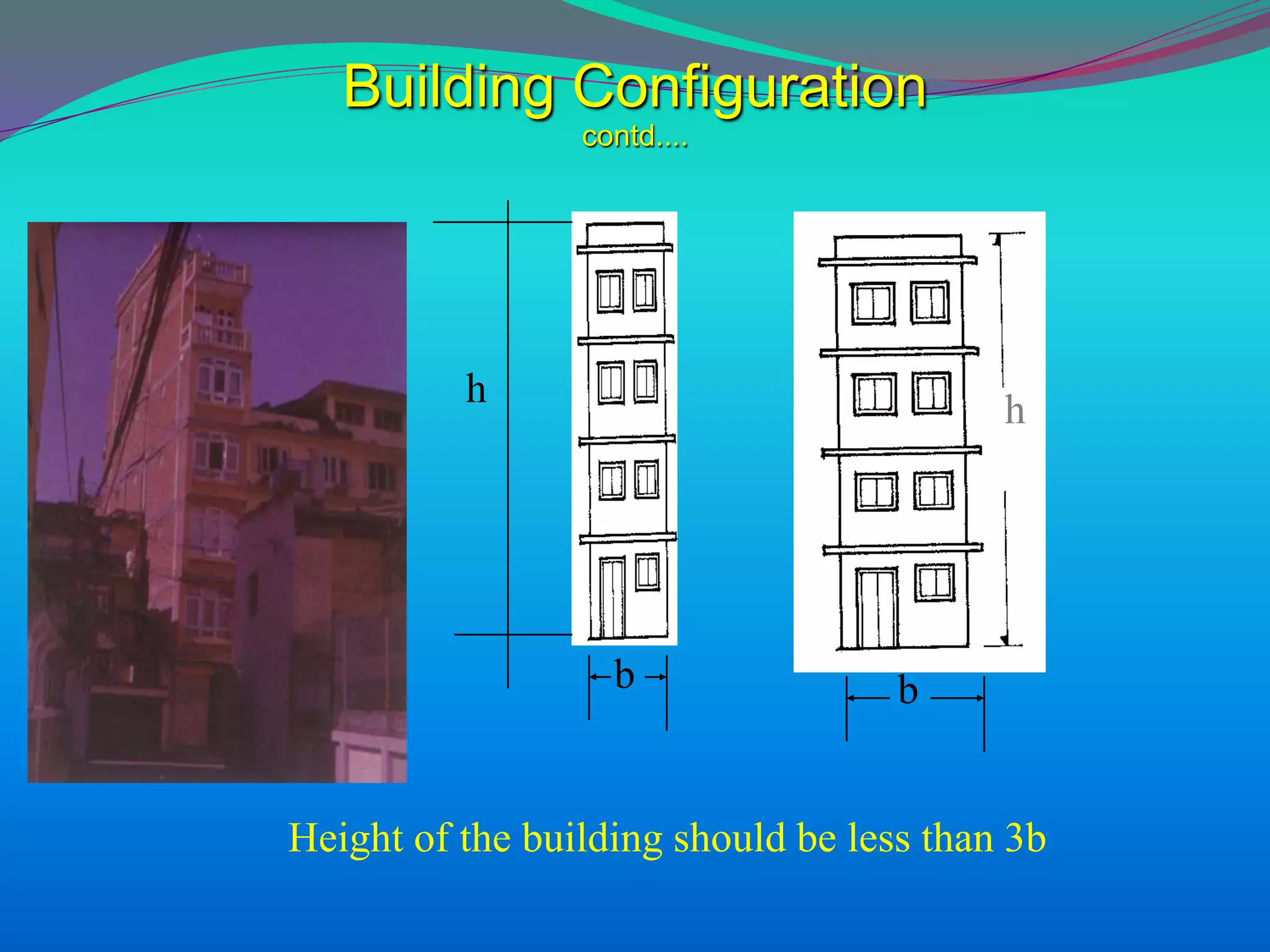
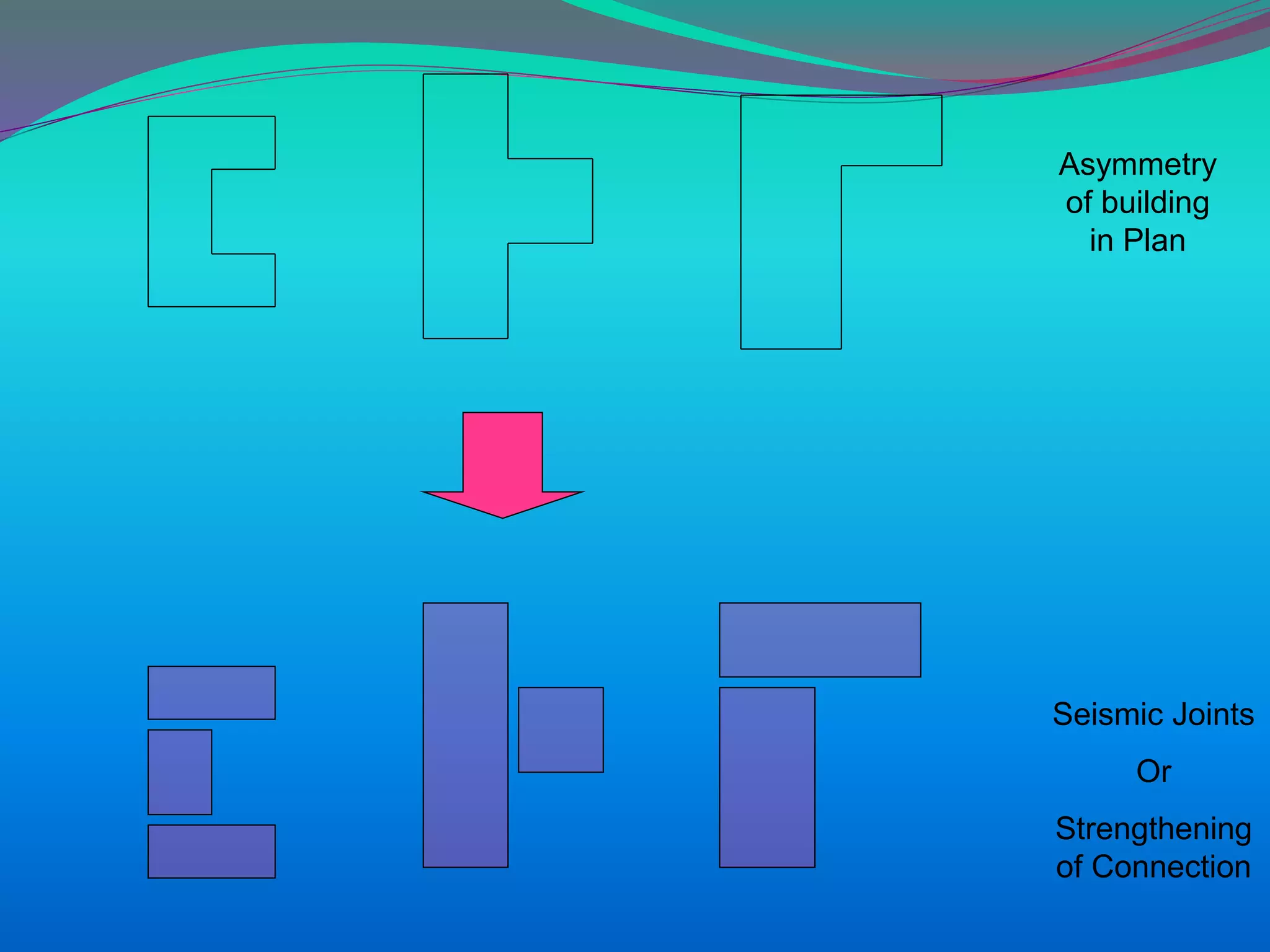
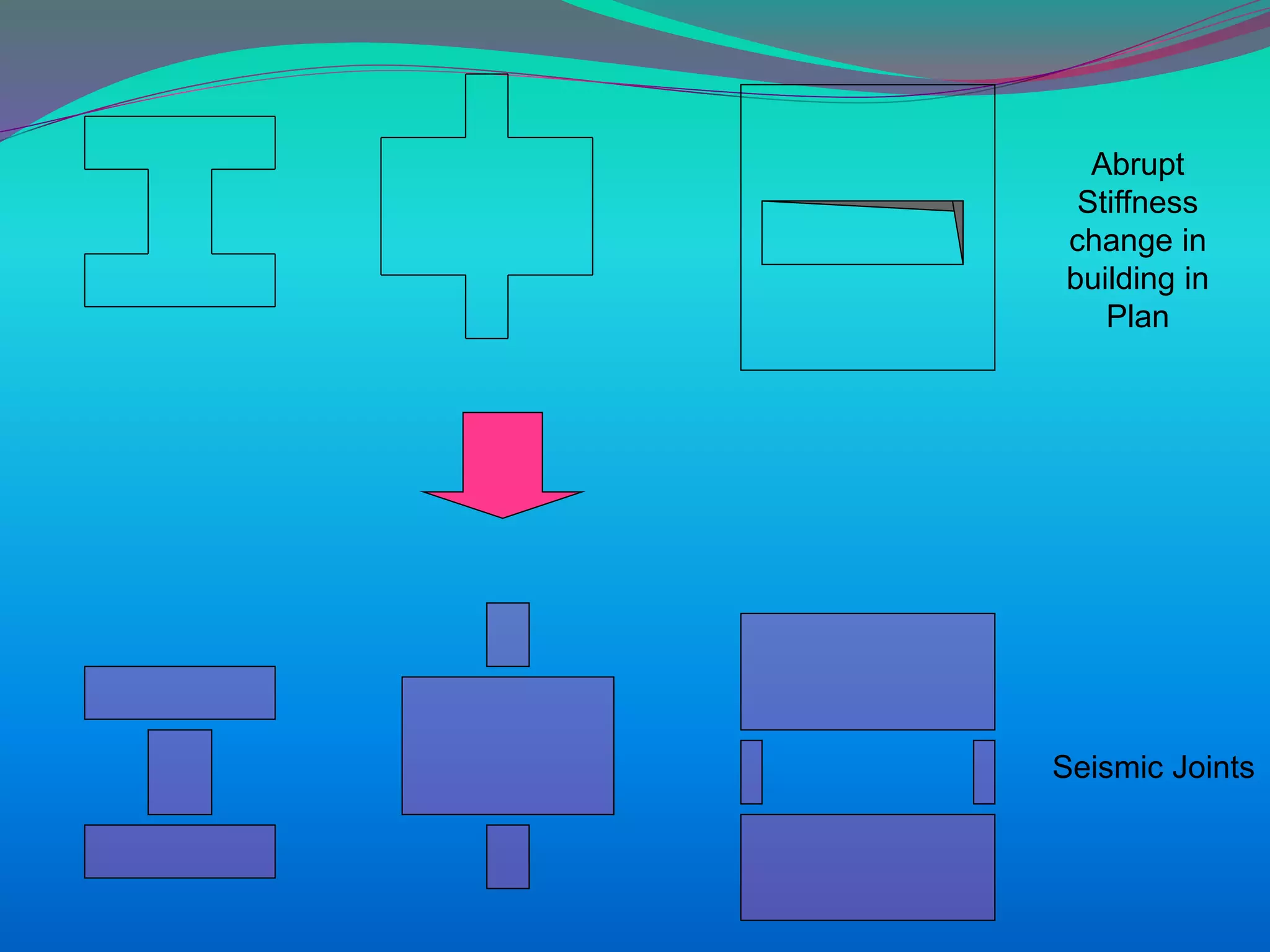
