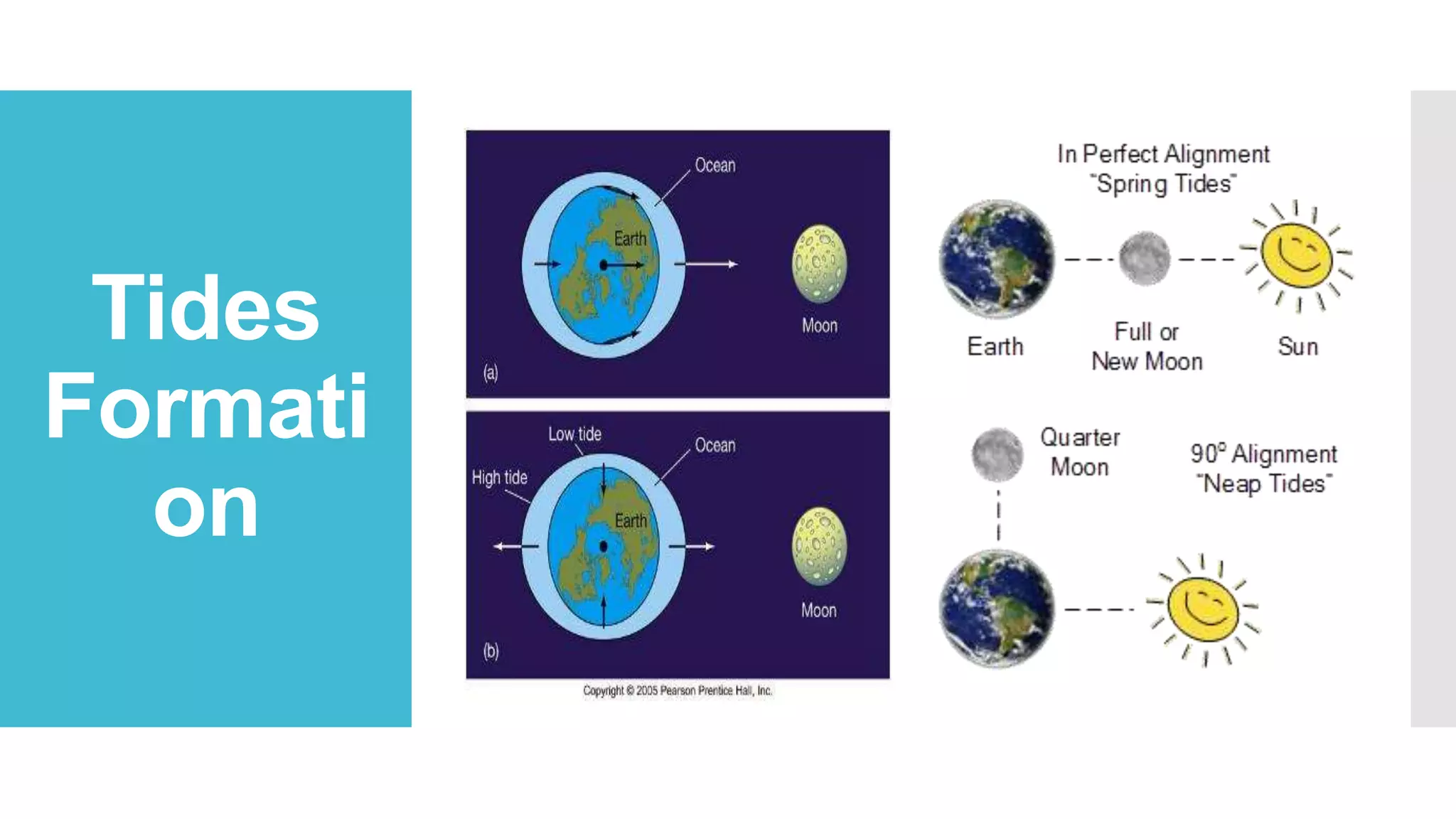
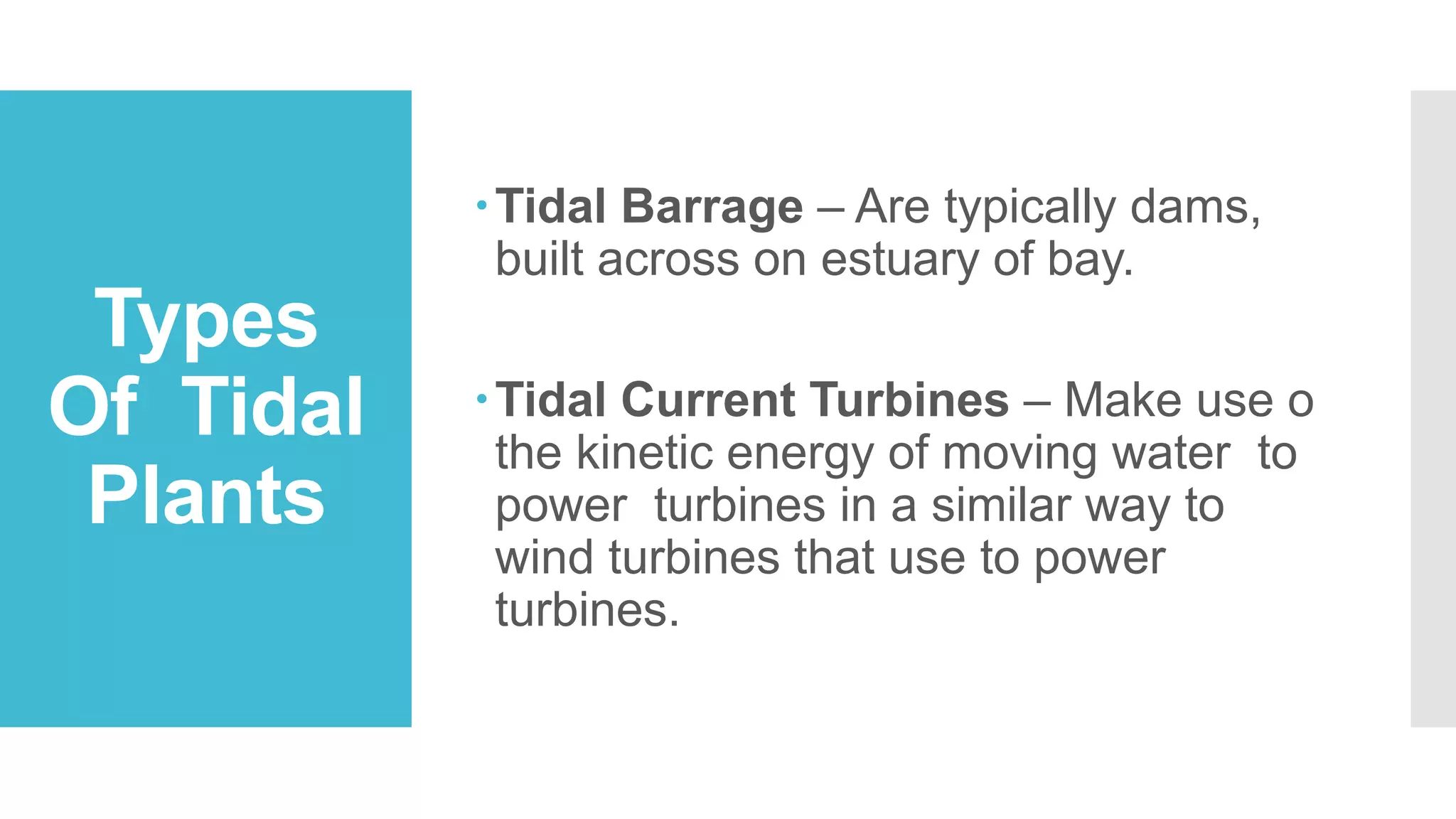
This document discusses tidal energy and how it works. It describes how the first tidal power plant was built in 1966 in France and generates 240MW. Tidal power plants harness the energy from tides rising and falling caused by gravitational forces from the moon and sun. There are two main types - tidal barrages which are dams across estuaries and bays, and tidal current turbines which capture the kinetic energy of moving water similar to wind turbines. Tidal power is a renewable source but has high construction costs and may impact aquatic life. It could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from other power sources.