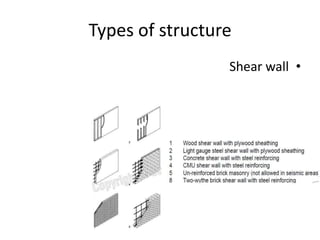
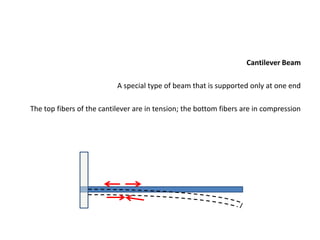
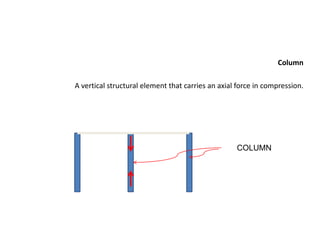
1. Structural systems include architectural structures like buildings that are assemblages of components designed to support loads through interconnected members.
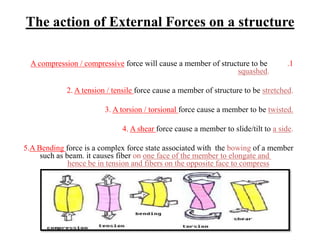
2. Loads on structures can be static like dead loads or dynamic like wind loads, and forces like tension, compression, bending, and shear act on structural members.
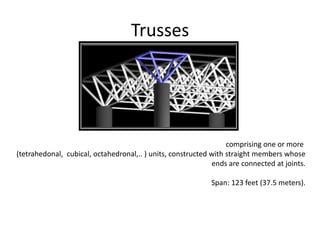
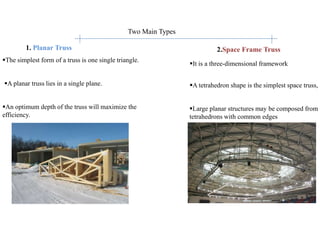
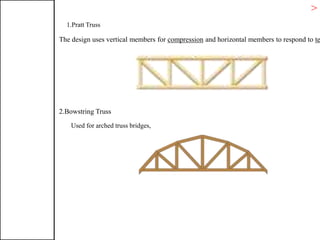
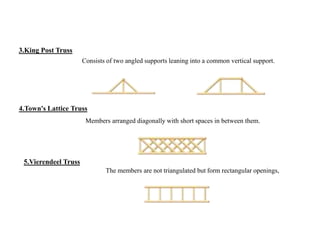
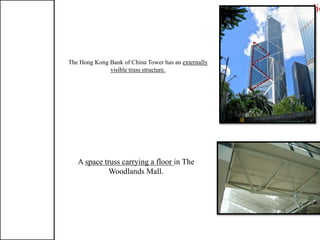
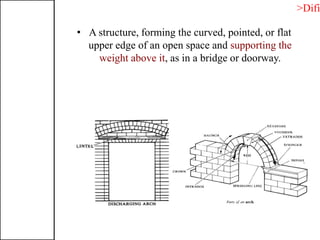
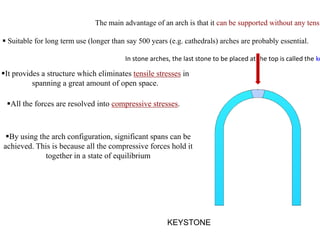
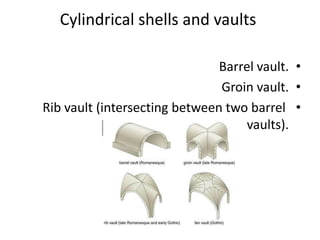
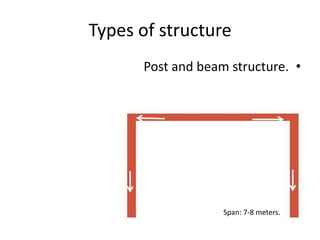
3. Common structural forms include trusses, arches, shells, frames, and cable nets which use specific geometries and materials like steel and concrete to transfer loads.