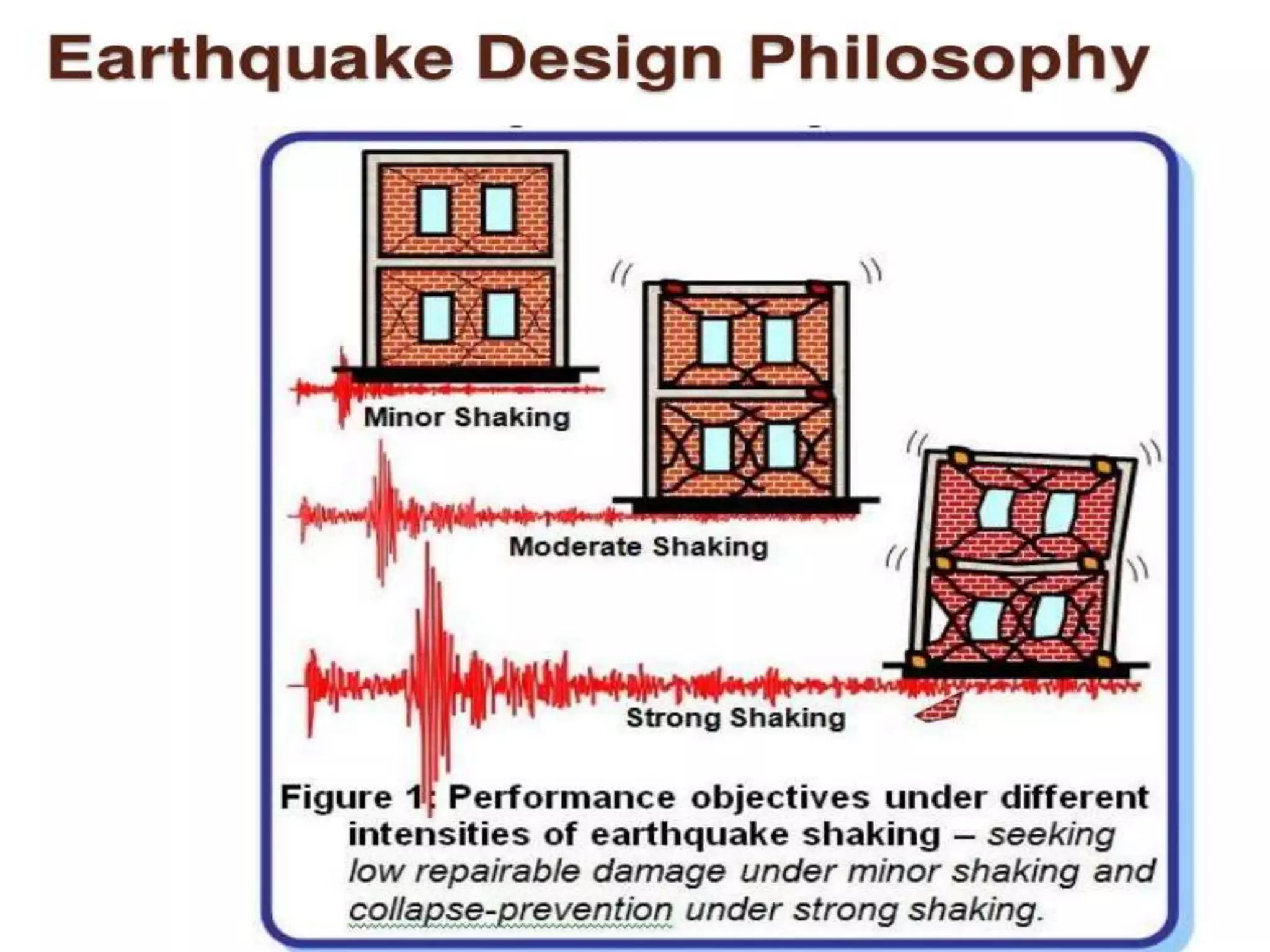
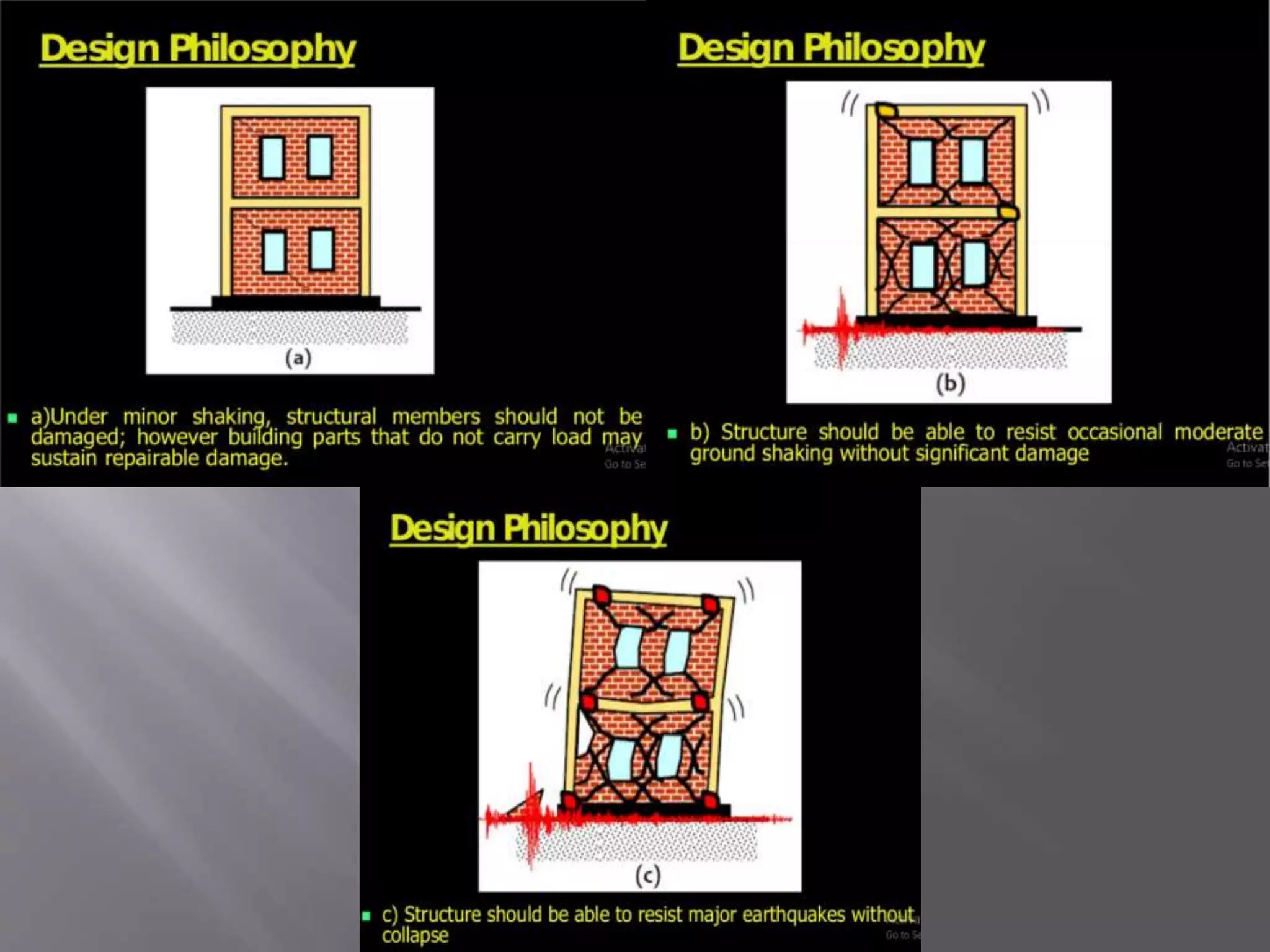
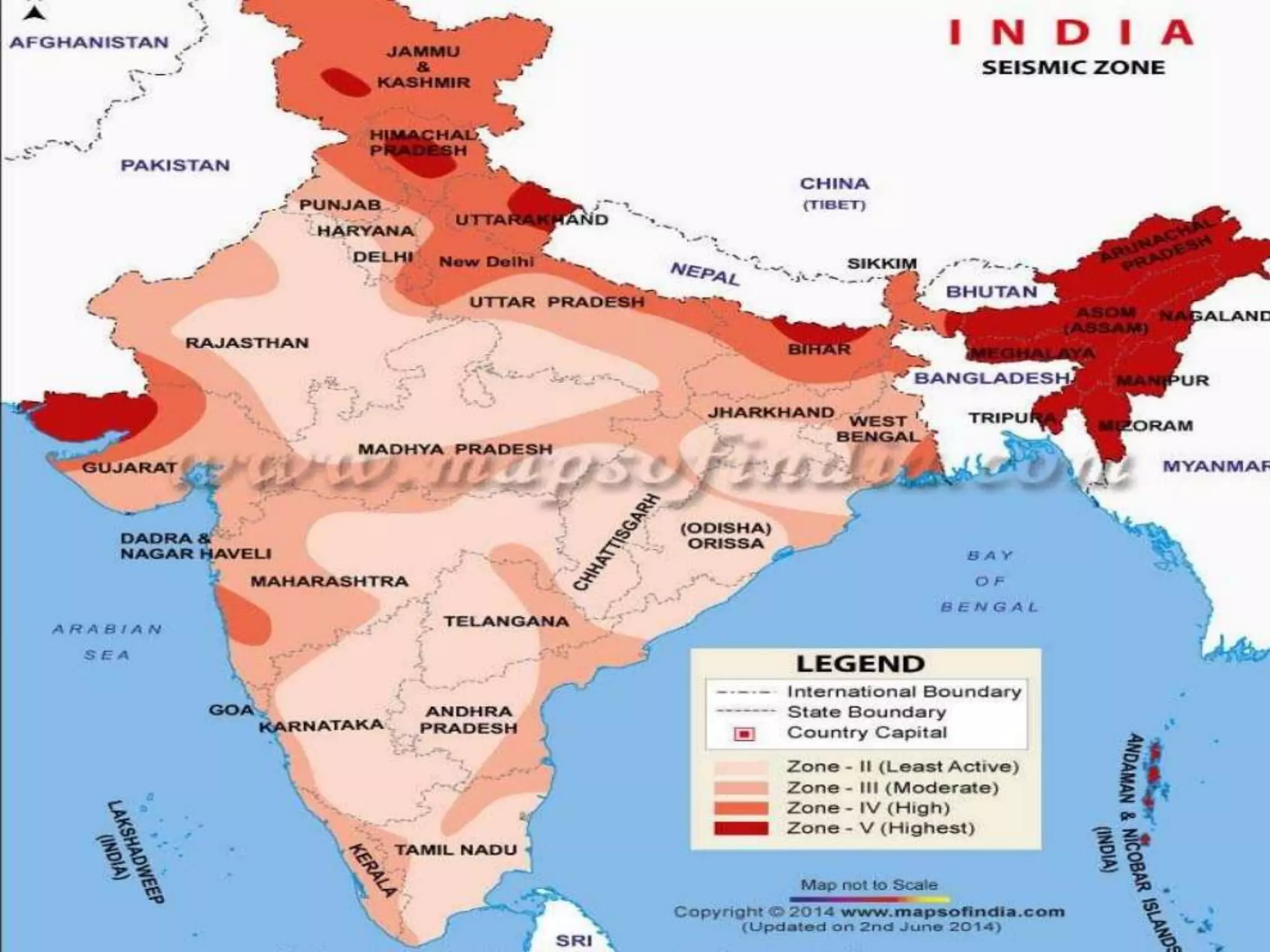
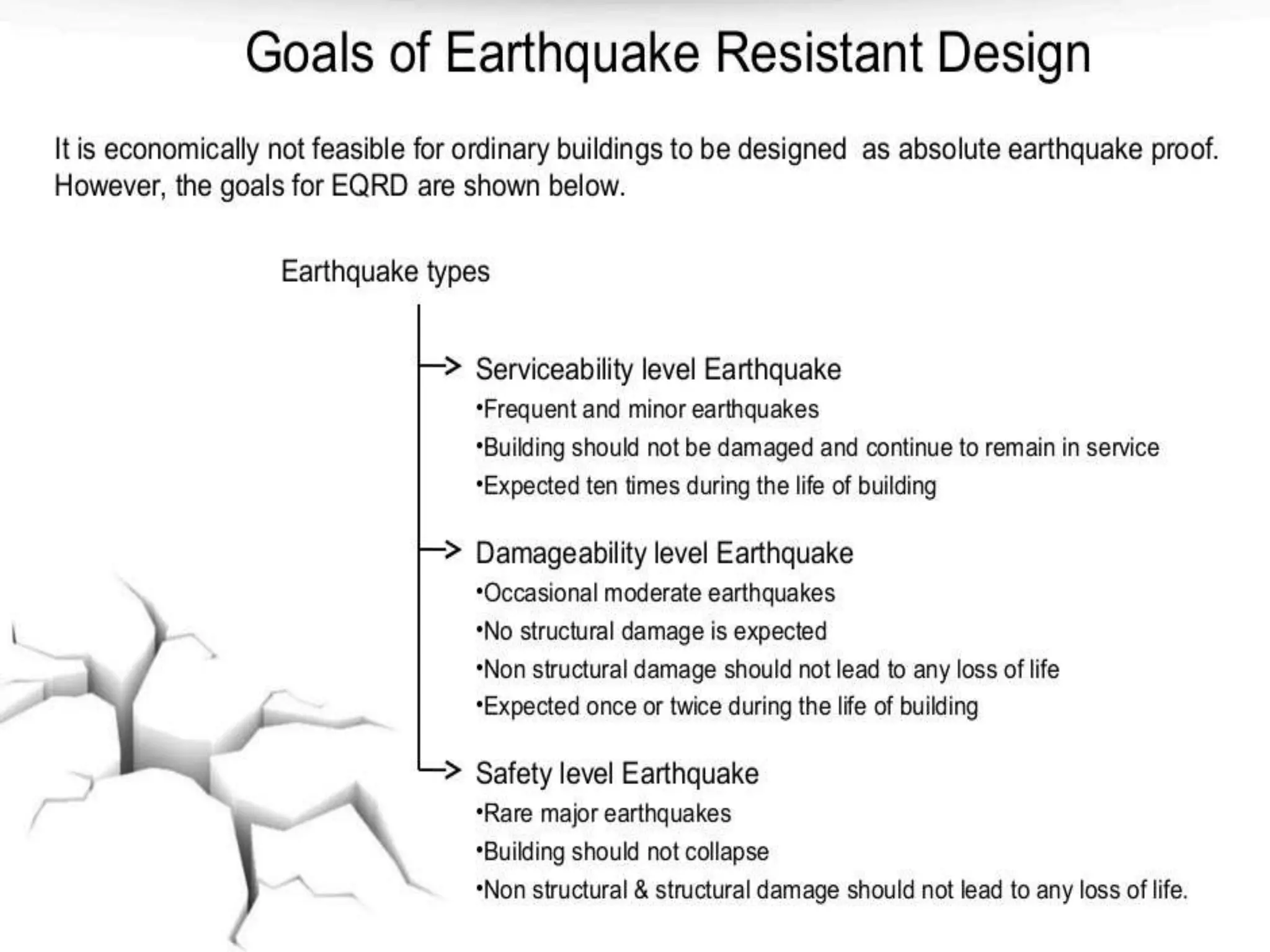
