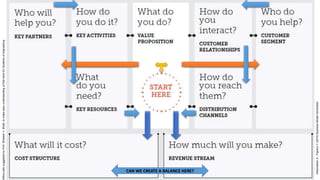
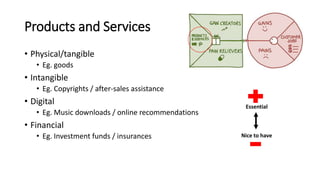
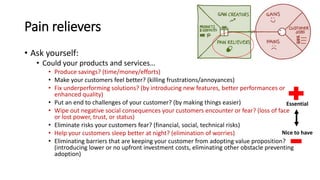
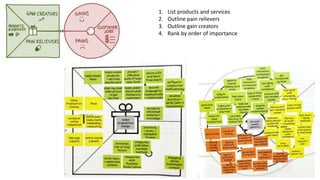
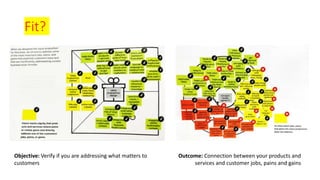
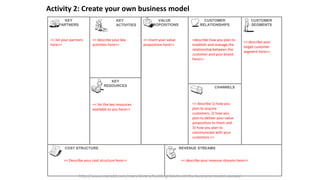
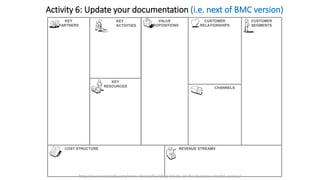
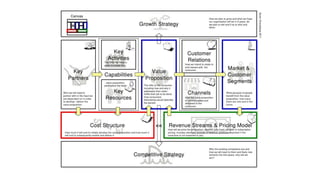
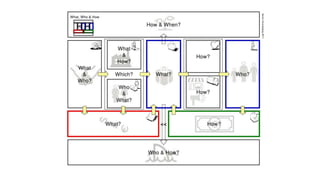
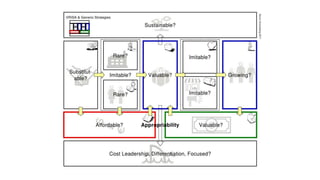
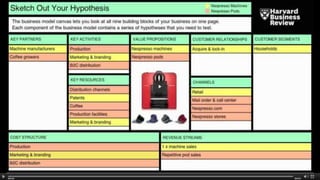
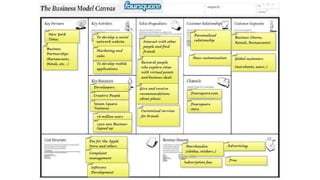
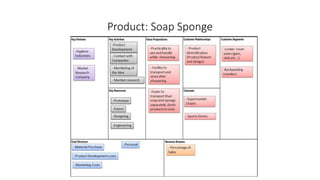
The document outlines the Business Model Canvas methodology, emphasizing its role in structuring start-up strategies and facilitating discussions about business models. It includes practical activities for entrepreneurs to define their value propositions, customer relationships, and cost structures while highlighting the importance of understanding customer needs and preferences. It also provides guidelines for testing assumptions related to the business model and steps for engaging with potential customers.