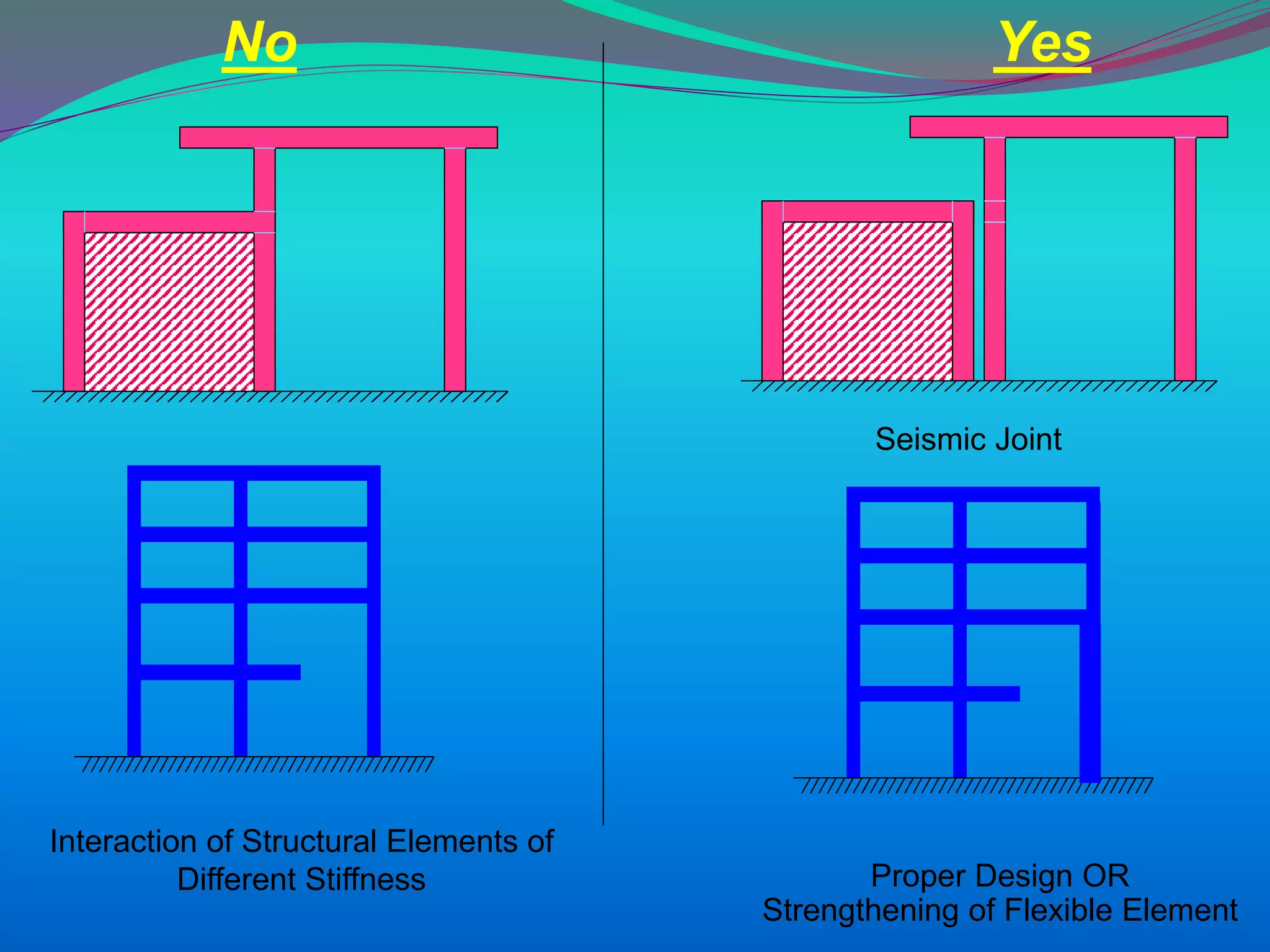
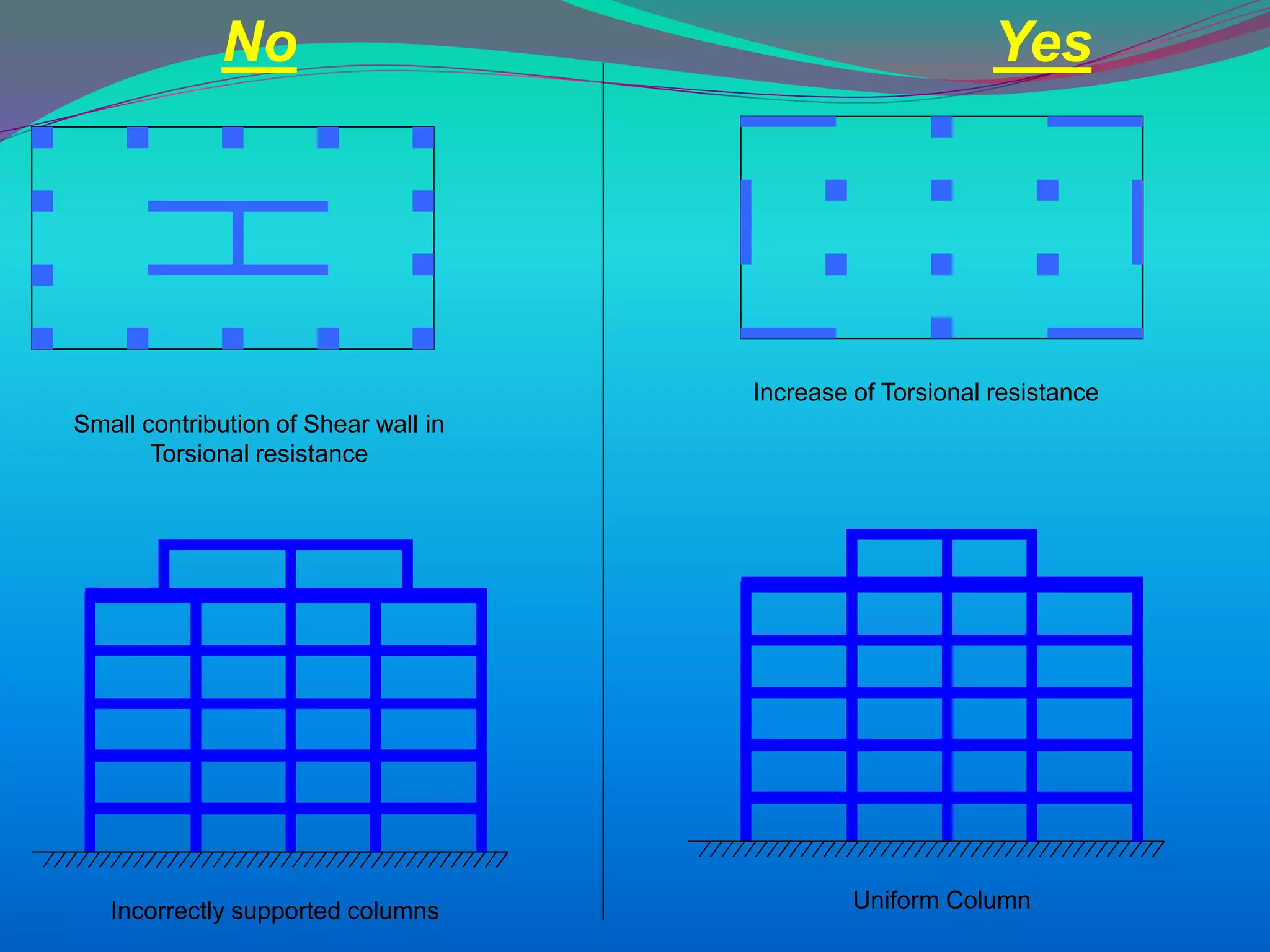
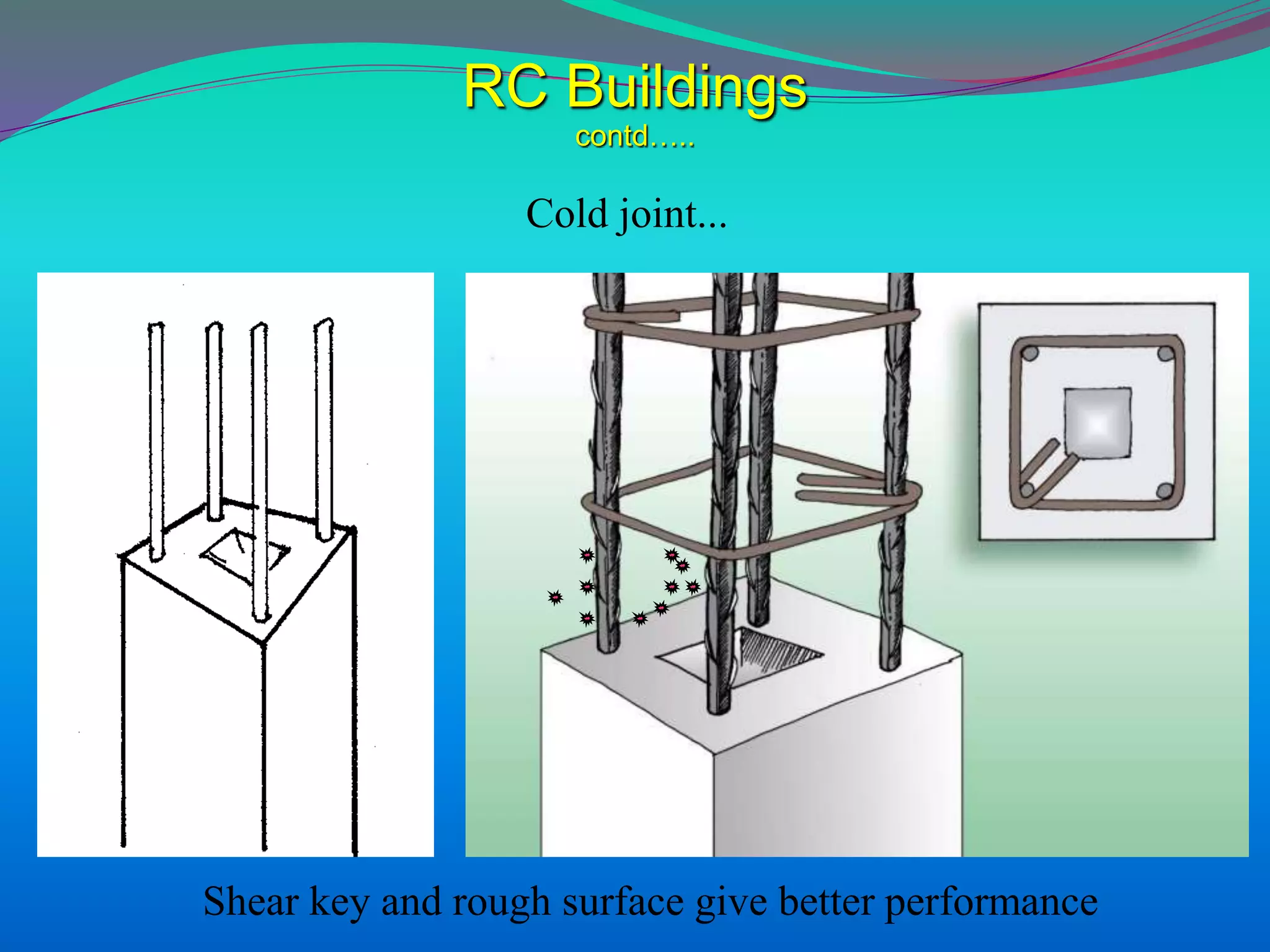