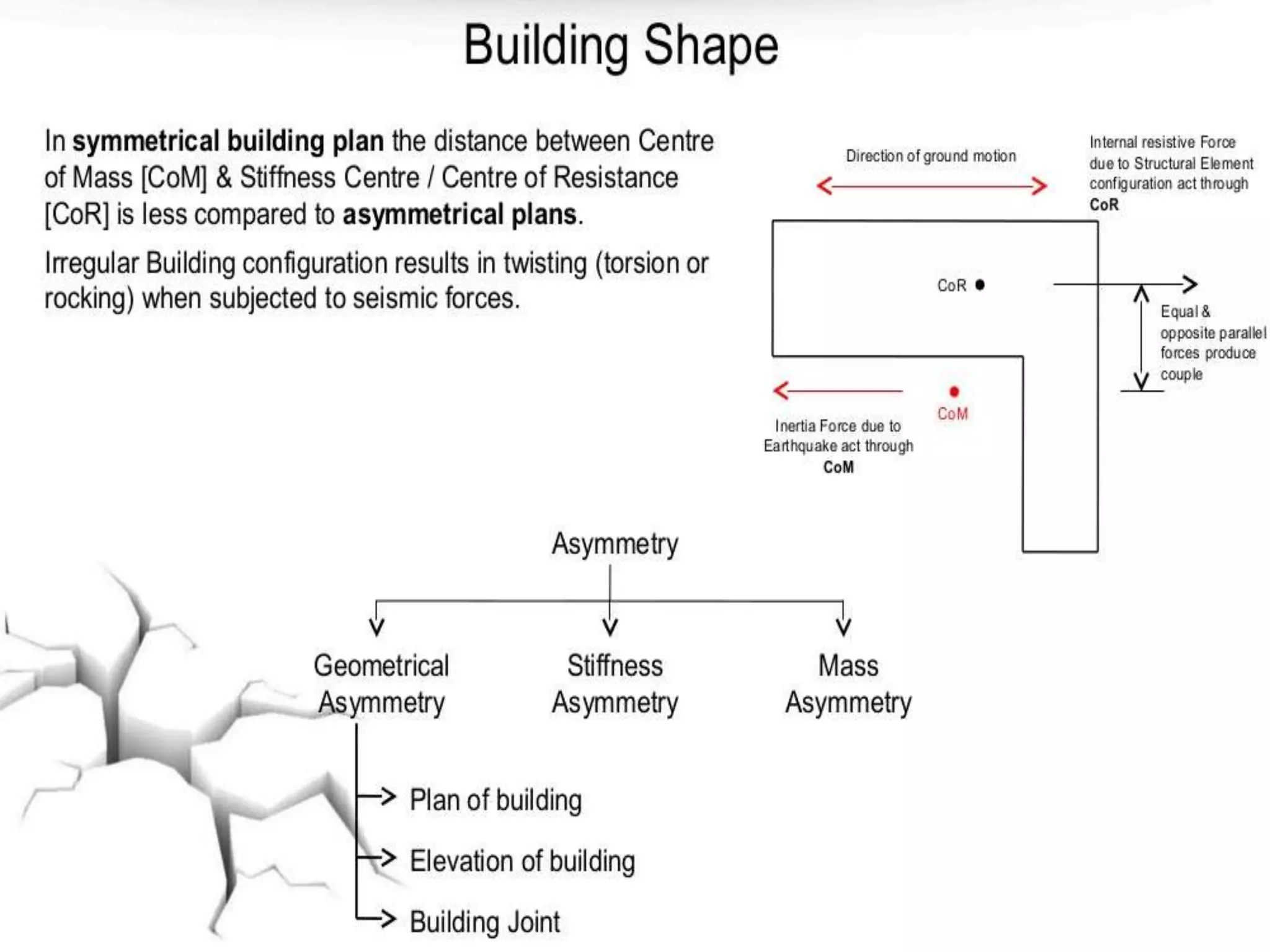
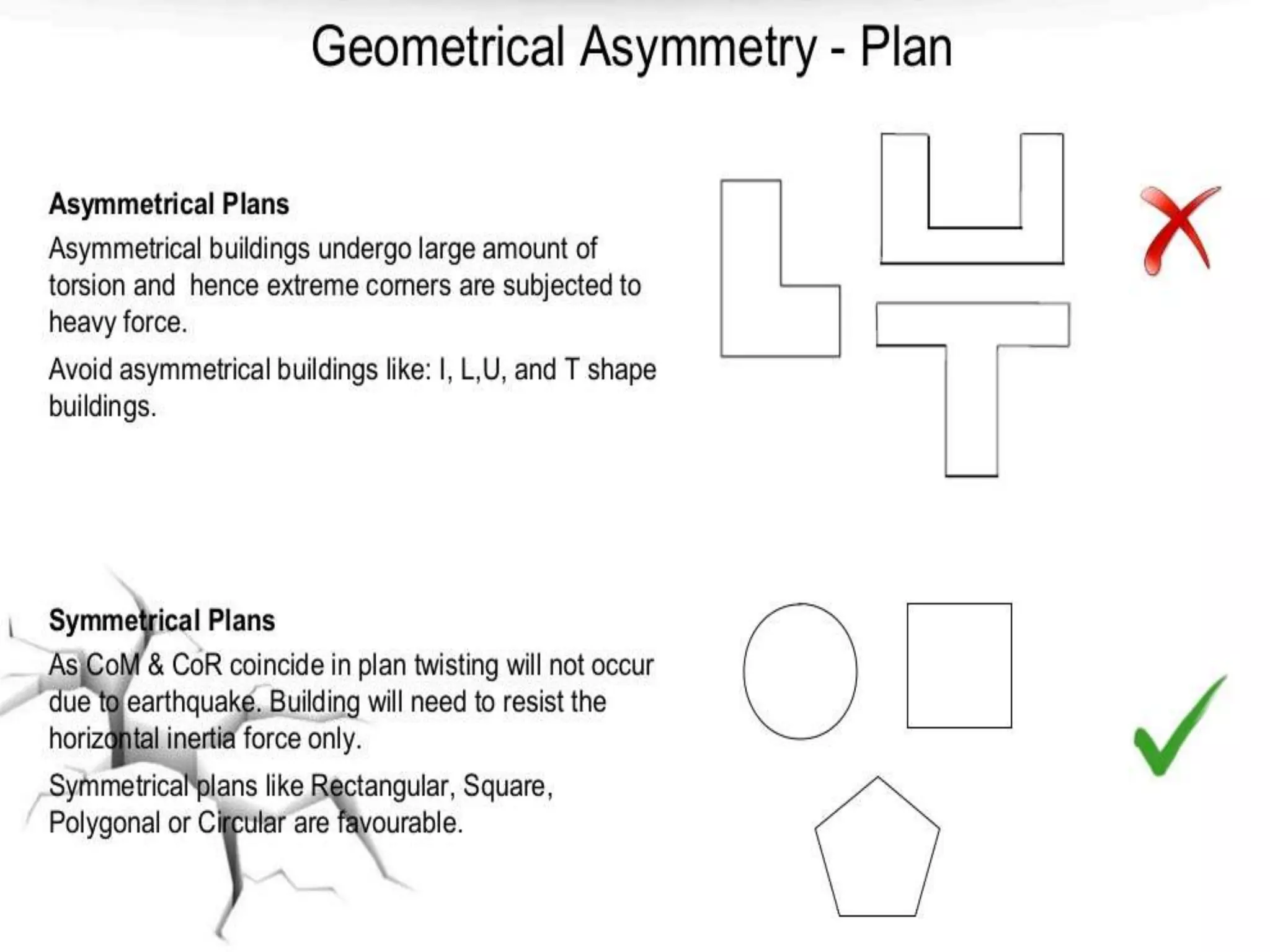
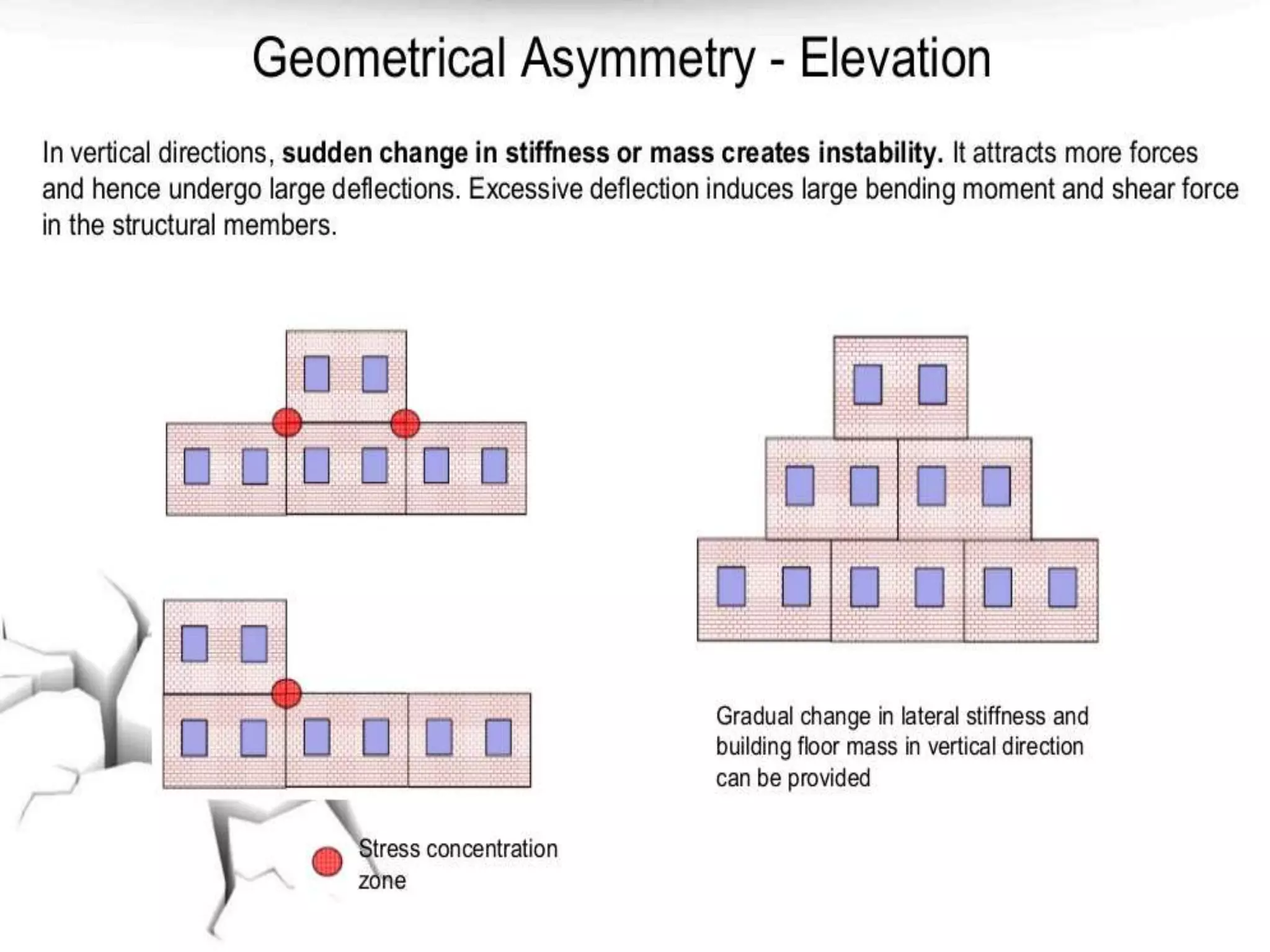
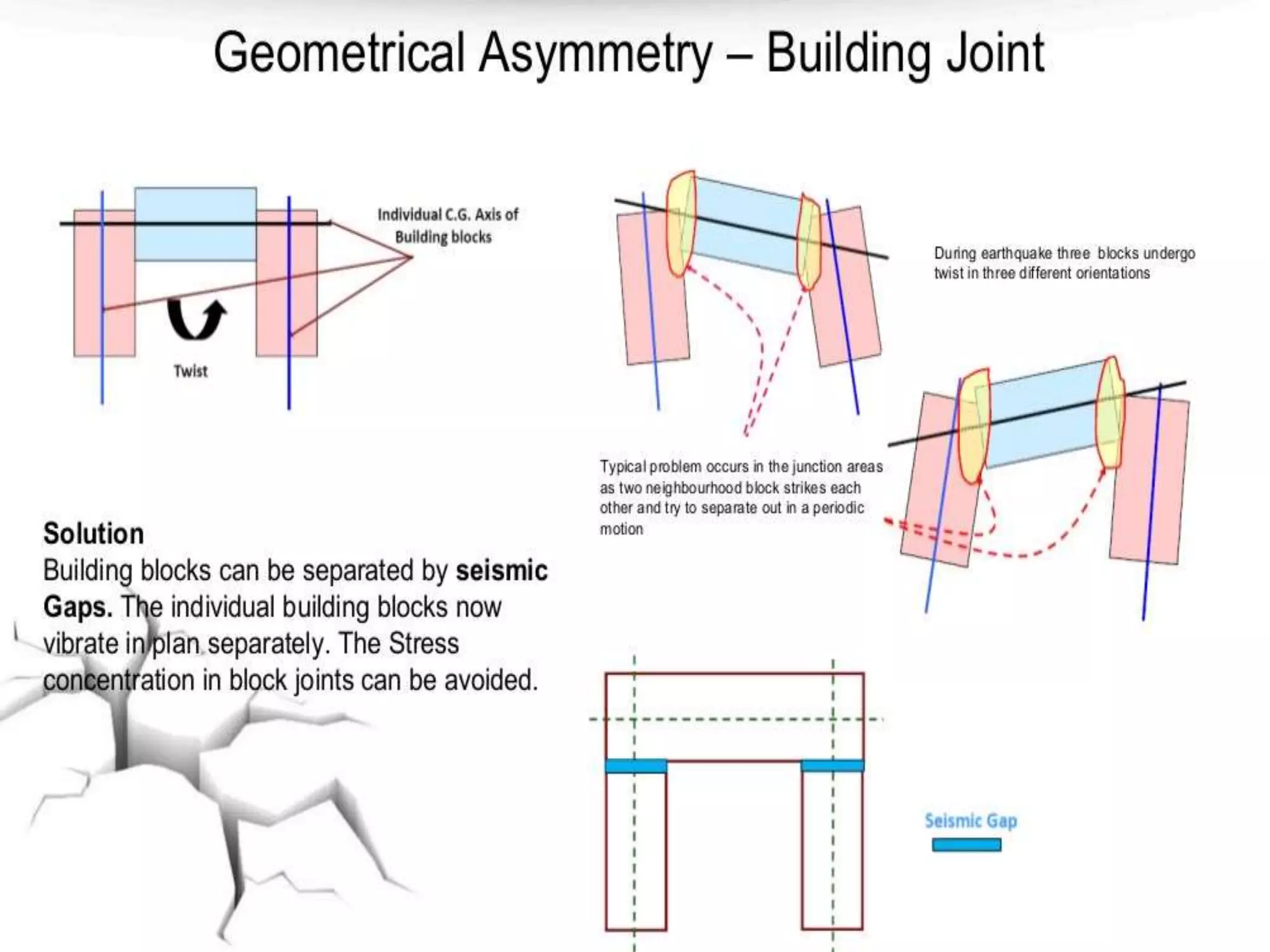
