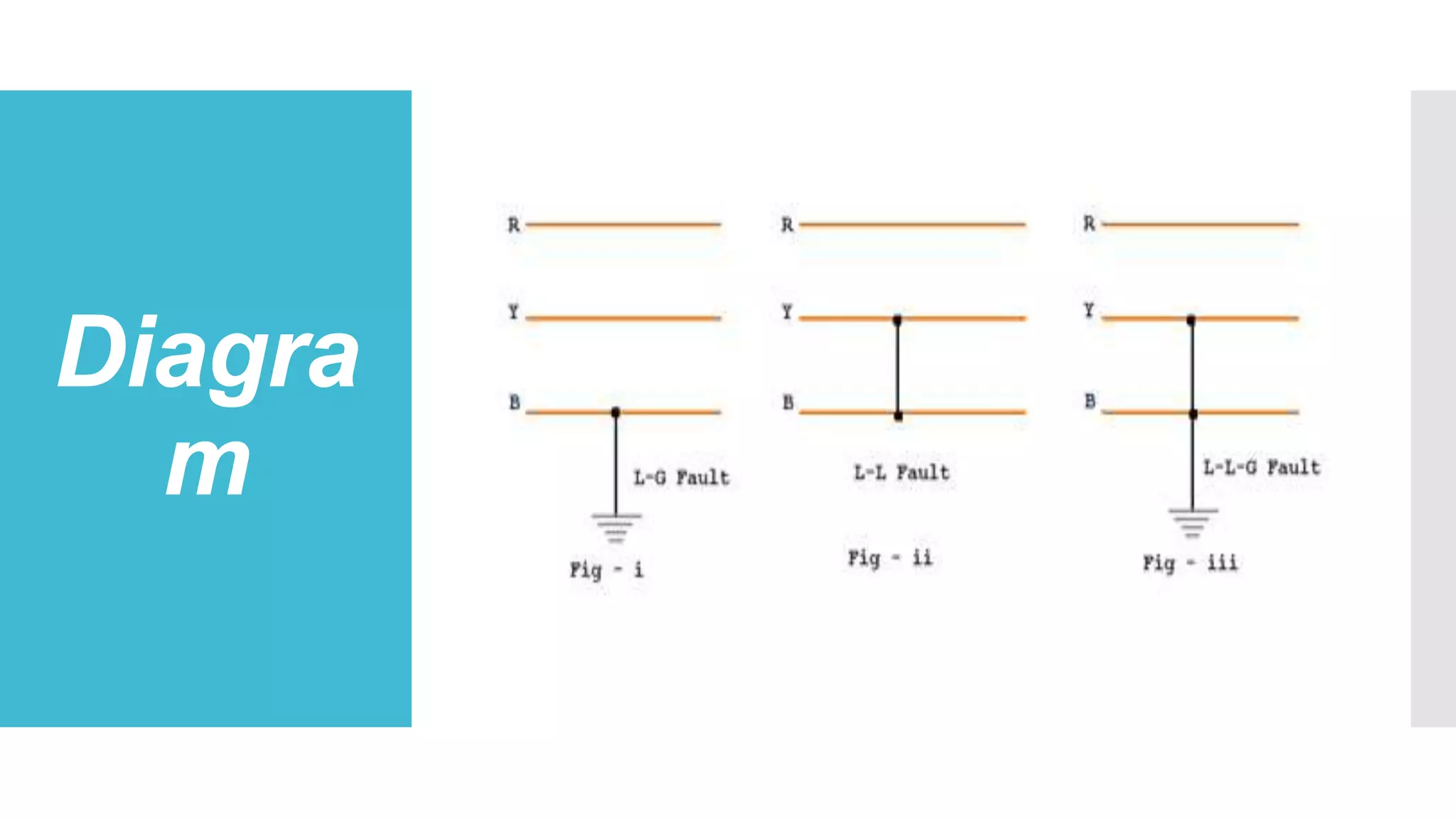
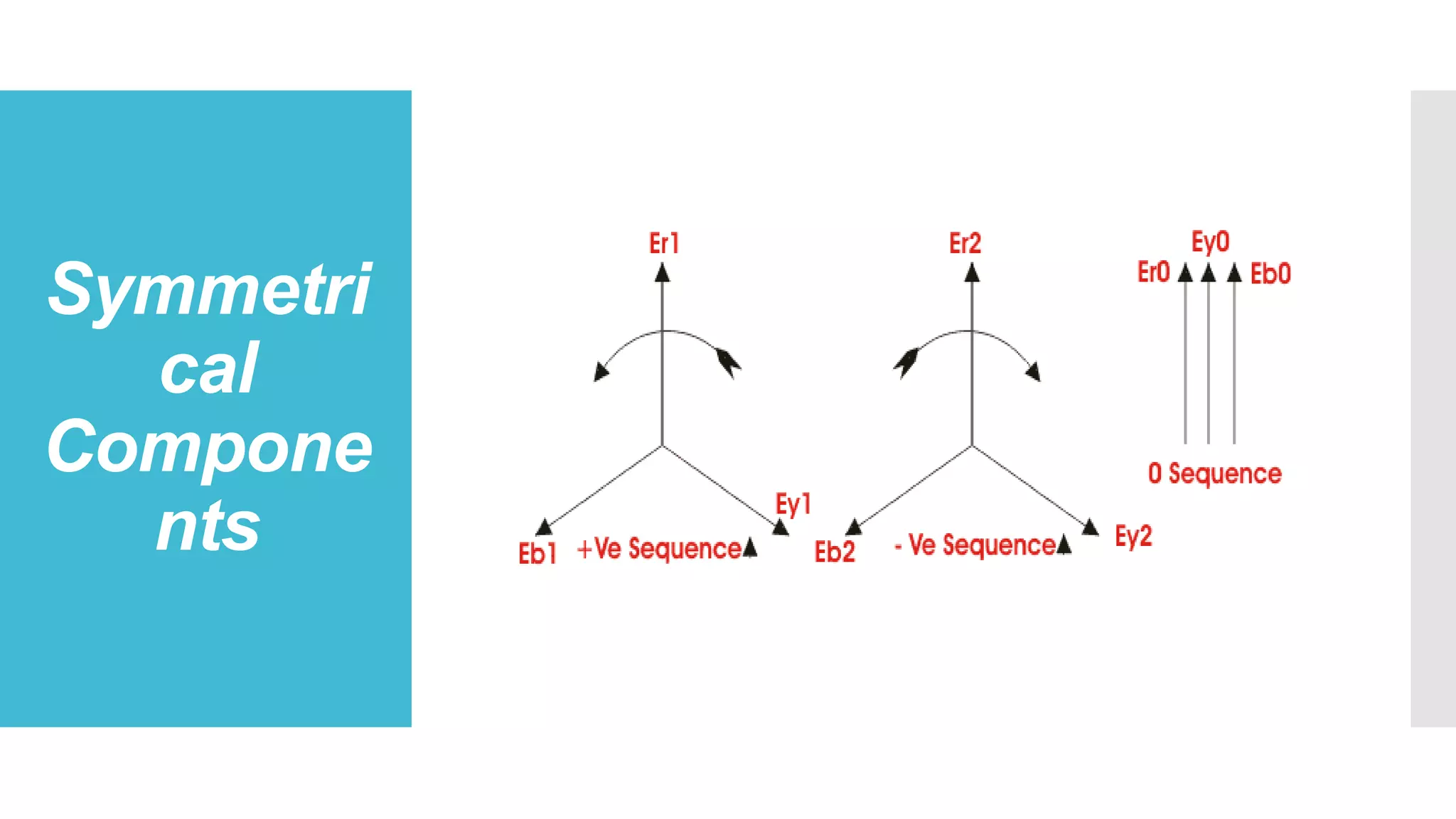
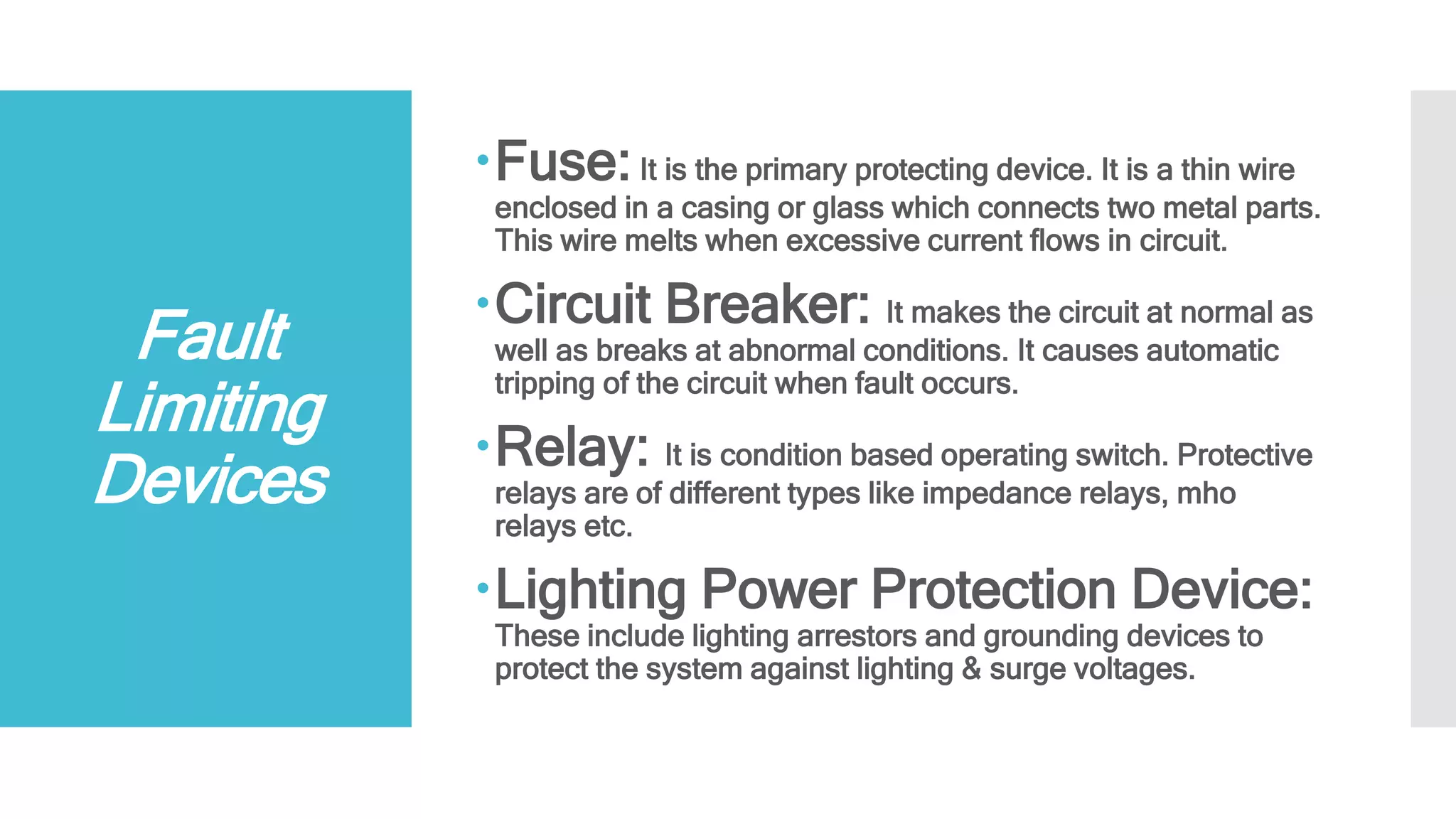
This document discusses unsymmetrical faults in power systems. It begins by defining unsymmetrical faults as faults that result in unequal line currents and displacement. It then discusses the causes of unsymmetrical faults such as falling trees, wind, and insulation failures. The document also summarizes the effects of faults such as overcurrent, equipment loss, and electrical fires. It describes the types of unsymmetrical faults and introduces symmetrical components and Fortescue's Theorem for analyzing unsymmetrical faults using positive, negative, and zero sequence networks. Finally, it briefly discusses fault limiting devices like fuses, circuit breakers, and protective relays.