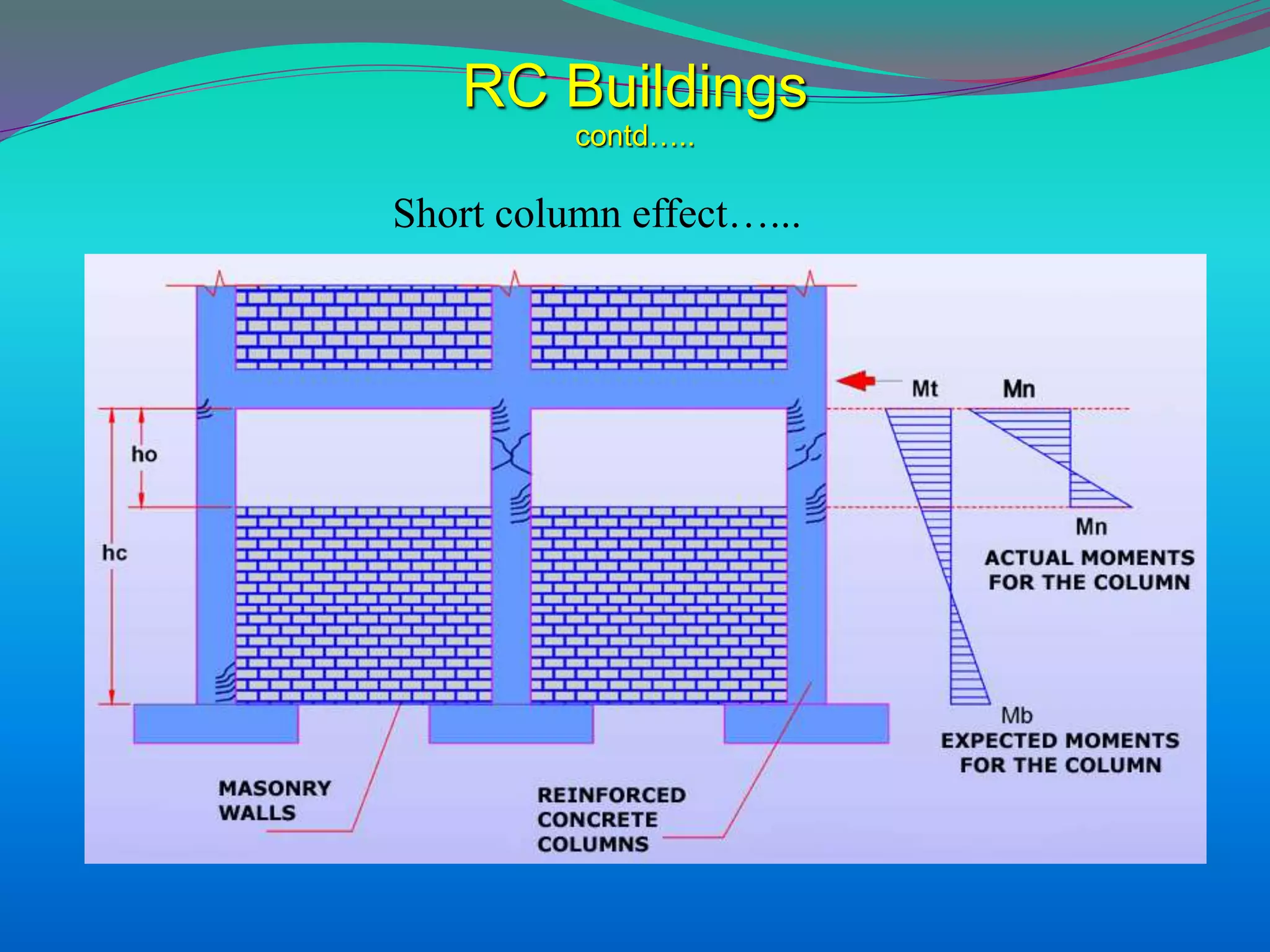
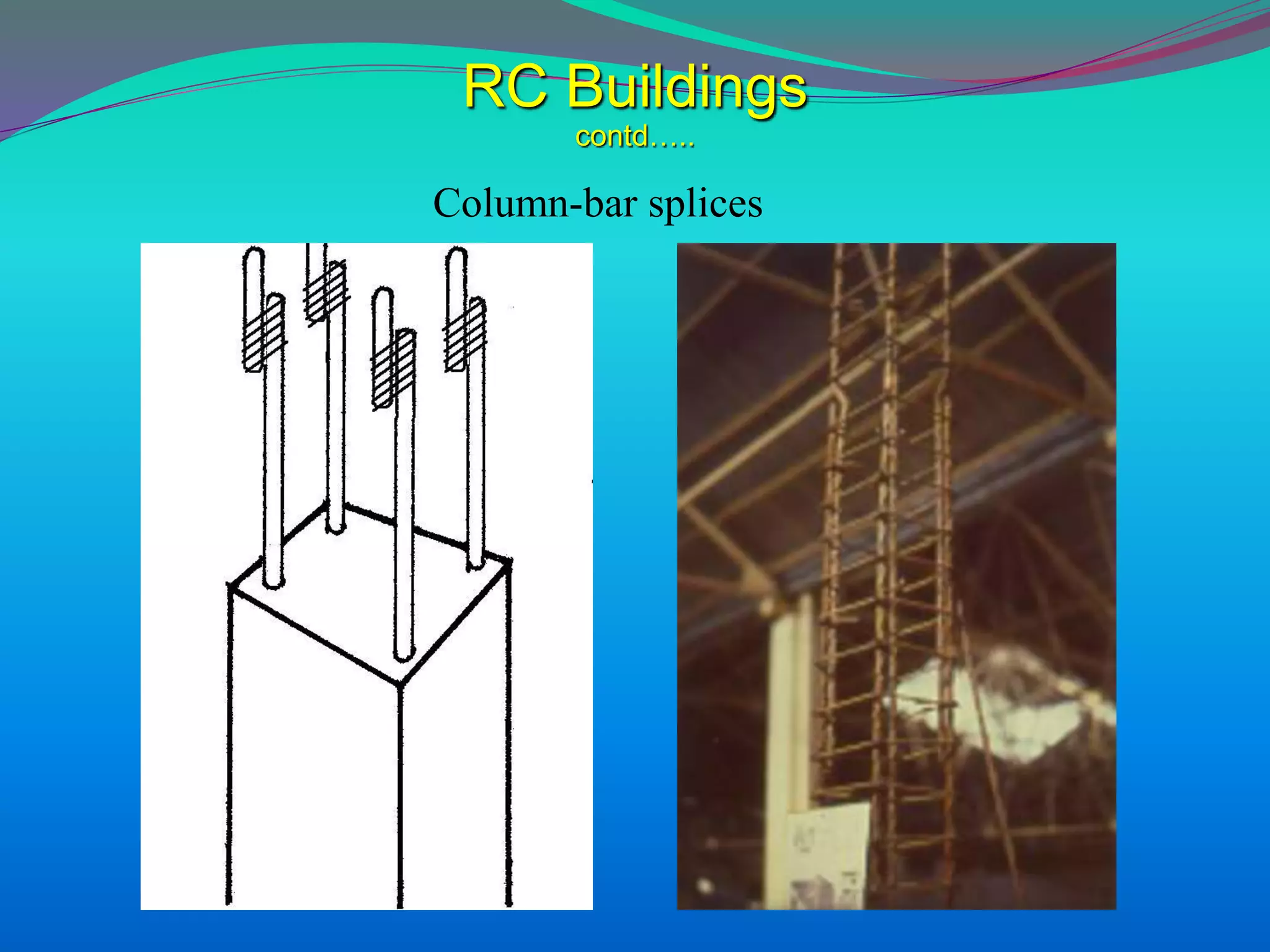
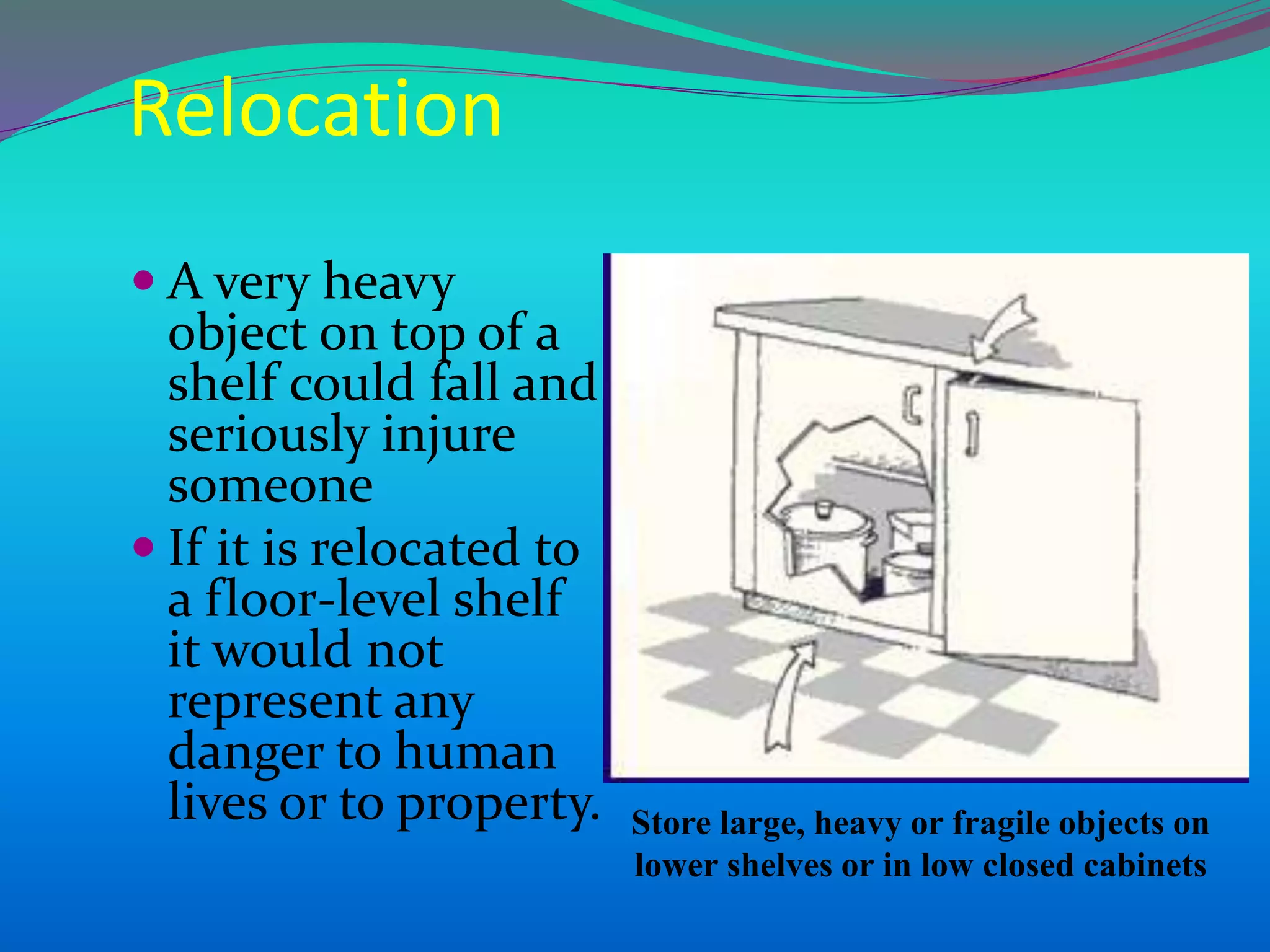