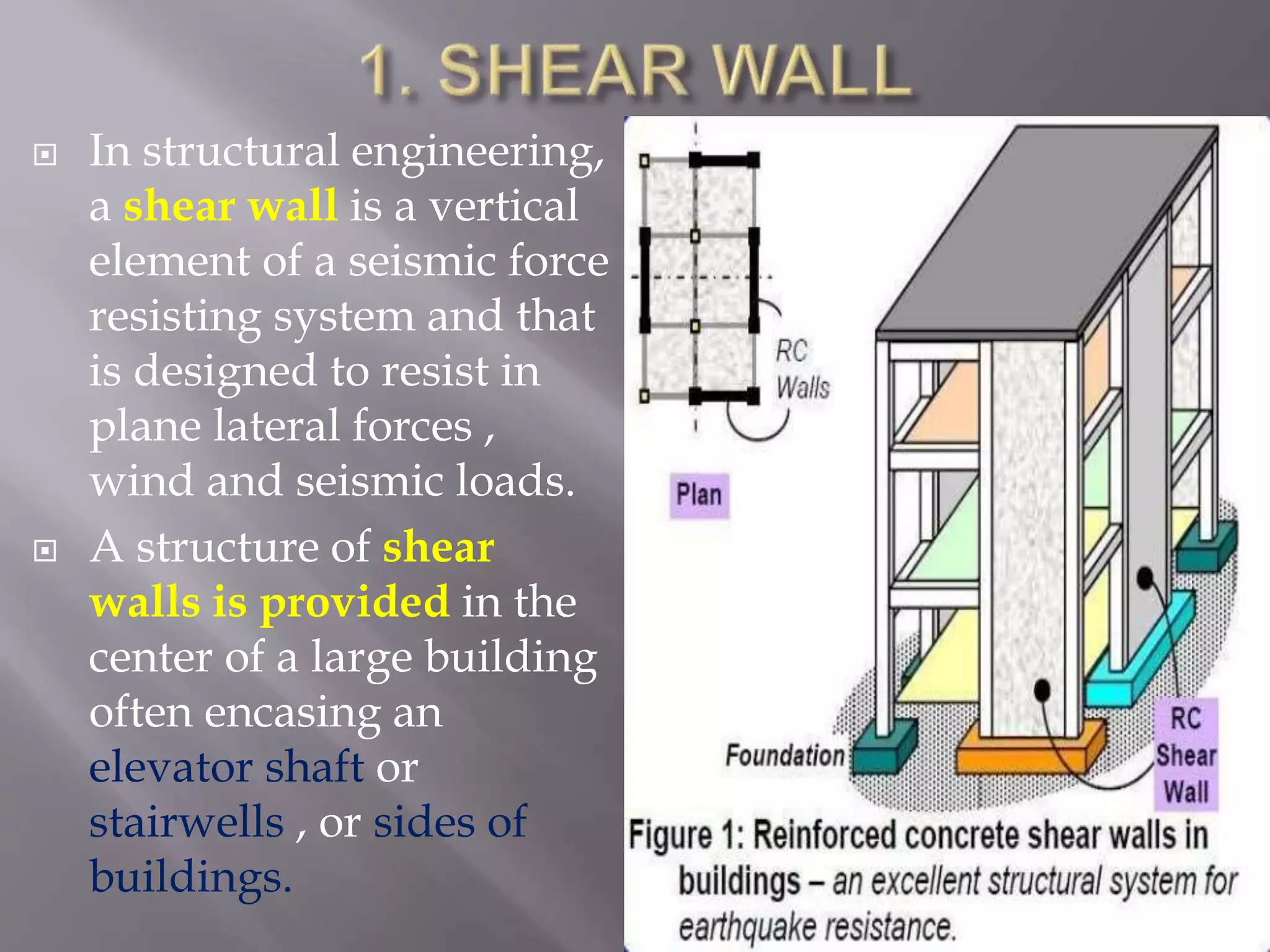
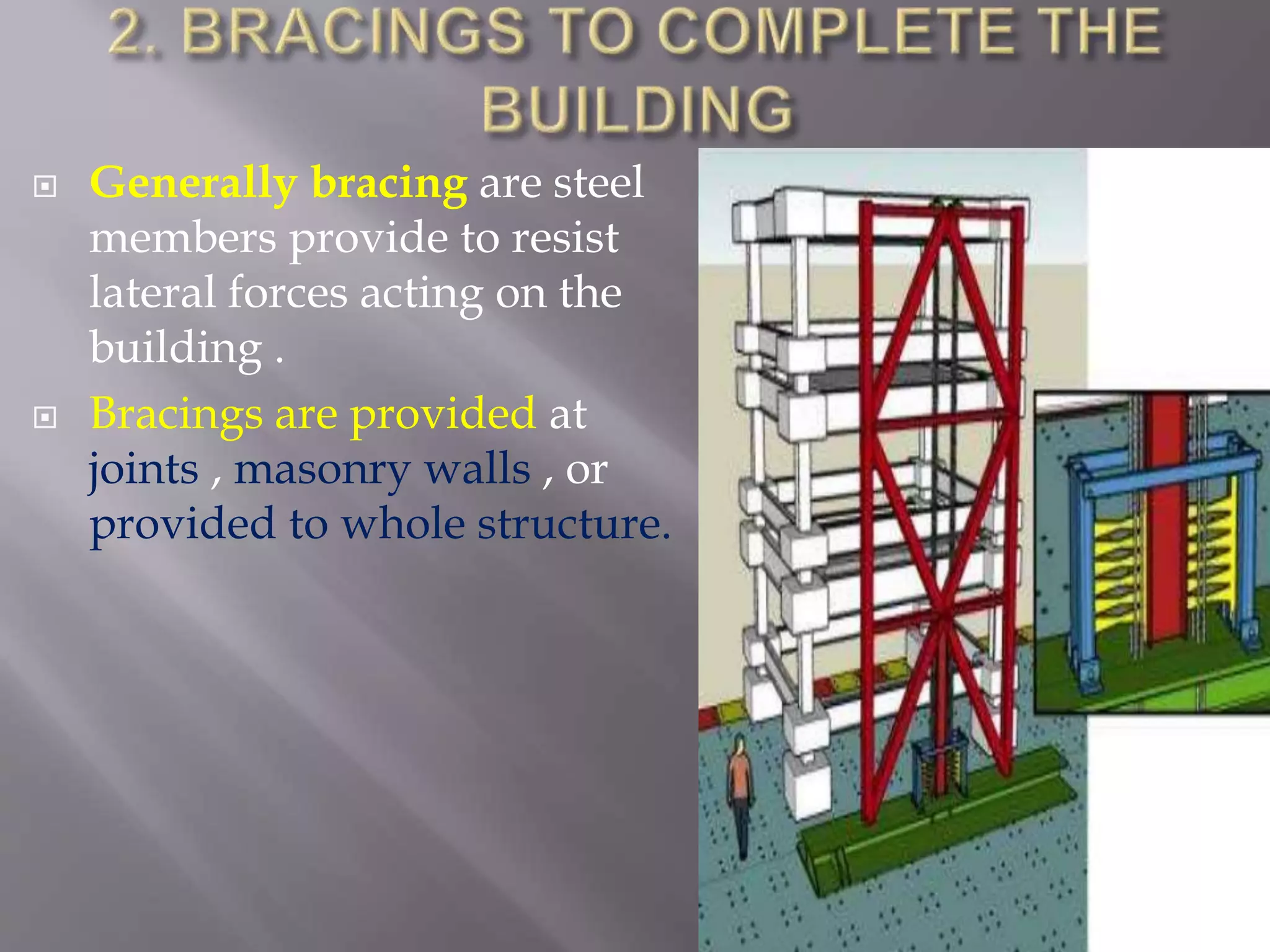
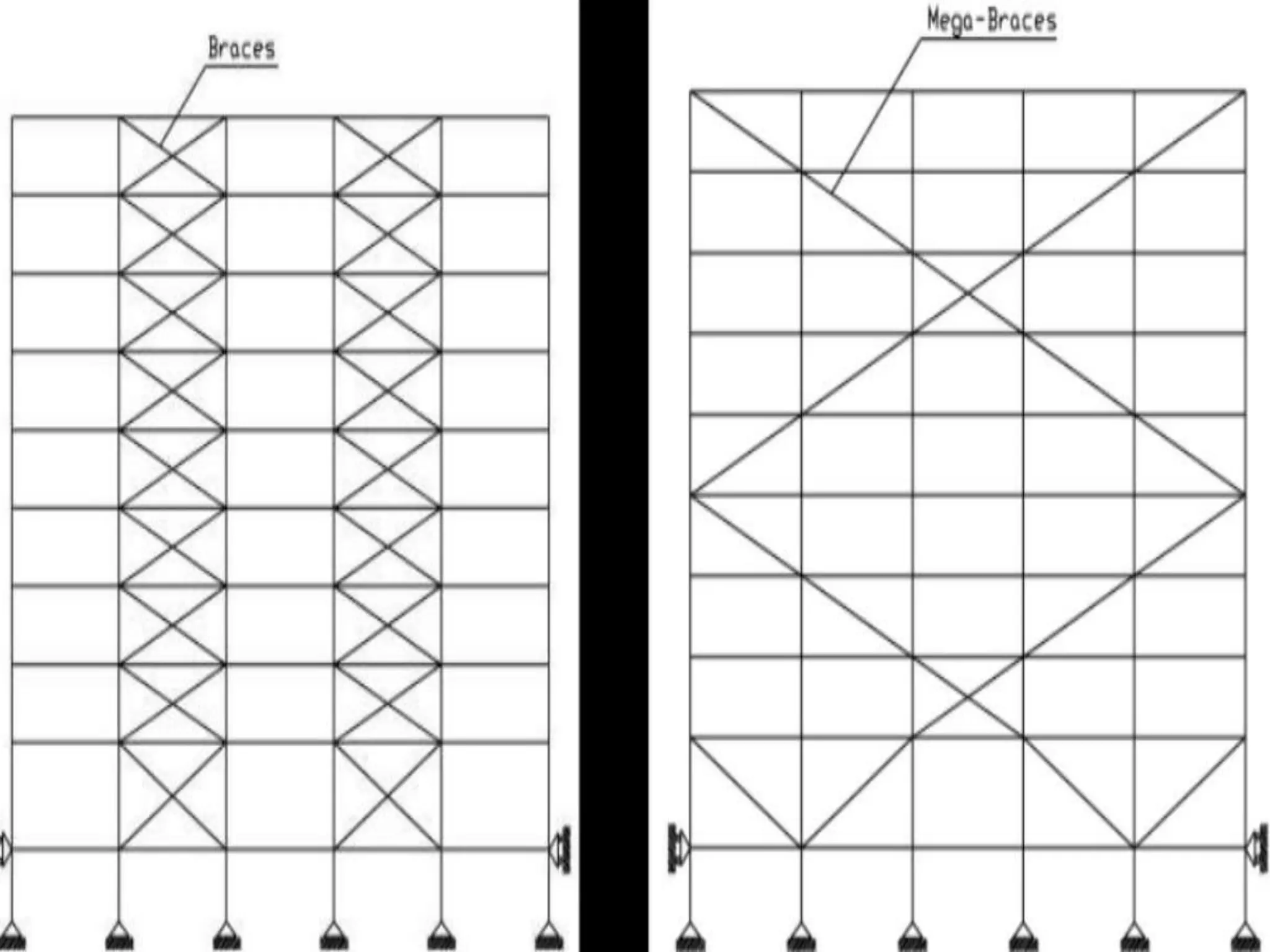
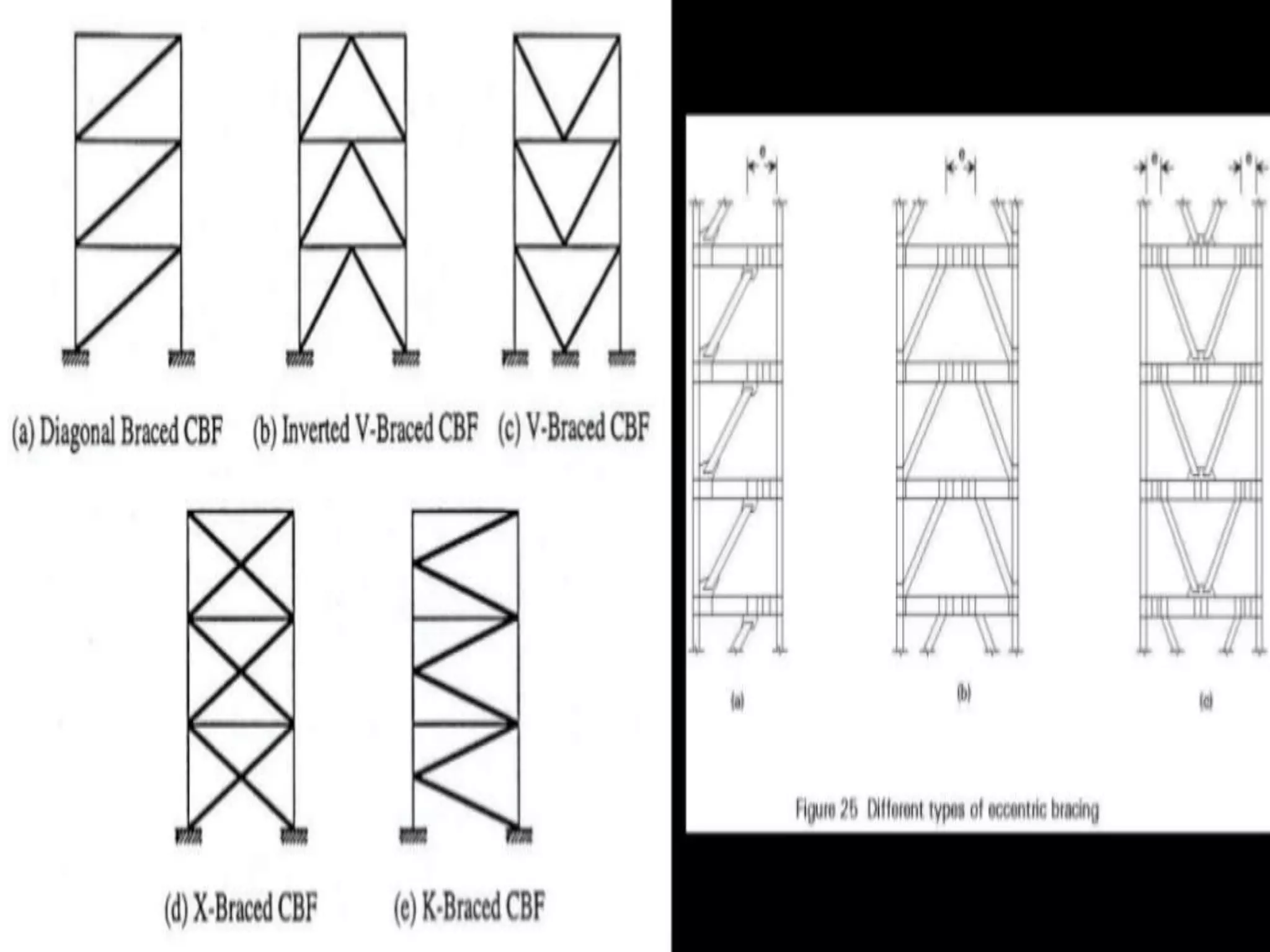
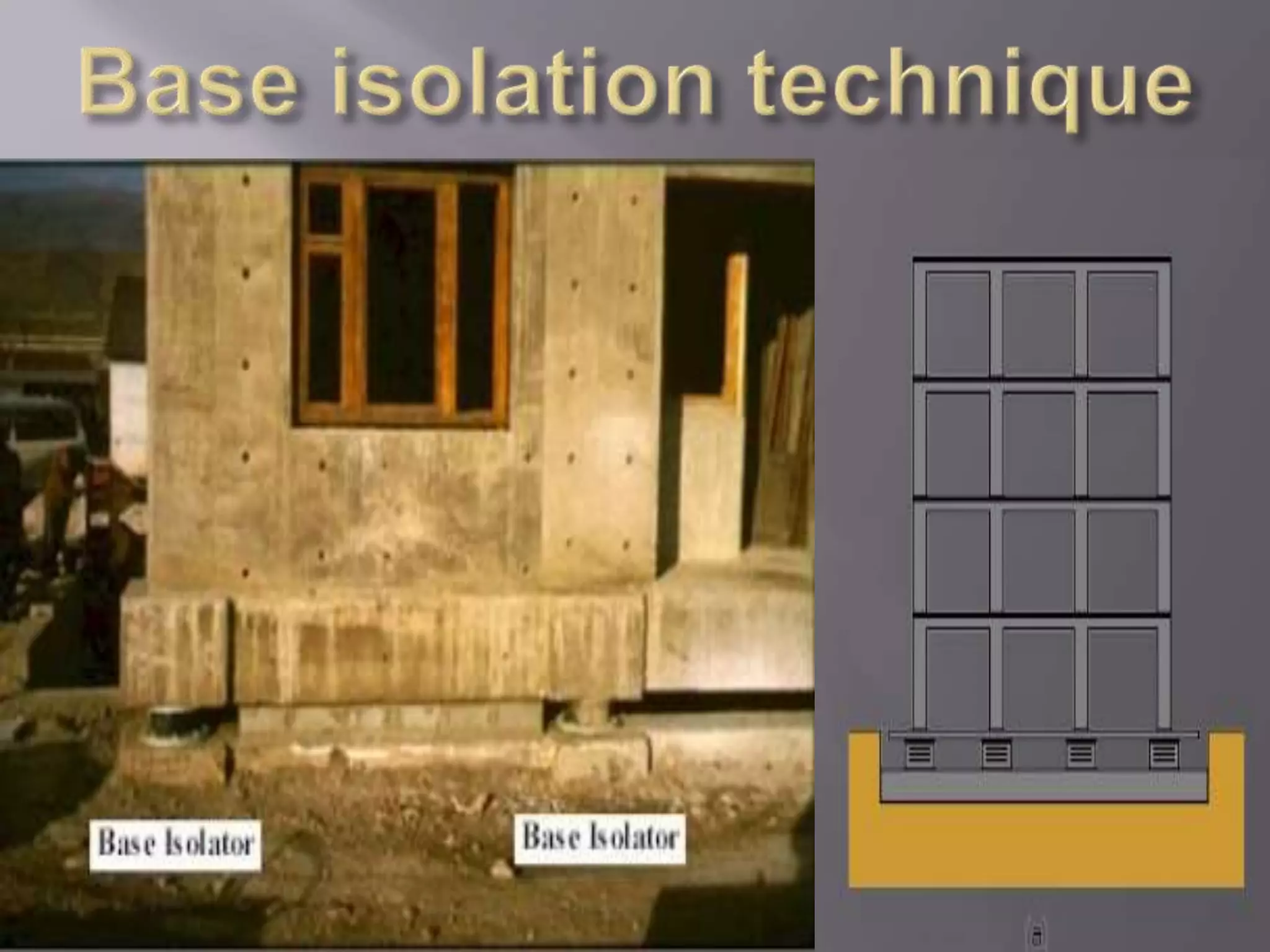
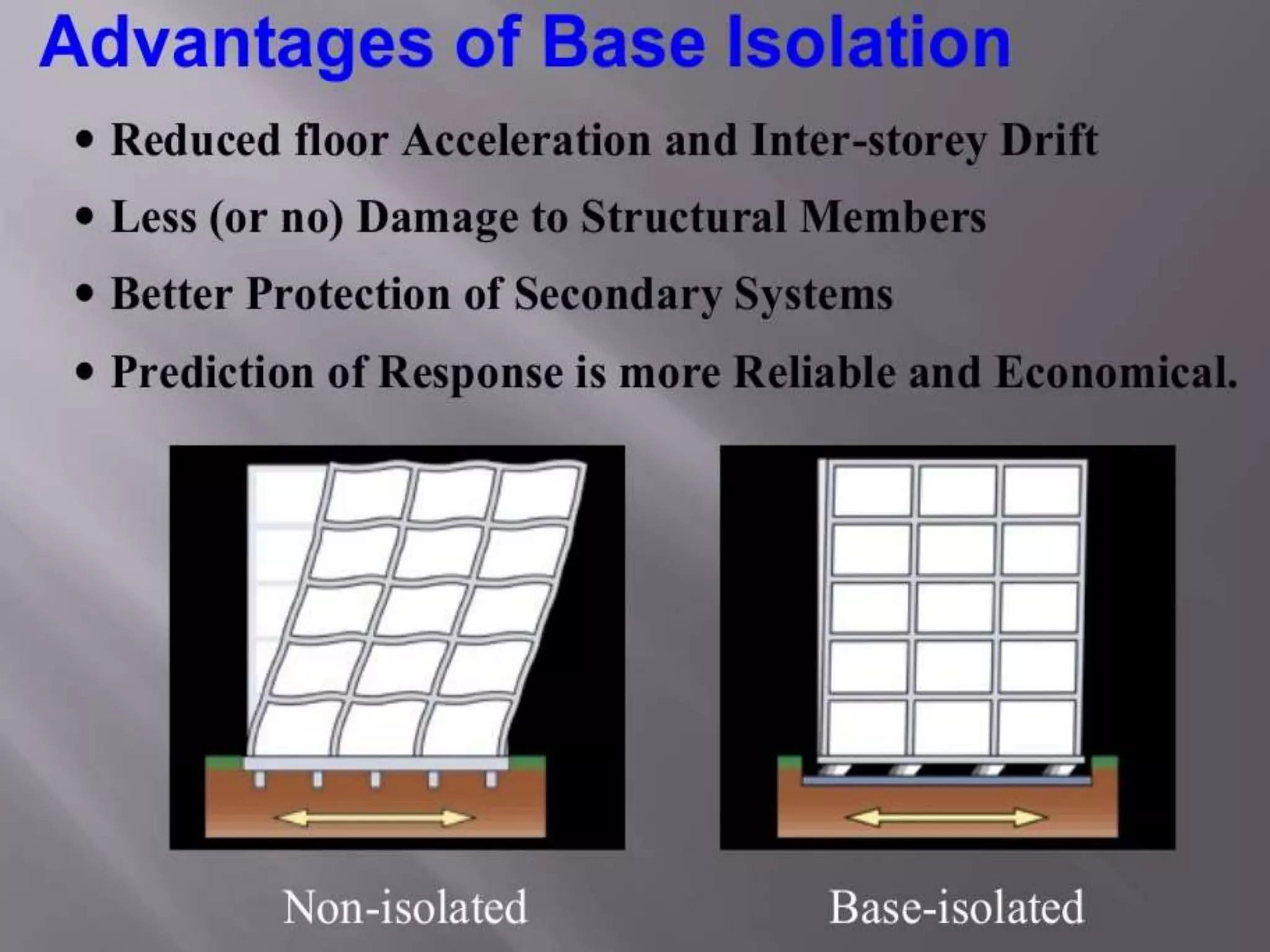
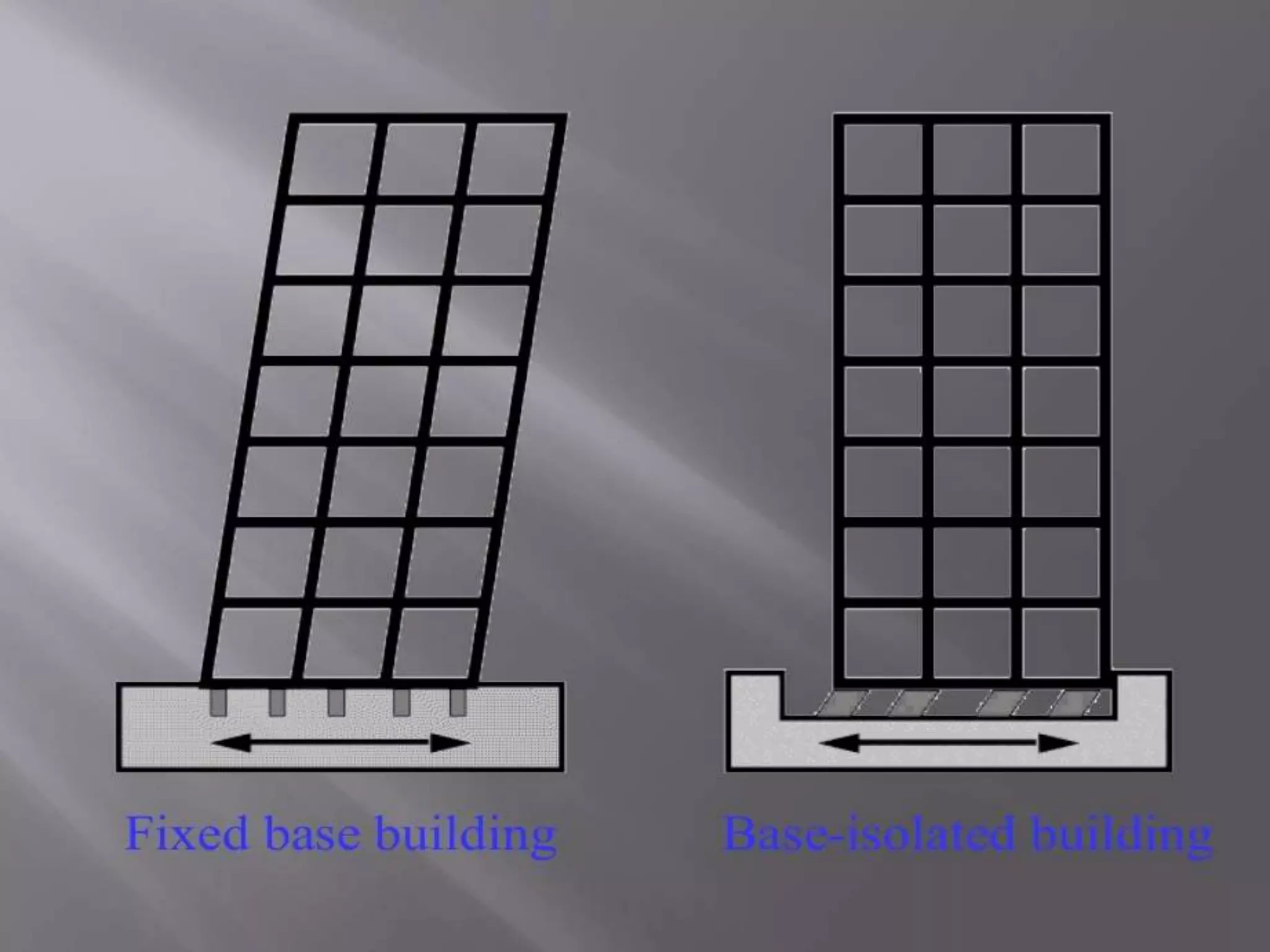
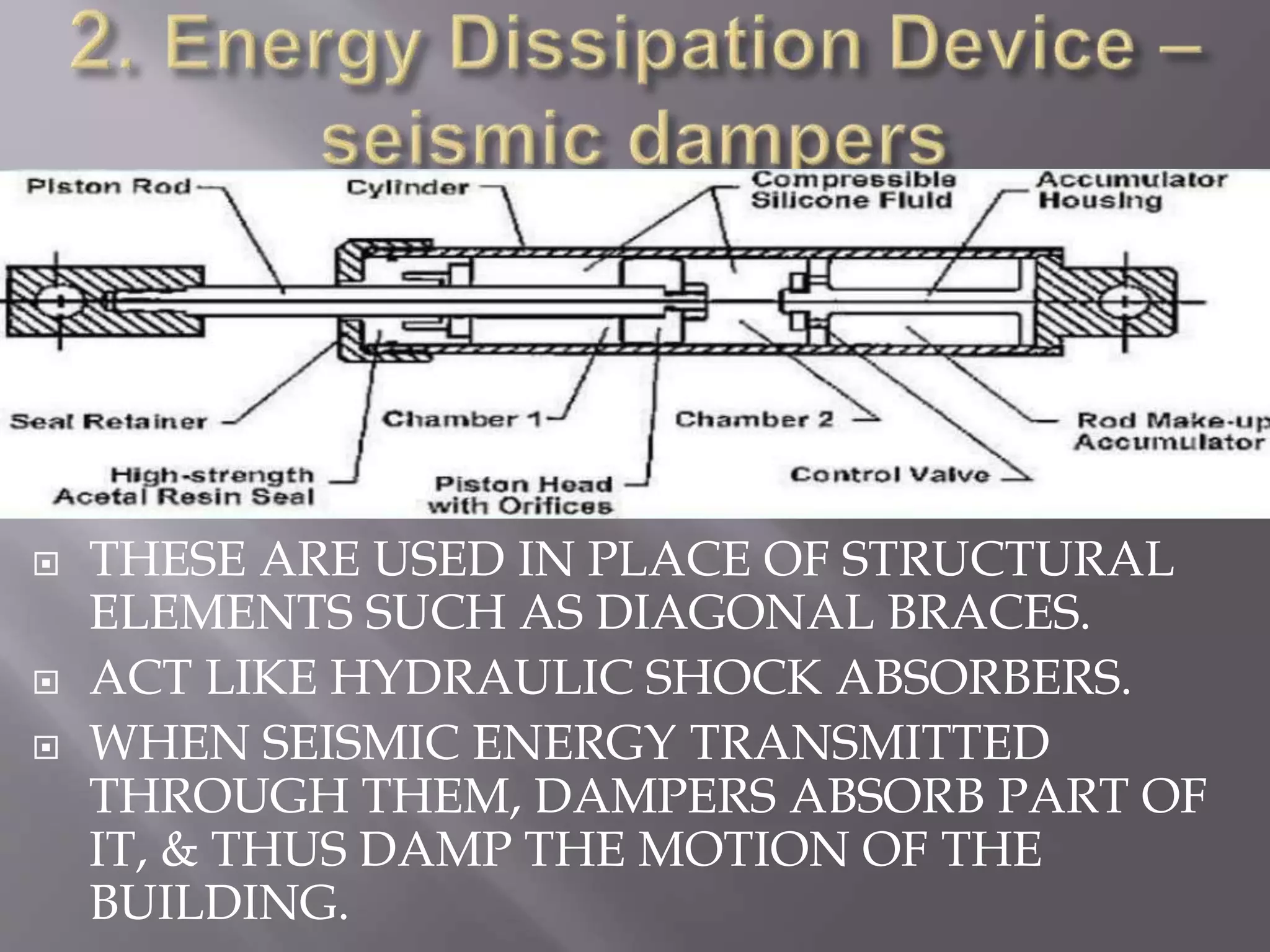