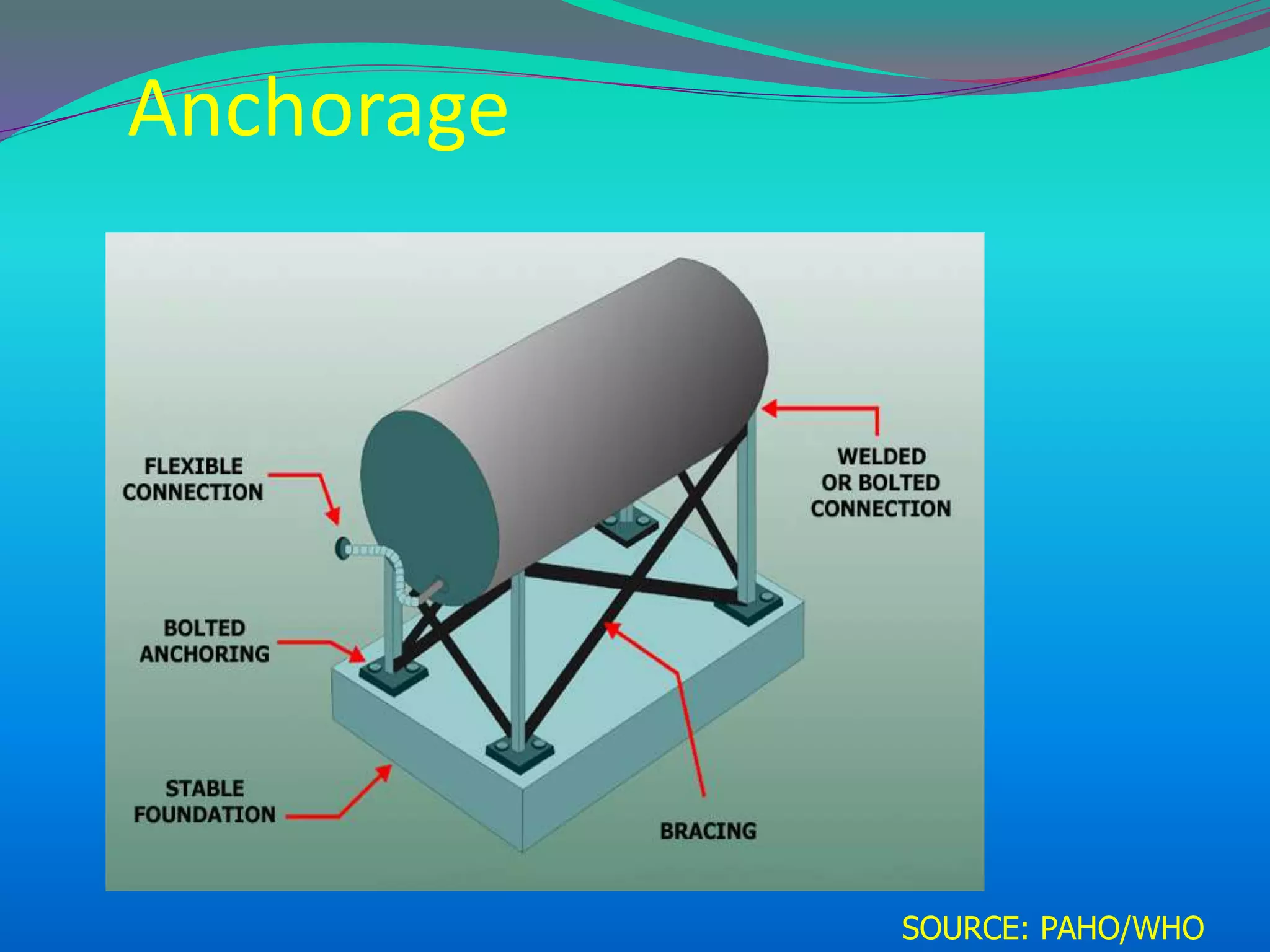
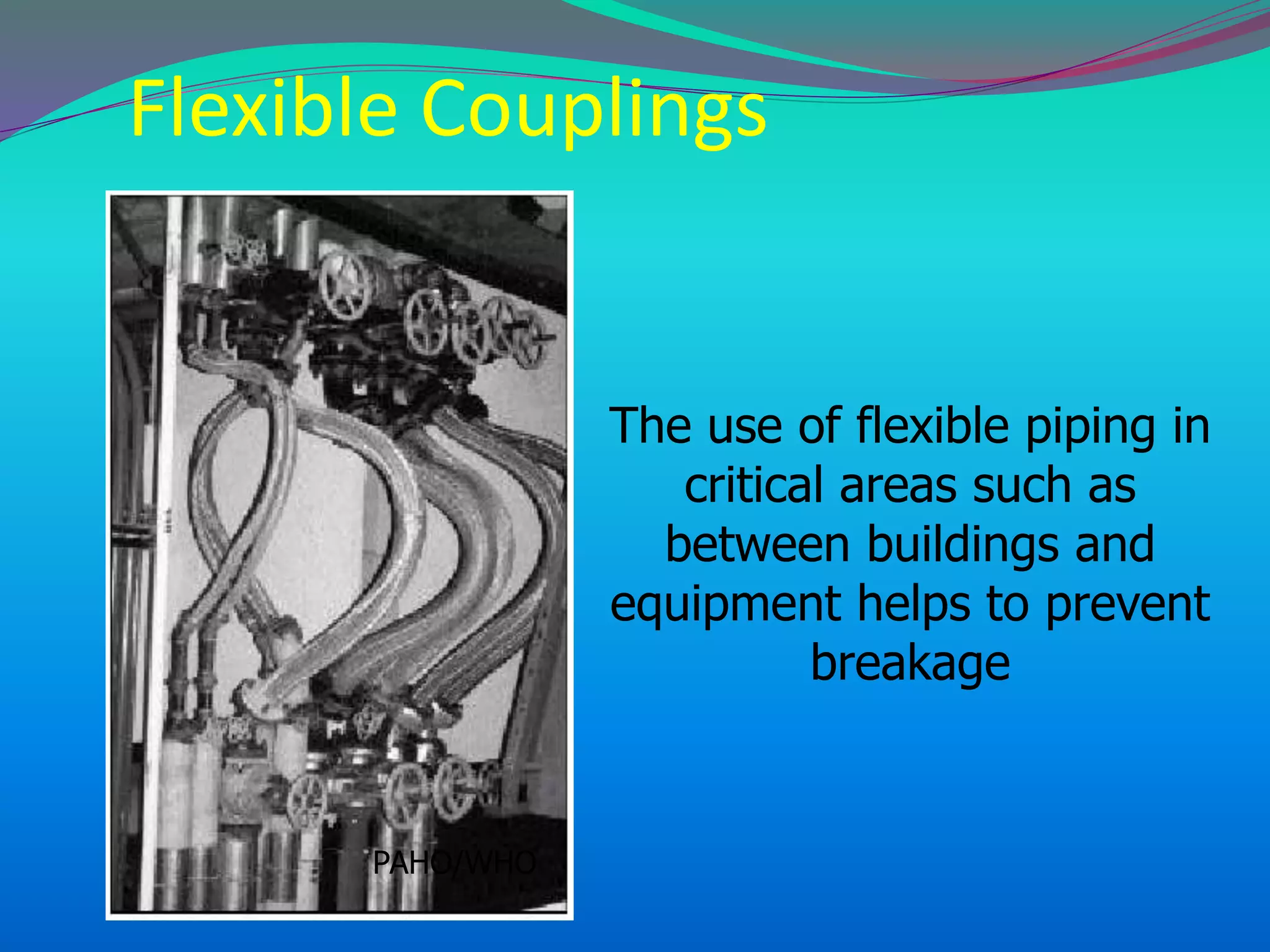
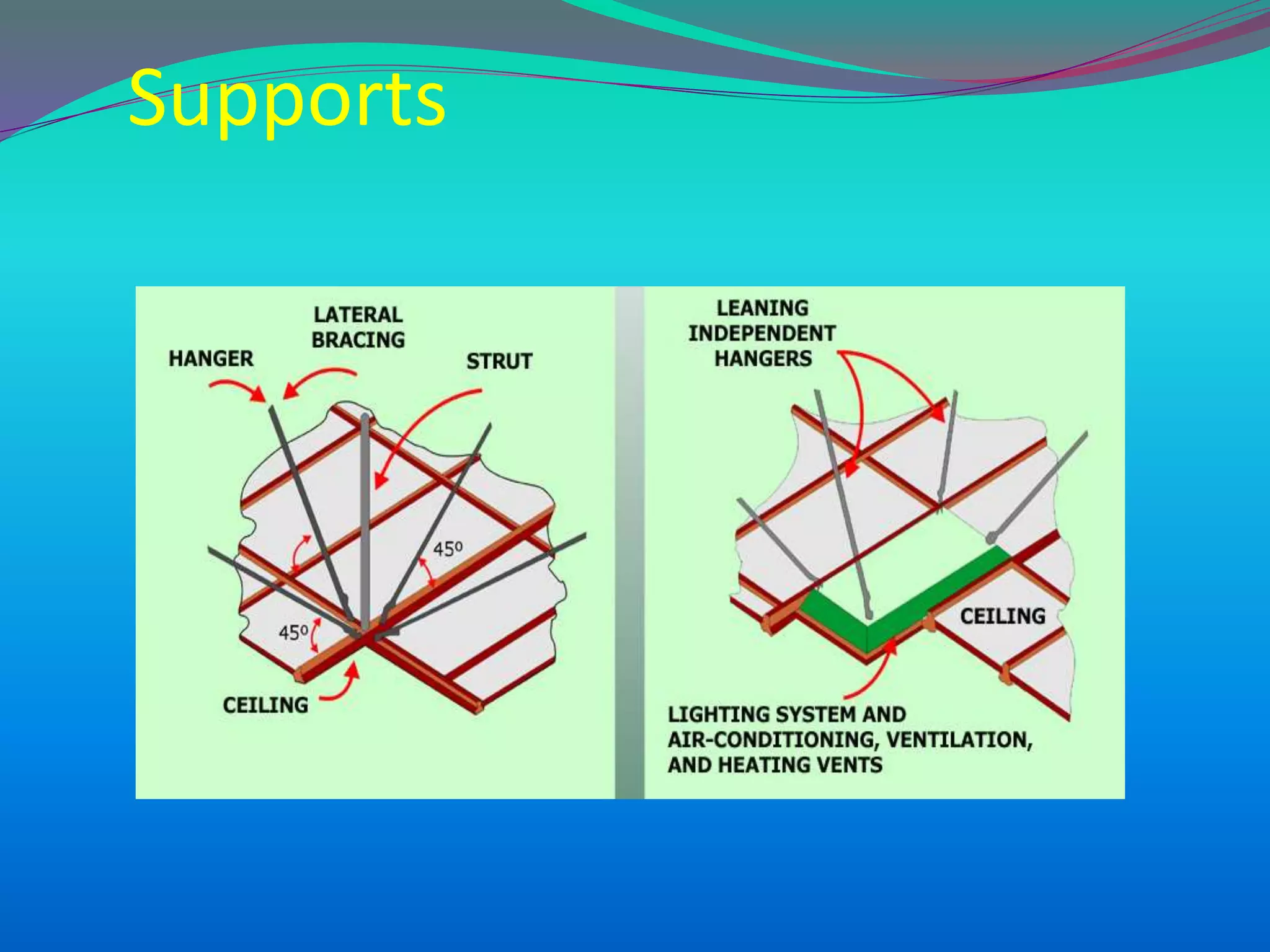
The document discusses the mechanisms, causes, and effects of earthquakes, emphasizing structural vulnerability and building design considerations for earthquake resistance. It outlines the significance of life safety, property loss, and loss of function during an earthquake, along with mitigation measures for non-structural damages. Recommendations include proper building configuration, reinforced structures, and safety practices in construction to minimize risks associated with earthquakes.