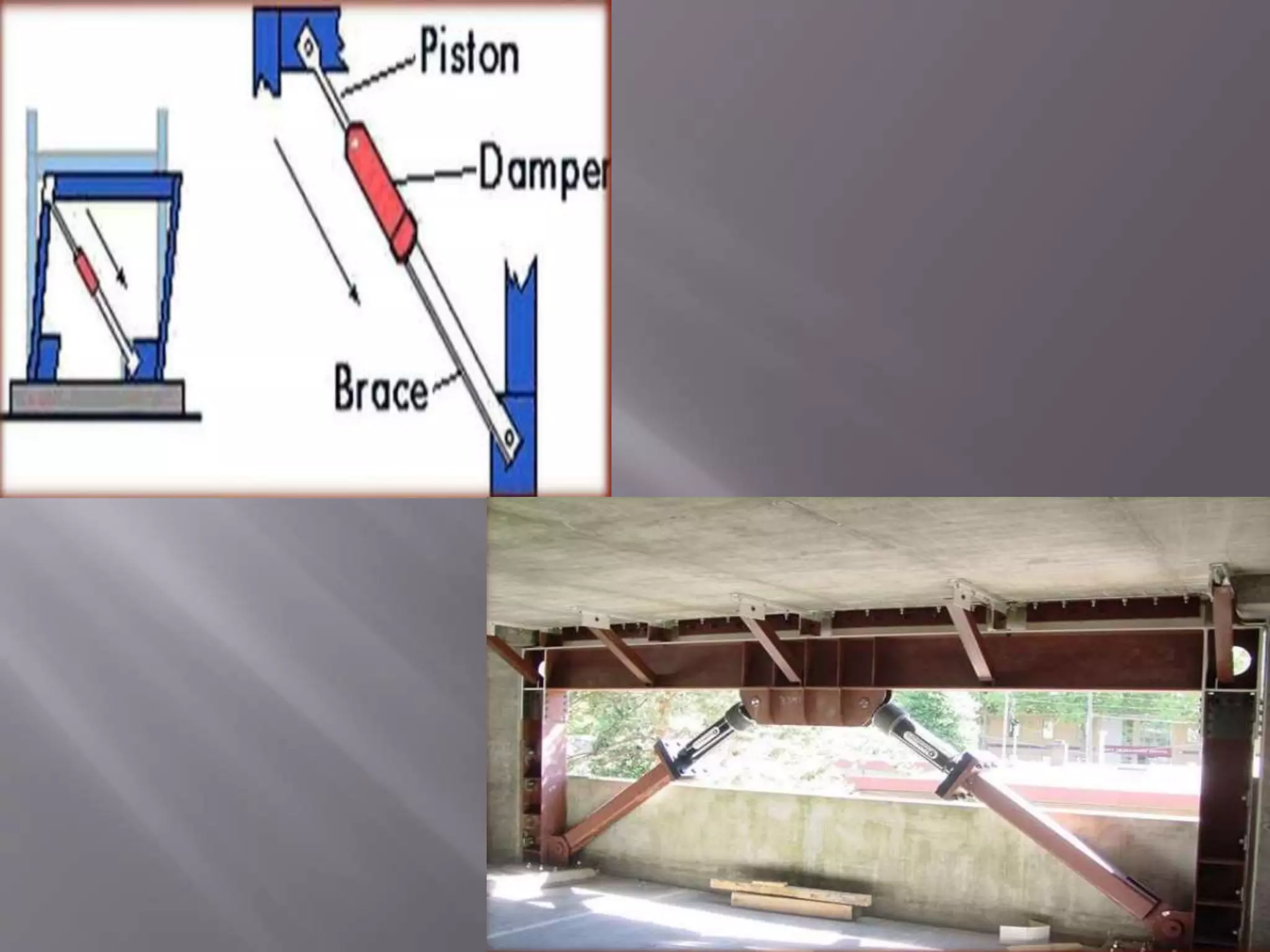
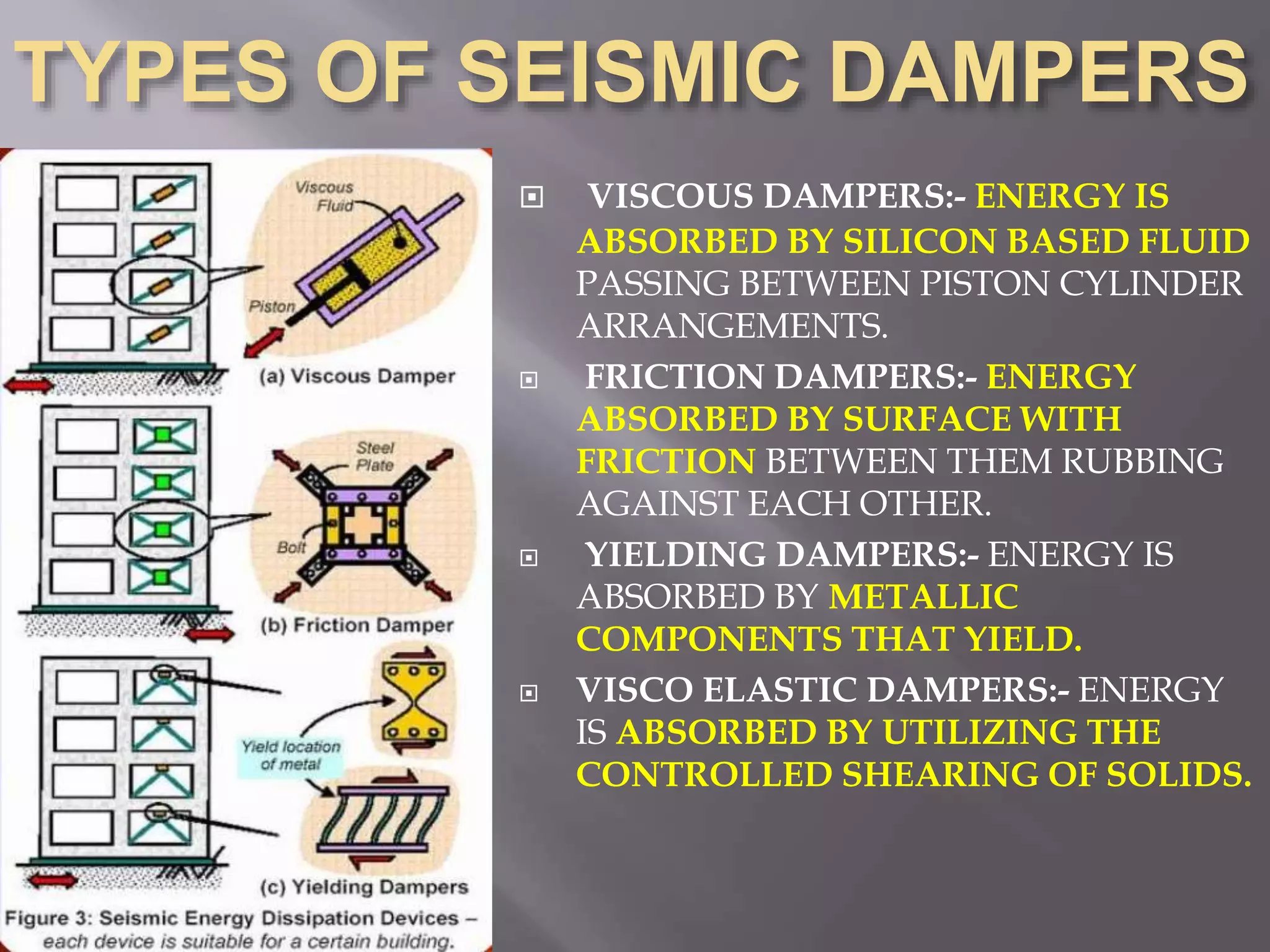
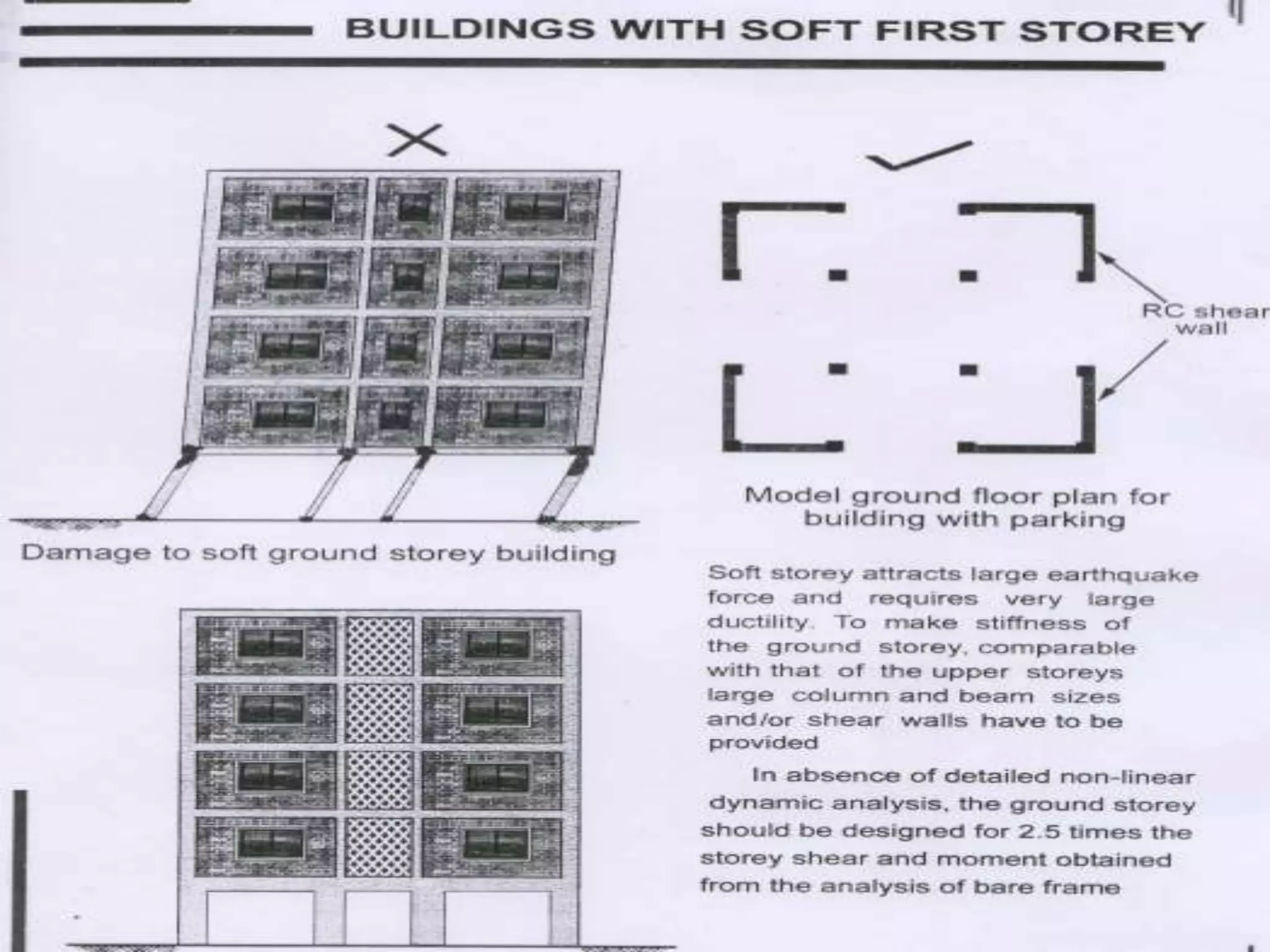
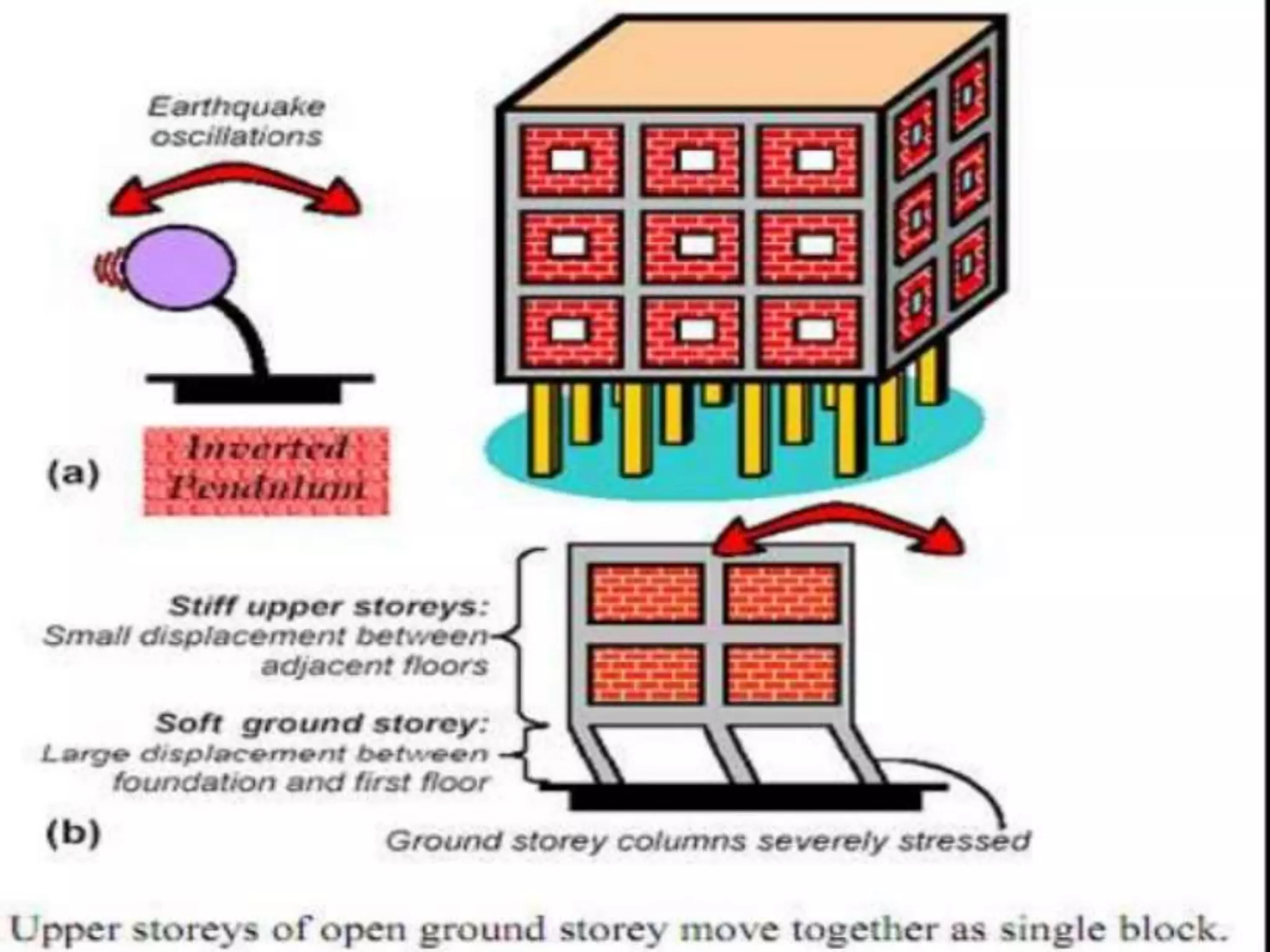
The document discusses the effects of earthquakes on building structures and the various engineering techniques to safeguard them, such as shear walls, braces, and base isolation. It emphasizes the importance of designing structures to resist both vertical and horizontal forces during seismic events and highlights different types of dampers used to absorb seismic energy. Additionally, it advocates for regular and symmetrical building designs to enhance earthquake resistance and promote a culture of safety.